SAA Human genome
advertisement
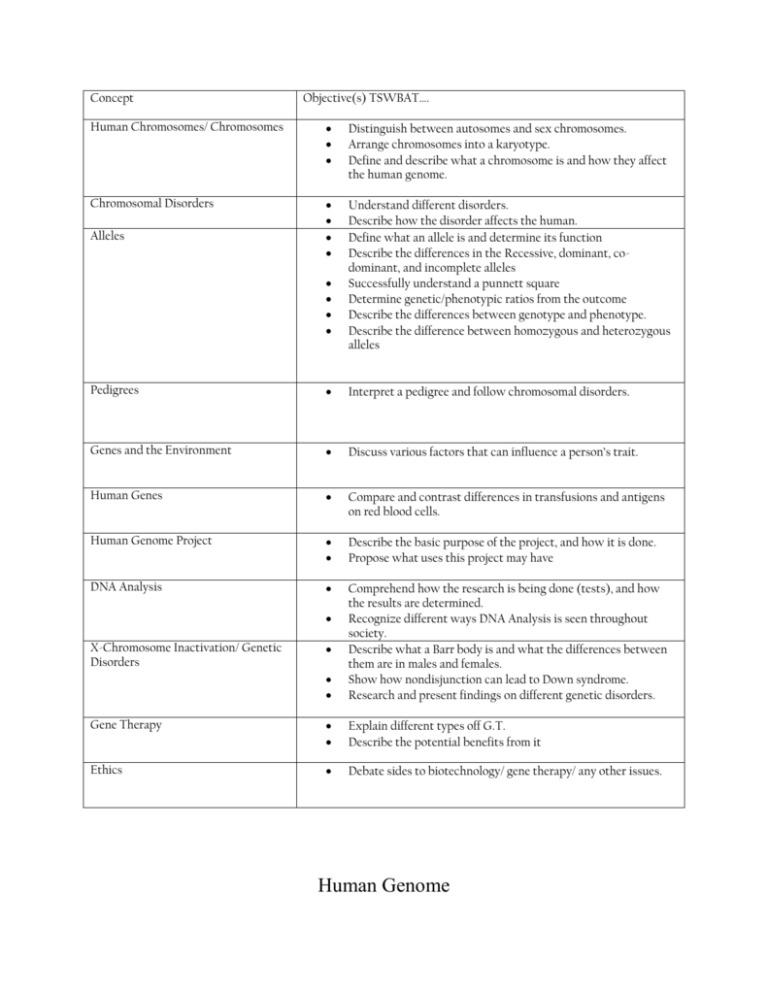
Concept Objective(s) TSWBAT…. Human Chromosomes/ Chromosomes Distinguish between autosomes and sex chromosomes. Arrange chromosomes into a karyotype. Define and describe what a chromosome is and how they affect the human genome. Chromosomal Disorders Understand different disorders. Describe how the disorder affects the human. Define what an allele is and determine its function Describe the differences in the Recessive, dominant, codominant, and incomplete alleles Successfully understand a punnett square Determine genetic/phenotypic ratios from the outcome Describe the differences between genotype and phenotype. Describe the difference between homozygous and heterozygous alleles Alleles Pedigrees Interpret a pedigree and follow chromosomal disorders. Genes and the Environment Discuss various factors that can influence a person’s trait. Human Genes Compare and contrast differences in transfusions and antigens on red blood cells. Human Genome Project Describe the basic purpose of the project, and how it is done. Propose what uses this project may have DNA Analysis Comprehend how the research is being done (tests), and how the results are determined. Recognize different ways DNA Analysis is seen throughout society. Describe what a Barr body is and what the differences between them are in males and females. Show how nondisjunction can lead to Down syndrome. Research and present findings on different genetic disorders. Gene Therapy Explain different types off G.T. Describe the potential benefits from it Ethics Debate sides to biotechnology/ gene therapy/ any other issues. X-Chromosome Inactivation/ Genetic Disorders Human Genome Unit Test 1. The variation of genes is called a. Alleles b. Traits c. Genes d. Characters 2. The principle of dominance states that a. All alleles are dominant b. All alleles are recessive c. Some alleles are dominant and others are recessive d. Alleles are neither dominant nor recessive 3. Organisms that have two identical alleles for a particular trait are said to be a. Hybrid b. Homozygous c. Heterozygous d. Dominant 4. A punnett square shows all of the following EXCEPT a. All possible results of a genetic cross. b. The genotypes of the offspring. c. The alleles in the gametes of each parent d. The actual results of a genetic cross 5. If you made a Punnett square showing Gregory Mendel’s cross between true-breeding (TT) tall plants and the true breeding (tt) short plants, the square would show that the offspring had a. The genotype of one of the parents b. A phenotype that was different from that of both parents c. A genotype that was different from that of both parents d. The genotype of both parents 6. Situations in which one allele for a gene is not completely dominant over another allele for that gene are called a. Multiple alleles b. Incomplete dominance c. Polygenic inheritance d. Multiple alleles 7. A cross of a black chicken (BB) with a white chicken (WW) produces all speckled offspring (BBWW). This type of inheritance is known as a. b. c. d. Incomplete dominance Polygenic inheritance Co-dominance Multiple alleles T= Tall T=short T t T T ***Complete this punnett square and use to complete questions 8-12**** 8. In the punnett square shown, which of the following is true about the offspring resulting from the cross? a. About half are expected to be short b. All are expected to be short c. About half are expected to be tall d. All are expected to be tall 9. The phenotypic ratio of the offspring is a. 2 tall: 2short b. 0 tall: 4 short c. 4 tall: 0 short d. 3 tall: 1 short 10. What is the chance of the offspring being heterozygous? a. 25% b. 50% c. 100% d. 0% 11. Tall plants is an example for a. Phenotype b. Genotype c. Allele d. Protein 12. TT is an example of a(n) a. Phenotype b. Genotype c. Allele d. Protein Match the disorder to the major symptoms. 13. Cystic Fibrosis _______ 14. Tay-Sachs Disease_____ 15. Huntington Disease______ 16. Sickle Cell Disease______ a)Misshapen red blood cells, and damage many tissues b) Mental deterioration and uncontrollable movements. c) Lipid accumulation in brain cells, mental deficiency, blindness, death in early childhood d) Excess mucus in lungs, digestive tract, and liver; Increased susceptibility to infections 17. Explain what is meant by homozygous and heterozygous and give an example of each. 18. Fill out the remainder of the blood group box below Blood type A B AB Antigens on RBC Donate Receive O 19. What is the difference between an autosome and a sex chromosome? 20. Give one example of how DNA analysis is used in society and described how it’s used in that scenario. 21. Compare and contrast gene therapy to how the environment could change genes. 22. Describe what the human genome project is, and what major uses it may have. ***Circle the correct answer. If false correct it to make it true. *** 23. T or F Genes on chromosomes are the units of inheritance. 24. T or F A dihybrid cross involves two pairs of contrasting traits. 25. T or F Heterozygous individuals have two of the same alleles for a particular gene. 26. Describe what gene therapy is and describe some possible issues as well as benefits involved with it. 27. What does the above picture represent? 28. What is the sex of the person? Also what do Barr bodies have to do with the determination of sexes? 29. How many chromosomes does this person have? 30. What disorder is present above and what causes it? 31. On the pedigree, identify the genotype for the following marker. A= B= C= D=








