Genetic Engineering Class Notes
advertisement
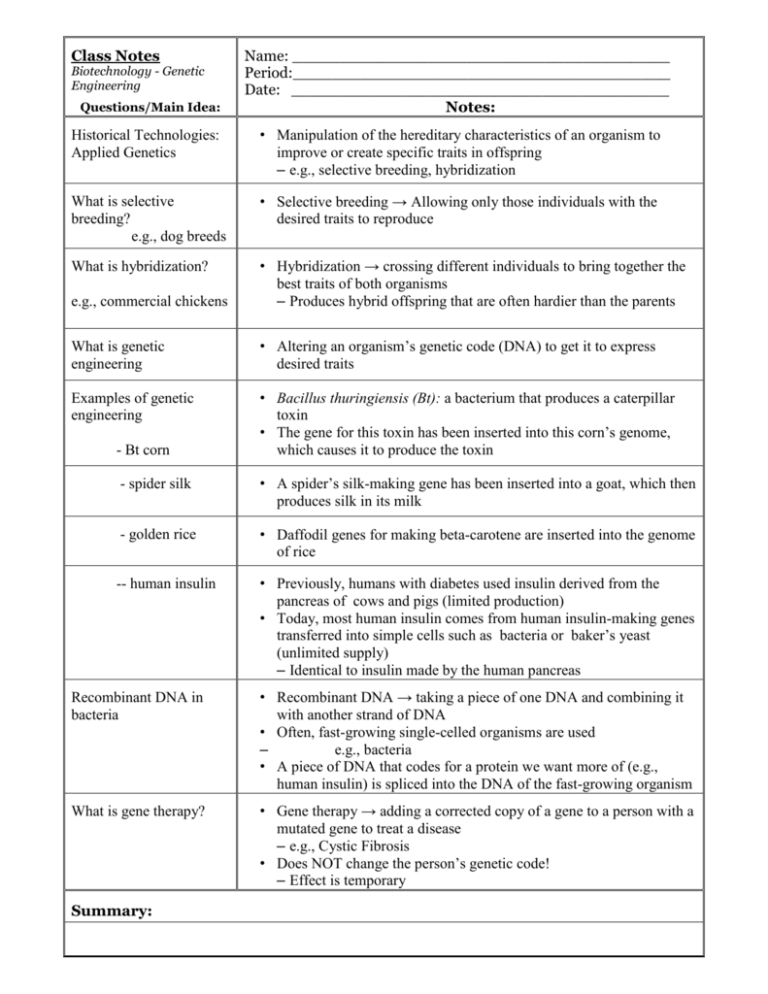
Class Notes Biotechnology - Genetic Engineering Questions/Main Idea: Name: _______________________________________ Period:_______________________________________ Date: _______________________________________ Notes: Historical Technologies: Applied Genetics • Manipulation of the hereditary characteristics of an organism to improve or create specific traits in offspring – e.g., selective breeding, hybridization What is selective breeding? e.g., dog breeds • Selective breeding → Allowing only those individuals with the desired traits to reproduce What is hybridization? e.g., commercial chickens • Hybridization → crossing different individuals to bring together the best traits of both organisms – Produces hybrid offspring that are often hardier than the parents What is genetic engineering • Altering an organism’s genetic code (DNA) to get it to express desired traits Examples of genetic engineering • Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): a bacterium that produces a caterpillar toxin • The gene for this toxin has been inserted into this corn’s genome, which causes it to produce the toxin - Bt corn - spider silk • A spider’s silk-making gene has been inserted into a goat, which then produces silk in its milk - golden rice • Daffodil genes for making beta-carotene are inserted into the genome of rice -- human insulin • Previously, humans with diabetes used insulin derived from the pancreas of cows and pigs (limited production) • Today, most human insulin comes from human insulin-making genes transferred into simple cells such as bacteria or baker’s yeast (unlimited supply) – Identical to insulin made by the human pancreas Recombinant DNA in bacteria • Recombinant DNA → taking a piece of one DNA and combining it with another strand of DNA • Often, fast-growing single-celled organisms are used – e.g., bacteria • A piece of DNA that codes for a protein we want more of (e.g., human insulin) is spliced into the DNA of the fast-growing organism What is gene therapy? • Gene therapy → adding a corrected copy of a gene to a person with a mutated gene to treat a disease – e.g., Cystic Fibrosis • Does NOT change the person’s genetic code! – Effect is temporary Summary: