Study guide for unit 1 test
advertisement

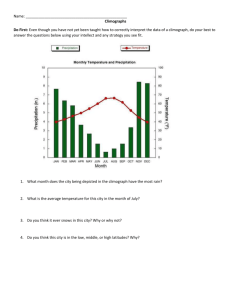
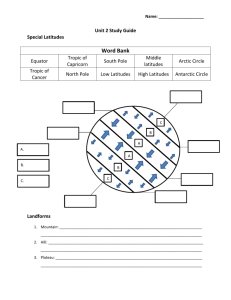
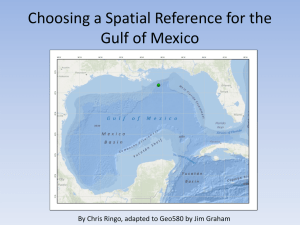
Study guide for test Vocabulary you should be able to DEFINE: 1. Five themes of Geography (location, region, place, 16. The different landforms: movement, human-environment interaction) Mountain/hill/plains/plateau/desert/peninsula/island/is 2. Globe thmus/valley/canyon/river/stream/ocean/sea/bay/gulf/ 3. Map delta/Reef/Sound/archipelago/strait/coast/beach/dunes 4. Types of maps (ex. Political, physical, climate, specialty /glacier/ice sheet/ice berg/inlet/lake/volcano/mountain etc) range 5. Projection 17. The different climates: arid/semi arid/tropical 6. Cylindrical projection wet/tropical wet and dry/humid subtropical/Marine west 7. Conical projection coast/ humid 8. Planer projection continental/subarctic/highlands/arctic/tundra/ice cap 9. Mercator projection 18. Time-zone 10. Gall-Peters projection 19. Longitude/Latitude (direction of lines + how to read them) 11. Robinson Projection 20. Latitudes 12. Distortion in projection (area/shape/distance) 21. Parallel/Meridians 13. Graphic scale 22. High latitudes/polar zone 14. Map scale: large scale/small scale 23. Middle latitudes 15. Compass Rose 24. Low latitudes 25. Precipitation 26. Temperature 27. Climate/weather Concepts you should be able to explain: 1. Latitudes (what does latitudes have to do with climate?) 2. Climate vs weather (what’s the difference?) 3. The Five themes and how they help you study geography 4. Globes vs. maps (the types of distortion, the challenge of creating flat maps etc) 5. Large scale vs small scale (what’s the difference? What are they each used for?) 6. Climate and landforms (how do they affect each other) 7. The process of how to read and understand a map (what do you do first, second, third etc) Study guide for test Vocabulary you should be able to DEFINE: 1. Five themes of Geography (location, region, place, 16. The different landforms: movement, human-environment interaction) Mountain/hill/plains/plateau/desert/peninsula/island/is 2. Globe thmus/valley/canyon/river/stream/ocean/sea/bay/gulf/ 3. Map delta/Reef/Sound/archipelago/strait/coast/beach/dunes 4. Types of maps (ex. Political, physical, climate, specialty /glacier/ice sheet/ice berg/inlet/lake/volcano/mountain etc) range 5. Projection 17. The different climates: arid/semi arid/tropical 6. Cylindrical projection wet/tropical wet and dry/humid subtropical/Marine west 7. Conical projection coast/ humid 8. Planer projection continental/subarctic/highlands/arctic/tundra/ice cap 9. Mercator projection 18. Time-zone 10. Gall-Peters projection 19. Longitude/Latitude (direction of lines + how to read them) 11. Robinson Projection 20. Latitudes 12. Distortion in projection (area/shape/distance) 21. Parallel/Meridians 13. Graphic scale 22. High latitudes/polar zone 14. Map scale: large scale/small scale 23. Middle latitudes 15. Compass Rose 24. Low latitudes 25. Precipitation 26. Temperature 27. Climate/weather Concepts you should be able to explain: 1. Latitudes (what does latitudes have to do with climate?) 2. Climate vs weather (what’s the difference?) 3. The Five themes and how they help you study geography 4. Globes vs. maps (the types of distortion, the challenge of creating flat maps etc) 5. Large scale vs small scale (what’s the difference? What are they each used for?) 6. Climate and landforms (how do they affect each other) 7. The process of how to read and understand a map (what do you do first, second, third etc)