Algebra-II-Honors-Q3.. - Franklin County Community School
advertisement
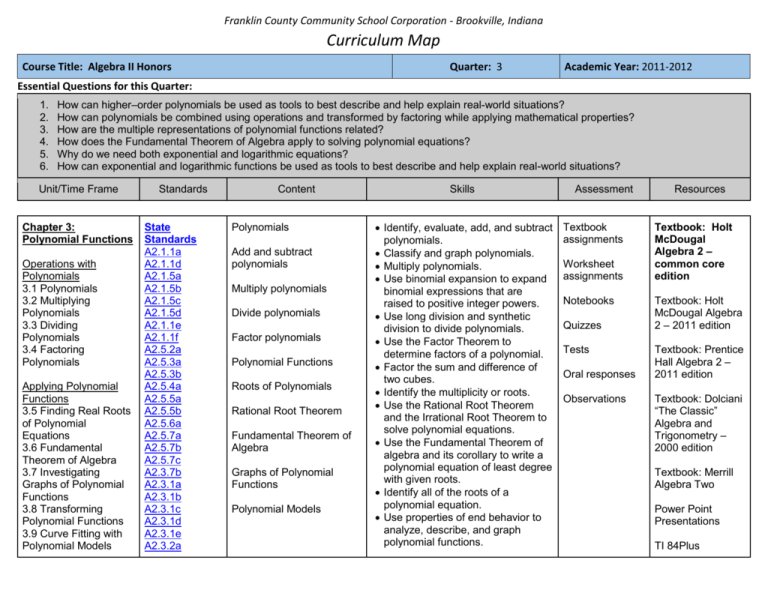
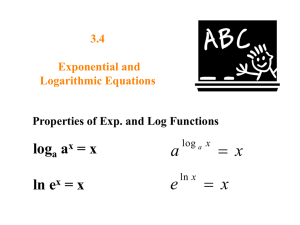
Franklin County Community School Corporation - Brookville, Indiana Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra II Honors Quarter: 3 Academic Year: 2011-2012 Essential Questions for this Quarter: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. How can higher–order polynomials be used as tools to best describe and help explain real-world situations? How can polynomials be combined using operations and transformed by factoring while applying mathematical properties? How are the multiple representations of polynomial functions related? How does the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra apply to solving polynomial equations? Why do we need both exponential and logarithmic equations? How can exponential and logarithmic functions be used as tools to best describe and help explain real-world situations? Unit/Time Frame Chapter 3: Polynomial Functions Operations with Polynomials 3.1 Polynomials 3.2 Multiplying Polynomials 3.3 Dividing Polynomials 3.4 Factoring Polynomials Applying Polynomial Functions 3.5 Finding Real Roots of Polynomial Equations 3.6 Fundamental Theorem of Algebra 3.7 Investigating Graphs of Polynomial Functions 3.8 Transforming Polynomial Functions 3.9 Curve Fitting with Polynomial Models Standards State Standards A2.1.1a A2.1.1d A2.1.5a A2.1.5b A2.1.5c A2.1.5d A2.1.1e A2.1.1f A2.5.2a A2.5.3a A2.5.3b A2.5.4a A2.5.5a A2.5.5b A2.5.6a A2.5.7a A2.5.7b A2.5.7c A2.3.7b A2.3.1a A2.3.1b A2.3.1c A2.3.1d A2.3.1e A2.3.2a Content Polynomials Add and subtract polynomials Multiply polynomials Divide polynomials Factor polynomials Polynomial Functions Roots of Polynomials Rational Root Theorem Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Graphs of Polynomial Functions Polynomial Models Skills Identify, evaluate, add, and subtract polynomials. Classify and graph polynomials. Multiply polynomials. Use binomial expansion to expand binomial expressions that are raised to positive integer powers. Use long division and synthetic division to divide polynomials. Use the Factor Theorem to determine factors of a polynomial. Factor the sum and difference of two cubes. Identify the multiplicity or roots. Use the Rational Root Theorem and the Irrational Root Theorem to solve polynomial equations. Use the Fundamental Theorem of algebra and its corollary to write a polynomial equation of least degree with given roots. Identify all of the roots of a polynomial equation. Use properties of end behavior to analyze, describe, and graph polynomial functions. Assessment Textbook assignments Worksheet assignments Notebooks Quizzes Tests Oral responses Observations Resources Textbook: Holt McDougal Algebra 2 – common core edition Textbook: Holt McDougal Algebra 2 – 2011 edition Textbook: Prentice Hall Algebra 2 – 2011 edition Textbook: Dolciani “The Classic” Algebra and Trigonometry – 2000 edition Textbook: Merrill Algebra Two Power Point Presentations TI 84Plus Franklin County Community School Corporation - Brookville, Indiana Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra II Honors Quarter: 3 Academic Year: 2011-2012 Essential Questions for this Quarter: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. How can higher–order polynomials be used as tools to best describe and help explain real-world situations? How can polynomials be combined using operations and transformed by factoring while applying mathematical properties? How are the multiple representations of polynomial functions related? How does the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra