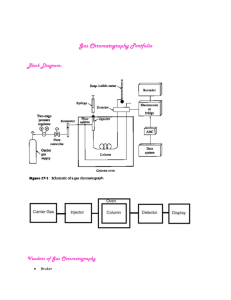
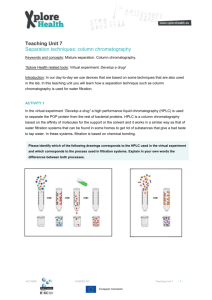
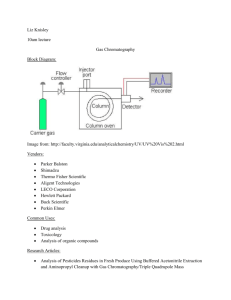
Theory
advertisement

COURSE BOOK for Analytical Chemistry for Third Stage Course name: Separation Methods Academic Year: 2013-2014 Lecture's name: Dr. Azad T. Faizullah Department of Chemistry College of Science University of Salahaddin Email: drazad53@yahoo.com Course Objective “Separation Science”, is a senior level of undergraduate course within the analytical chemistry lecture series. It is concerned with all aspects of the chemical and physical separation of substances, with particular emphasis on separation as a tool for chemical identification and measurement. Throughout this course, lecture topics will be illustrated with examples from biological, pharmaceutical, food & drink, environmental sample analysis. This will give a sense of the scope and impact of separation science on society, as well as providing concrete examples on how to identify appropriate separation and analysis strategies depending on the target analyte(s) and sample matrix. Course Syllabus: 2 There are 2 hr lectures weekly. The following provides an overview of the topics covered during the semester: 1- Introduction Important total analysis process steps: Sampling Methods Separation Quantitation Evaluation 2- Separation Science -Definition of Separation Science -Classification and Application of Separations I- Separation by Phase-Formation methods Volatilization Methods (conversion of Solid to Gas) Distillation Methods (conversion of Liquid to Gas) Separation by Precipitation II- Separation by Phase- transformation methods Extraction 1Solvent extraction (Liquid Extraction) 1.1. The equilibrium constant 1.2. Efficiency of extraction 1.3. Selectivity of extraction 1.4. Nature of partition forces 1.4.1. Dispersion interaction 1.4.2. Dipole-Dipole interaction 1.4.3. Induction interaction 1.4.4. 4-Hydrogen bonding 1.5. Extraction system 1.5.1. Extraction of Covalent, Neutral Molecules 1.5.1.1. pH effect 1.5.1.2. Effect of complex formation 1.5.1.3. Effect of association 1.6. Methods of Extraction 1.6.1. Batch extraction 1.6.2. Continuous extraction 1.6.3. Multistage extraction 2- Solid-Phase Extraction (Liquid-Solid Extraction) Chromatographic Methods 1- Introduction and some important definition in Chromatography 3 2- Chromatographic Methods 2.1. Plate theory 2.2. Rate theory 3- Chromatographic resolution 4- Classifications of chromatographic Methods 5- Adsorption Chromatography 6- Partition Chromatography 7- Plane Chromatography 7.1. Paper Chromatography (PC) 7.1.1. Techniques of Paper Chromatography 7.1.2. Preparative paper chromatography 7.1.3. Qualitative and Quantitative application of PC 8- Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) 9- Liquid Chromatography (LC) 10- High performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) 10.1. Bonded-Phase Column 10.2. Elution System 11- Ion-Pair Chromatography 12- Ion Exchange Chromatography (IEC) 13- Affinity Chromatography 14- Gas-Chromatography (GC) Evaluation, Examination and Marking Scheme Students will be expected to make full use of the supplementary materials and case studies made available through both lecture handouts and reference books. 4 Familiarity with the basic principles and calculations employed in extraction, general separation and chromatography will be assumed. Students should consult the available notes and supplemental examples for specimen calculations and problems. The students are required to do two closed exams and one optional exam during the course period. All exams have 15% marks; the quiz tests have 5% marks, the attendance, classroom, activities, absence count 5% marks. So that the final grade will be based upon the following criteria: Exams (closed and optional): 15% The quiz tests and homework: 5% Classroom participation and assignments: 5% Practical Course 15% Final Exam: 60% which include 45% for theoretical and 15% for practical. Course Material The student can find additional information and examples in the following references 1- Modern Analytical Chemistry; by David Harvey. 5 2- Ion Exchange and Solvent Extraction; Volume 13, by Jacob A. Marinsky and Yizhak Marcus. 3- Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry; Eighth Edition, by Douglas A. Skoog, Donald M. West, F. James Holler and Stanley R. Crouch. 4- Chromatography and Separation Science; by Satinder Ahuja. 5- Chromatography : Concepts and Contrasts, by James M. Miller. 6- Chromatography: Fundamentals and Applications of Chromatography and Related Differential Migration Methods Part A: Fundamentals and Techniques; Journal of Chromatography Library — Volume 69A; Sixth Edition, by E. Heftmann. 7- Chemical Separations :Principles, Techniques, and Experiments; by Clifton E. Meloan. 8- A Century of Separation Science; by Haleem J. Issaq. 9- Solvent Extraction Principle and Practice; Edition, by Jan Rydberg,Claude Second Musikas and Gregory R. Choppin. 10- Quantitative Chromatographic Analysis; by Thomas E. Beesley, Benjamin Buglio and Raymond P. W. Scott. Course Program (Separation Methods) Week 1: 1- Introduction Important total analysis process steps: Sampling 6 Methods Separation Quantitation Evaluation 2- Separation Science -Definition of Separation Science -Classification and Application of Separations Week 2: I- Separation by Phase-Formation methods Volatilization Methods (conversion of Solid to Gas) Distillation Methods (conversion of Liquid to Gas) Separation by Precipitation II- Separation by Phase- transformation methods Extraction Week 3: 1. Solvent extraction (Liquid extraction) 1.5. The equilibrium constant 1.6. Efficiency of extraction 1.7. Selectivity of extraction 1.8. Nature of partition forces 1.8.1. Dispersion interaction 1.8.2. Dipole-Dipole interaction 1.8.3. Induction interaction 1.8.4. 4-Hydrogen bonding Week 4: 1.5. Extraction system 1.5.1. Extraction of Covalent, Neutral Molecules 1.5.1.1. pH effect 1.5.1.2. Effect of complex formation 1.5.1.3. Effect of association 1.6. Methods of Extraction 7 1.6.1. Batch extraction 1.6.2. Continuous extraction 1.6.3. Multistage extraction 2. Solid-Phase Extraction (Liquid-Solid Extraction) Week 5: First Examination Week 6: Chromatographic Methods 1. Introduction and some important definition in Chromatography 2. Chromatographic Methods 2.2. Plate theory 2.2. Rate theory 3. Chromatographic resolution 4. Classifications of chromatographic Methods Week 7: 5. Adsorption Chromatography 6. Partition Chromatography Week 8: 7. Plane Chromatography 7.1. Paper Chromatography (PC) 7.1.1. Techniques of Paper Chromatography 7.1.2. Preparative paper chromatography 7.1.3. Qualitative and Quantitative application of PC Week 9: 8- Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) Week 10: 9- Liquid Chromatography (LC) 10- High performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) 8 10.1. Bonded-Phase Column 10.2. Elution System Week 11: Second Examination Week 12: 11- Ion-Pair Chromatography 12- Ion Exchange Chromatography (IEC) 13- Affinity chromatography Week 13 13- Gas-Chromatography (GC) Week 14: Optional Examination Week 15: Seminar 9