business systems - Eastern Illinois University
advertisement

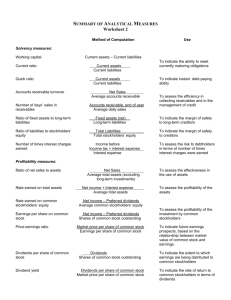
Eastern Illinois University BUS 2101 Exam One Topics Calculations will be required for items in bold. INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Chapter 1 Reading: Pages 2-23 1) Forms of business organization a) Sole proprietorships i) Advantages ii) Disadvantages b) Partnerships i) Advantages ii) Disadvantages c) Corporations i) Advantages of incorporation ii) Disadvantages of incorporation 2) Users and uses of accounting information a) Internal users i) Management b) External users i) Investors ii) Creditors: iii) Financial analysts: 3) Three types of business activity a) Operating activities: buying and selling goods; providing services b) Investing activities: purchase of property, plant and equipment needed for business c) Financing activities: obtaining funds to buy property and equipment if operating activities don’t provide enough cash 4) Content and purpose of each financial statement a) Income Statement: summarizes revenue and expenses over a period of time b) Statement of Retained Earnings: discloses all the earnings that have not been distributed to owners c) Balance Sheet: as of a certain date, what the business owns, owes and what’s left over. i) Contains accounting equation: assets = liabilities + owners equity d) Statement of Cash Flows: it discloses the sources and uses of cash i) From operating, investing and financing activities ii) Also, beginning and ending cash balances e) Financial statements are interrelated i) Net income from income statement included in Statement of Retained Earnings ii) Retained Earnings included on Balance Sheet iii) Cash from Statement of Cash Flows is included on Balance Sheet 5) Accounting equation 6) Other components of annual report a) Management’s discussion and analysis: explain what happened and why and plans for the future b) Notes to the Financial Statements: provide further elaboration on items in financial statements such as accounting methods used c) Auditor’s report: financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP 7) Assumptions and principles underlying financial statements a) Cost principle: assets should be recorded at cost 1 b) Full disclosure principle: disclose any information that would impact decisions of financial statement users A FURTHER LOOK AT FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Chapter 2 Reading: Pages 48-67 1) Generally accepted accounting principles: (GAAP): provide guidance in preparing financial statements a) FASB: b) SEC 2) Characteristics of useful accounting information a) Relevance b) Reliability: c) Comparability: d) Consistency: 3) Constraints which modify GAAP a) Cost-benefit: b) Material c) Conservatism: 4) Classified balance sheet a) Current assets b) Property, plant and equipment (1) Accumulated Depreciation c) Current liabilities: to be paid within one year d) Long-term liabilities: to be paid in more than one year 5) Comparative analysis: a single number such as earnings per share means nothing a) Intracompany basis: compare amount with same item for the company in the prior year b) Industry averages c) Intercompany averages i) It is very hard to find similar companies 6) Ratio analysis: a) Liquidity ratios i) Working capital: current assets - current liabilities ii) Current ratio = current assets/current liabilities iii) Quick ratio = current assets - inventory/current liabilities b) Profitability ratios: of concern to stockholders and long-term creditors i) Earnings per share = net income/number of outstanding shares of common stock ii) Profit margin = net income/net sales iii) Return on assets = net income/average total assets (1) Measures net income generated by assets iv) Return on equity = net income/average stockholders equity c) Market ratios: of concern to stockholders i) Price/Earnings ratio = Stock price/earnings per share (1) Reflects future prospects for a company d) Solvency ratios: of concern to long-term creditors such as bond holders i) Debt to assets = total liabilities/total assets THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM Chapter 3 Reading: Pages 94-122 1) Recording Transactions in T Accounts a) Transaction: 2 b) Accounting equation must balance after recording each transaction 2) Recording and Posting Transactions a) General journal b) Ledger accounts 3) The Trial Balance a) If debits do not equal credits: b) If debits do equal credits could still have errors ACCRUAL ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS Chapter 4 Reading: Pages 148-166; 170-180 1) Time period assumption: a) Fiscal year: can be a calendar year or a time period ending during a time of slow economic activity 2) Revenue recognition: when should a transaction be recorded? 3) Matching principle: expenses should be recognized in the period they help generate revenue 4) Cash basis accounting: a) Record revenue when you receive the cash b) Record expenses when you pay them 5) Accrual accounting a) Uses matching rule to record revenue and expenses b) Adjusting the accounts at the end of the accounting period i) Some accounts require adjustment due to transactions that cover more than one accounting period: (1) Prepaid expense adjusting entries (2) Unearned revenue (3) Accrued revenue (4) Accrued expenses c) Adjusted trial balance i) Trial balance is updated to reflect adjustments prepared at the end of the accounting period. 6) Closing entries: a) journal entries made at the end of the accounting period to: i) Eliminate balances in the revenue, expense and dividend accounts ii) Transfers revenue and expense to the Income Summary account iii) From Income Summary account, net income is transferred to Retained Earnings 7) Overview of the accounting cycle using a worksheet a) Steps in the accounting cycle i) Analyze business transactions from source documents ii) Record transaction in journal entries iii) Post the journal entries to the ledger accounts iv) Prepare a trial balance on the worksheet v) Enter adjusting entries in the adjustments columns of the work sheet vi) Prepare adjusted trial balance vii) Extend adjusted columns to appropriate statement columns viii) Total the statement columns, compute net income and enter in income statement and balance sheet columns to balance both. ix) Prepare financial statements x) Close the temporary accounts xi) Prepare a post-closing trial balance 3