apply to solving polynomial equations? Why do we need both exponential and logarithmic equations? How can exponential and logarithmic functions be used as tools to best describe and help explain real-world situations? Unit/Time Frame Chapter 4: Expponential and Logarithmic Functions Exponential Functions and Logarithms 4.1 Exponential Functions, Growth and Decay 4.2 Inverses of Relations and Functions 4.3 Logarithmic Functions 4.4 Properties of Logarithms Standards A2.3.2b A2.3.3b A2.7.1a A2.7.1b A2.7.1c A2.7.2a A2.7.2b A2.7.2c A2.7.3a A2.7.3b A2.7.4a A2.7.4b A2.7.4c A2.7.4d A2.7.5a A2.7.6a A2.7.6b A2.7.7a A2.7.8a A2.7.8b Standards for Mathematical Practice SMP1-8 Content Exponential Functions Inverses of Relations and Functions Logarithms Logarithmic Functions Common Logarithms Properties of Logarithms Skills Identify and use maxima and minima of polynomial functions to solve problems. Transform polynomial functions. Use finite differences to determine the degree of a polynomial that will fit a given set of data. Use technology to find polynomial models for a given set of data. Write and evaluate exponential expressions to model growth and decay situations. Graph and recognize inverses of relations and functions. Find inverses of functions. Write equivalent forms for exponential and logarithmic functions. Write, evaluate, and graph logarithmic functions. Use properties to simplify logarithmic expressions. Translate between logarithms and any base. Assessment Resources Graphing Calculator ADP Core 40 Algebra II Item Sampler SAT sample tests from the college board Franklin County Community School Corporation - Brookville, Indiana Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra II Honors Quarter: 3 Academic Year: 2011-2012 Essential Questions for this Quarter: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. How can higher–order polynomials be used as tools to best describe and help explain real-world situations? How can polynomials be combined using operations and transformed by factoring while applying mathematical properties? How are the multiple representations of polynomial functions related? How does the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra apply to solving polynomial equations? Why do we need both exponential and logarithmic equations? How can exponential and logarithmic functions be used as tools to best describe and help explain real-world situations? Unit/Time Frame Standards Applying Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities 4.6 The Natural Base,e 4.7 Transforming Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.8 Curve Fitting with Exponential and Logarithmic Models Common Core Standards CC.9-12: N.CN.7-9 A.SSE.1,2 A.CED.1-3 A. APR.1-6 A.REI.11 F.IF.5 F.IF.7 F.IF.8 F.BF.3-5 F.LE.4 Content Exponential and Logarithmic Equations The Natural Base, e Natural Logarithms Exponential and Logarithmic Graphs Exponential and Logarithmic Models Skills Solve exponential and logarithmic equations and inequalities. Solve problems involving exponential and logarighmic equations. Use the number e to write and graph exponential functions representing real-world situations. Solve equations and problems involving e or natural logarithms. Transform exponential and logarithmic functions by changing parameters. Describe the effects of changes in the coefficients of exponential and logarithmic functions. Model data by using exponential and logarithmic functions. Use exponential and logarithmic models to analyze and predict. Assessment Resources Franklin County Community School Corporation - Brookville, Indiana COMMON CORE AND INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS