Global_Englishes_handbook_2013-14
advertisement

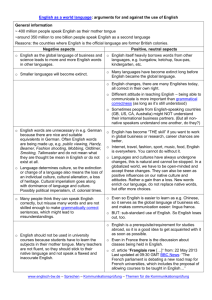
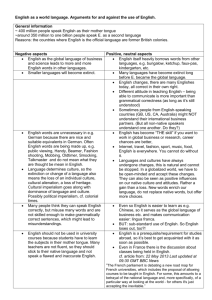
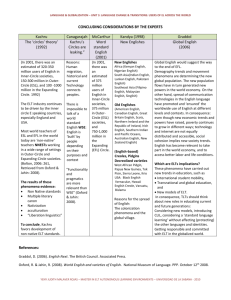
Global Englishes Semester 1, 2013-14 LASC10056 and LASC11079 Course organiser: Dr Claire Cowie claire.cowie@ed.ac.uk Office 1.11a DSB Extension 508392 Venues and Times: Tues 9:00-10:50am Thurs 10-10:50am DSB 3.10/3.11 DSB 3.10/3.11 Office hour for Global Englishes: Wednesdays 12:00-1pm Or email me for an appointment. What’s this course about? This course not only describes varieties of English outside of Britain, but also provides theories for their structure and development. Thus we pay attention to the linguistic structure of these varieties, but also to the radically different socio-historical contexts which have given rise to Contact Englishes:. The course has four main strands: The demand for and the teaching of English as a “foreign language”; the varieties of English selected for this purpose; and language attitudes among teachers and learners World Englishes or “L2” varieties in Asia and Africa; their histories of colonisation; acquisition through education; grammatical and phonological features of L2 varieties; substrate influence; development of local norms; local variation The social and historical settings that give rise to pidgin and creole varieties; debates about the role of substrate languages versus “universal” creole features; the use of standard English in creole settings; and post-creole continua. The most recent forms of English found in immigrant or diaspora communities in North America and the UK What will I learn? On successful completion of this module, students will be able to: Show understanding of the current challenges and choices that face English speakers and learners in different countries Describe and critique the main issues and debates over the emergence of extraterritorial Englishes Show understanding of the histories and social contexts that have given rise to contact Englishes Discriminate between and define key terms in the field Demonstrate familiarity with quantitative approaches to the study of variation in Contact Englishes Demonstrate familiarity with research methods to investigating attitudes towards Contact Englishes 1 Demonstrate familiarity with the ways that these varieties and attitudes towards them are represented in a range of media How is teaching organised? Each week consists of 2 hours of seminar style sessions and a more practical one hour workshop session. Students are expected to keep up with the key readings for the seminars, and encouraged to explore some of the recommended reading, links and films. In weeks where timetabling permits I will arrange to see MSc students separately, but in many sessions we will find that it is useful to have a mix of international students and UK students. You will find the following on Learn: This handbook and bibliography in an easier to use format! Powerpoint slides for the seminars which will appear on Learn the previous day, so that you can print them out if you would like a paper copy with you. I encourage you to annotate the presentation on a laptop or similar in class. Please bear in mind that the version you may download on Learn before the lecture may be a DRAFT version (i.e. there may be some bits missing), but the final version used in the seminar will be uploaded to Learn after the seminar Follow-up material to workshop sessions Discussions: I will prompt you to send questions related to seminars and workshops. All questions related to the content of assessments will be directed to Discussions on Learn. This is so that everyone can benefit from guidance, discussion and debate. You can of course also discuss your approach to assessments with me in my office hour. PDFs Where possible I will also place papers, chapters and other materials on Learn. Bear in mind that documents can be subject to copyright restrictions and that data can be subject to confidentiality agreements. Textbooks The key readings for each week are the most important, and I am likely to have referred to the background material in class. I can recommend the following textbooks: Seargeant, Philip (2012). Exploring World Englishes: Language in a Global Context. Routledge Introductions to Applied Linguistics. Abingdon: Routledge. Mesthrie, Rajend and Rakesh M. Bhatt (2008) World Englishes: The Study of New Linguistic Varieties. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Many World Englishes textbooks are very descriptive – these offer somewhat more theoretical discussion. There are other very good textbooks which are more suitable for prehonours: 2 Schneider, Edgar W. (2011) English Around the World: An Introduction. Cambridge: CUP Jenkins, Jennifer (2003) World Englishes: a resource book for students. London: Routledge The Bibliography is very long and is not a list of required reading! Any references that I use in class will appear in the Bibliography (which will be updated continuously and reloaded to Learn). It’s also intended as a helpful resource for you to trawl through when you are looking for reading for assessments. Assessment The first assessment is a short essay (1500 words) which is primarily a literature review. The second assessment (2500 words) is a project which requires you to analyse primary data. The two assessments are explicitly linked so that the first formative assessment can inform your data project. The first assessment is due in week 7 and returned at the end of week 10. First assessment (worth 30%): Short essay on set topics (1500 words). Topics will be issued by the beginning of week 3. Due: 12 noon Thursday 31st October 2013 Second assessment (worth 70%): A longer essay of 2500 words which contains an empirical component (e.g. data analysis, survey or critical reading of text/film). Topics will be issued by the beginning of week 3. Due: Thursday 12th December 12 noon Programme Week 1 English as a Global Language Topics: What does it mean to be a “Global Language”? How many people speak English? The real and symbolic capital of English The politics of English as a Global Language Modelling English as a Global Language Key Reading: Graddol, David (2006) English Next: Why global English may mean the end of ‘English as a foreign language’?. British Council. Part 2.2. pp81-102 Learning English www.britishcouncil.org/learning-research-englishnext.htm Pennycook A. D. (2003) Global Englishes, rip slyme, and performativity. Journal of Sociolinguistics 7/4: 513-33. Recommended Reading: Davies, A., Hamp‐Lyons, L., & Kemp, C. (2003). Whose norms? International proficiency tests in English. World Englishes, 22(4), 571-584. 3 Mesthrie, Rajend and Rakesh M. Bhatt (2008) World Englishes: The Study of New Linguistic Varieties. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Chapter 1. Phillipson, R. (1998). Globalizing English: Are linguistic human rights an alternative to linguistic imperialism?. Language Sciences, 20(1), 101-112. Seargeant, Philip (2012). Exploring World Englishes: Language in a Global Context. Routledge Introductions to Applied Linguistics. Abingdon: Routledge.Chapters 12 and 13 Seargeant, Philip and Erling, Elizabeth (2011). The discourse of English as a language for international development: policy assumptions and practical challenges. In: Coleman, Hywel ed. Dreams and Realities: Developing Countries and the English Language. London: British Council, pp. 248- 267. Week 2 English as a Foreign Language (EFL) Topics: Learners’ attitudes to varieties of English The target variety for learners of English as a foreign language English Learning and Identity Intelligibility Native speaker attitudes to non-native speaker accents Workshop: Conducting a survey of attitudes towards varieties of English Interview with an English learner in your class Key Readings: Erling, Elizabeth J. (2002) ’I learn English since ten years’: The Global English debate and the German university classroom’ English Today 18/2: 8-13 Jenkins, Jennifer (2007) English as a Lingua Franca: Attitude and Identity. Oxford: OUP. Chapter 6 [copy of ch 6 on ereserve; good to read chapter 1 as well if you can get the book from the library.] Recommended Reading: Chiba, R. H Matsuura and A. Yamamoto (1995) ‘Japanese attitudes towards English accents’. World Englishes 14/1: 77-86 Dalton-Puffer, Kaltenboeck and Smit (1997) ‘Learner attitudes and L2 pronunciation in Austria’. World Englishes 16/1 Deterding, David and Andy Kirkpatrick (2006) Emerging South-East Asian Englishes and intelligibility. World Englishes 25: 391-409. Hu, Xiaoqiong (2004) Why China English should stand alongside British, American and the other World Englishes. English Today 20:26-33 Kang, O., & Rubin, D.L. (2009). Reverse linguistic stereotyping: Measuring the effect of listener expectations on speech evaluation. Journal of Language and Social Psychology, 28:4, 441-456. Kubota, Ryuko (1998) ‘Ideologies of English in Japan’ in World Englishes 17:3 Lindemann, Stephanie (2011) Who’s “unintelligible”? The perceiver’s role. Issues in Applied Linguistics 18(2) 223-232. 4 Lindemann, Stephanie (2005) Who speaks 'broken English'? US undergraduates' perceptions of non-native English. International Journal of Applied Linguistics 15(2), 187-212 Lindemann, Stephanie (2003) Koreans, Chinese, or Indians? Attitudes and ideologies about non-native English speakers in the United States. Journal of Sociolinguistics 7(3), 348-364. Munro, M. J. and Derwing, T. M. (1995), Foreign Accent, Comprehensibility, and Intelligibility in the Speech of Second Language Learners. Language Learning, 45: 73–97. Seargeant, Philip (2012). Exploring World Englishes: Language in a Global Context. Routledge Introductions to Applied Linguistics. Abingdon: Routledge.Chapter 4 Zhang, Wei & Lijuan Ding (2011) A preliminary study on Chinese EFL learners’ attitude towards their accent. ICPhS XVII Hong Kong Week 3 The English as a Lingua Franca movement Topics: The Kachru and Quirk debate in English Today What is ELF? Misunderstandings of ELF The practicalities of teaching ELF Evidence for what speakers do when using ELF Workshop: Using corpora to explore ELF Key readings: Jenkins, Jennifer (2002) ‘A sociolinguistically based, empirically researched pronunciation syllabus for English as an International Language’ Applied Linguistics 23/1: 83-103. Seidlhofer, B. (2005) ‘English as a Lingua Franca’. ELT Journal 59/4:339-41. Recommended reading: Breiteneder, Angelika (2009) English as a lingua franca in Europe: an empirical perspective. World Englishes 28:2. 356-269 Dewey, Martin and Alessio Cogo (2012) Analysing English as a Lingua Franca: A Corpusdriven Investigation. Continuum Kachru, Braj B (1991) ‘Liberation linguistics and the Quirk concern’ English Today 25 [on Learn] Prodromou, Luke (2008) English as a Lingua Franca: A Corpus-based Analysis. Continuum Quirk. R. (1990) Language varieties and standard language. English Today 21: 3-10 [on Learn] Seargeant, Philip (2012). Exploring World Englishes: Language in a Global Context. Routledge Introductions to Applied Linguistics. Abingdon: Routledge.Chapters 6 and 7 5 Week 4 World English and pidgins/creoles: histories and contexts Topics: Norm development in World Englishes Schneider’s model of the development of New Englishes The acquisition of English through mass education Education and World Englishes today Attitudes towards varieties of English in postcolonial contexts Workshop: Prescriptivism in Singapore Key Reading: Bamgbose, Ayo (1998) ‘Torn between the norms: innovations in World Englishes’. World Englishes 17/1: 1-14 Schneider, E. W. (2003) The dynamics of New Englishes: from identity construction to dialect birth. Language 79/2: 233- 81 Background Reading: Graddol, David (2010) English Next India: The future of English in India. British Council. www.britishcouncil.org/learning-research-englishnext.htm Brutt-Griffler, Janina (2002) World English: A study of its Development. Clevedon: Multilingual Matters. Chapters 3 and 4 Mesthrie and Bhatt (2008) Chapter 1. Mufwene, Salikoko (2001) The Ecology of Language Evolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press Schneider, E.W. (2006) Postcolonial Englishes. Cambridge: CUP. Igboanusi, H. (2008) Empowering Nigerian Pidgin: a challenge for status planning?, World Englishes, Vol. 27, No. 1, pp. 68-82 Rubdy, Rani (2001) Creative destruction: Singapore’s Speak Good English Movement. World Englishes 20:3. 341-355 Tsui, Amy B. M. and David Bunton (2003) The discourse and attitudes of English language teachers in Hong Kong. World Englishes 19/3: 287-303 Week 5 The grammatical features of contact varieties and their explanation Topics: Substrate influence and universals in creolistics Substrate influence and universals in World Englishes Aspect in Singlish The progressive in Indian English Workshop: Copula deletion in Singlish Key reading: Sharma, Devyani (2009) “Typological diversity in New Englishes, English World-Wide, Volume 30, Number 2, 2009 , pp. 170-195 6 Williams, Jessica. (1987) ‘Non-native varieties of English: a special case of language acquisition’. English World-Wide 8:2 Recommended reading: Ansaldo, U. 2004. The evolution of Singapore English: Finding the matrix. In L. Lim (ed.). Singapore English: A grammatical description. Varieties of English Around the World G33. Amsterdam/Philadelphia: John Benjamins. 127-149. Bao, Z. (2005) The aspectual system of Singapore English and the systemic substratist explanation. Journal of Linguistics 41: 237-67. Filppula, Marko, Juhani Klemola & Heli Paulasto “Vernacular Universals and Language Contacts: An Overview” in Filppula, Marko, Juhani Klemola & Heli Paulasto (eds.) (2009) Vernacular universals and language contacts: Evidence from varieties of English and beyond. New York & London: Routledge. Mesthrie and Bhatt (2008) Chapter 6. Meyerhoff, Miriam 2008. Bequia (is/Ø) sweet: Syntactic variation in a lesser-known variety of Caribbean English. English Today 93, 24. 31-37 Platt, J.T (1975) The Singapore English speech continuum and its basilect ‘Singlish’ as a creoloid. Anthropological Linguistics 17: 363-74 Platt, John T., Weber, Heidi and Mian Lian Ho (1984) The New Englishes. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul. Week 6 Work on assessment 1 Week 7 The grammatical features of contact varieties and their explanation Topics: Copula deletion in Singlish Copula deletion in Creoles Are Creoles and World Englishes really different? Article deletion Discourse features of World Englishes Workshop: Article deletion Key reading: Sharma, D (2005) Language Transfer and Discourse Universals in Indian English article use. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 27: 535-566 Lange, Claudia (2007) Focus marking in Indian English. English World Wide 28:1. 89-118 Recommended reading: Sand, A. (2004) Shared morpho-syntactic features in contact varieties of English: article use. World Englishes 23: 281-98. Mesthrie and Bhatt (2008) Chapters 2, 3 and 5 and 6. 7 Platt, John T., Weber, Heidi and Mian Lian Ho (1984) The New Englishes. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul. Week 8 The accents of World Englishes Sociolinguistic variation in Indian English Sociopolitical change and ethnic variation in South African English External and internal norm orientation: Rhoticity in Asian Englishes Workshop: External and internal norm orientation: consonant clusters in Nigeria and Singapore Key reading: Gut, Ulrike (2007) ‘First language influence and final consonant clusters in the new Englishes of Singapore and Nigeria’ World Englishes 26/3: 346-359 Mesthrie, Rajend (2010) Socio-phonetics and social change: Deracialisation of the GOOSE vowel in South African English. Journal of Sociolinguistics 14:1. 3-33 Background Reading Mesthrie and Bhatt (2008) Chapter 4 Chand, Vineeta (2009) “[v]at is going on? Local and global ideologies about Indian English”, Language in Society 38: 393-419 Chand, Vineeta. 2010. Postvocalic (r) in urban Indian English. English World-wide, 31(1):139. Deterding, David, Jennie Wong and Andy Kirkpatrick (2008) ‘The pronunciation of Hong Kong English’ English World-Wide, Volume 29, Number 2, pp. 148-175. Sahgal, A., & Agnihotri, R. K. (1988). Indian English Phonology: a sociolinguistic perspective. English World-Wide, 9, 51-64. Salbrina, Sharbawi and David Deterding (2010) Rhoticity in Brunei English English WorldWide 31:2. 121-137 Sharma, Devyani (2005) ‘Dialect stabilization and speaker awareness in non-native varieties of English’. Journal of Sociolinguistics 9 (2) Tan, Ying Ying (2012) To r or not to r: social correlates of /ɹ/ in Singapore English International Journal of the Sociology of Language vol. 218 Week 9 Mixing it up: is this English? Multilingualism, code-switching with English and mixed codes. Topics: Multilingualism and code-switching in postcolonial contexts English and Hindi code-switching in Bollywood movies and in real life Code-switching and mixed codes in urban African settings Mixed codes and global hip hop Workshop: English-Cantonese code-switching in Hong Kong. Discussion of the film Multilingual Hong Kong. 8 Reading: Myers-Scotton, C. (1990). Codeswitching with English: types of switching, types of communities. World Englishes 6, 33-48. Si, Aung (2010) A Diachronic Investigation of Hindi-English code-switching, using Bollywood film scripts. International Journal of Bilingualism XX(X):1-20 Background: Alim, H. Samy, Awad Ibrahim and Alistair Pennycook, eds. (2009) Global linguistic flows: Hip Hop Cultures, youth identities, and the politics of language. London and New York: Routledge Auer, Peter (1999) From codeswitching via language mixing to fused lects: toward a dynamic typology of bilingual speech. International Journal of Bilingualism 3(4). 309-332. Finlayson, Rosalie, Karen Calteaux, and Carol Myers-Scotton (1998) ‘Orderly mixing and accommodation in South African codeswitching’. Journal of Sociolinguistics 2/3: 395-420. Omoniyi, T. (2006) Hip-hop through the World Englishes lens: a response to globalization. World Englishes 25/2:195-208 Pennycook A. D. (2003) Global Englishes, rip slime, and performativity. Journal of Sociolinguistics 7/4: 513-33. Samy, Alim, H. (2009). Translocal style communities: Hip hop youth as cultural theorists of style, language, and globalization. Pragmatics 19(1). 103-128. Week 10 Diaspora Englishes and Immigrant Englishes Topics: Is there an identifiable British Asian English? What are the features of British Asian English? What is the relationship between Jamaican, London Jamaican and British Black English? Who speaks London Jamaican or “Jafrican”? Key readings: Cheshire, J., Kerswill, P., Fox, S., & Torgersen, E. (2011). Contact, the feature pool and the speech community: The emergence of Multicultural London English. Journal of Sociolinguistics, 15(2), 151-196. Sharma, Devyani and Lavanya Sankaran (2011) Cognitive and social forces in dialect shift: Gradual change in London Asian Speech. Language Variation and Change 23: 399428 Radio 4 broadcast on “ghetto grammar” in London http://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/b03brt2x Recommended Reading: Eckert, P. (2008). Where do ethnolects stop?. International Journal of Bilingualism, 12(1-2), 25-42. Mendoza-Denton, N. (2008). Homegirls: Language and cultural practice among Latina youth gangs. John Wiley & Sons. 9 Rampton, B. (1995). Crossing: Language and ethnicity among adolescents. London: Longman. Rampton, B. (1999). Crossing. Journal of Linguistic Anthropology, 9(1‐2), 54-56. Sebba, M. (1993). London Jamaican. London: Longman. Sebba, M., & Tate, S. (2002). “Global” and “Local” identities in the discourses of Britishborn Caribbeans. International Journal of Bilingualism, 6(1), 75-89. Sebba, M. (1986). London Jamaican and Black London English. The Language of the Black Experience, Oxford: Blackwell, 149-167. Sharma, D. (2011). Style repertoire and social change in British Asian English. Journal of Sociolinguistics, 15(4), 464-492. Week 11 Feedback meetings on assessment 1 and consultations for assessment 2 Bibliography Ahai, N and N. Faraclas, ‘The Products of English-medium education in Papua New Guinea’ Reprinted in: Graddol, David and Sharon Goodman eds. (1996) Redesigning English: new texts, new identities Routledge: London and New York [paper on WebCT] Agnihotri, Rama K and Amrit L Khanna (1997) Problematizing English in India New Delhi; London: Sage Al-Issa & Dahan eds. (2011) Global English and Arabic: Issues of language, culture, and identity. Oxford: Peter Lang, 2011. Alim, H. Samy, Awad Ibrahim and Alistair Pennycook, eds. (2009) Global linguistic flows: Hip Hop Cultures, youth identities, and the politics of language. London and New York: Routledge Anchimbe Eric A, ed. (2012) Language Contact in a Postcolonial Setting: The Linguistic and Social Context of English and Pidgin in Cameroon. De Gruyter Ansaldo, U. 2004. The evolution of Singapore English: Finding the matrix. In L. Lim (ed.). Singapore English: A grammatical description. Varieties of English Around the World G33. Amsterdam/Philadelphia: John Benjamins. 127-149. Appadurai, Arjun (1996) Modernity at large: cultural dimensions of globalization. University of Minnesota Press. Archibald , Alisdair, Alessia Cogo , & Jennifer Jenkins (2011) (eds.), Latest trends in ELF research. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Press, 2011. Pp. 311. Pb. $39.99. Auer, Peter (1999) From codeswitching via language mixing to fused lects: toward a dynamic typology of bilingual speech. International Journal of Bilingualism 3(4). 309-332. Balasubramahnian , Chandrika (2009) Register Variation in Indian English. Amsterdam/Philadelphia: Benjamins Bamgbose, Ayo (1998) ‘Torn between the norms: innovations in World Englishes’. World Englishes 17/1: 1-14 Bamgbose, Ayo (2001) ‘World Englishes and globalization’ in World Englishes 20:3 Bao, Z. (2005) The aspectual system of Singapore English and the systemic substratist explanation. Journal of Linguistics 41: 237-67. Baumgardner, Robert J (1996) South Asian English. Structure, Use, and Users. Urbana : University of Illinois Press Benati, Alessandro (2011) (ed.) Issues in second language proficiency. Continuum Berns, Margie (2005) ‘Expanding on the Expanding Circle: where do WE go from here?’ in World Englishes 24/1 10 Block, David and Deborah Cameron eds. (2002) Globalization and Language Teaching. London: Routledge Blommaert, Jan (2010) The Sociolinguistics of Globalization. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press [Moray house library] Bolton, Kingsley (2000) ‘The sociolinguistics of Hong Kong and the space for Hong Kong English’. World Englishes 19/3: 265-85 Bolton, Kingsley (2004) ‘World Englishes’ in The handbook of Applied Linguistics eds. Alan Davies and Catherine Elder. Malden, Mass.: Blackwell Bolton, Kingsley (2005) Chinese Englishes: A Sociolinguistic History. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press Bolton, Kingsley (2005) ‘Where WE stands: approaches, issues, and debate in world Englishes’ in World Englishes 24/1 Bolton, Kingsley ed. (2002). Hong Kong English: Autonomy and Creativity. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press. Breiteneder, Angelika (2009) English as a lingua franca in Europe: an empirical perspective. World Englishes 28:2. 356-269 Brutt-Griffler, Janina (2002) World English : A study of its Development. Clevedon: Multilingual Matters Bullock, Barbara E. and Almeida Jacqueline Toribio, eds. (2009) The Cambridge Handbook of Linguistic Code-switching. Cambridge University Press. Burchfield, Robert (ed.) (1994) The Cambridge History of the English Language, Vol. 5: English in Britain and Overseas. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press Cagliero, Roberto & Jennifer Jenkins (2010) (eds.), Discourses, communities, and Global Englishes. Bern: Peter Lang Canagarajah, A.S. (1999) Resisting Imperialism in English Language Teaching. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Chand, Vineeta (2009) “[v]at is going on? Local and global ideologies about Indian English”, Language in Society 38: 393-419 Chand, Vineeta. 2010. Postvocalic (r) in urban Indian English. English World-wide, 31(1):139. Chen, Katherine Hoi Ying (2008) Bilinguals in Style: Linguistic practices and ideologies of Cantonese-English codemixers in Hong Kong. PhD diss. University of Michigan, Department of Linguistics. Dissertation URL: http://deepblue.lib.umich.edu/bitstream/2027.42/58417/1/hoiyingc_1.pdf Chen Meilin and Hu Xiaoqiong (2006). Towards the acceptability of China English at home and abroad. English Today, , pp 44-52. Cheshire, J., Kerswill, P., Fox, S., & Torgersen, E. (2011). Contact, the feature pool and the speech community: The emergence of Multicultural London English. Journal of Sociolinguistics, 15(2), 151-196. Chiba, R. H Matsuura and A. Yamamoto (1995) ‘Japanese attitudes towards English accents’. World Englishes 14/1: 77-86 Collins, James, Stef Slembrouck and Mike Baynham (2009) eds. Globalization and languages in contact: Scale, migration and communicative practices. Continuum. Cook, V. (2008). Second Language Learning and Language Teaching (4th ed). London: Hodder Arnold. Coupland, Nikolas (Ed) (2012) The Handbook of Language and Globalization: Wiley-Blackwell. Cowie, Claire ‘(2007) The accents of outsourcing: the meanings of ‘neutral’ in the Indian call centre industry’ World Englishes 26/3: 316-330 Cowie, Claire (2010) "Anyone doing something phonetic can attract business these days: The demand and supply of accents in the Indian call centre industry": Language and the Market, eds. Helen Kelly-Holmes and Gerlinde Mautner. Palgrave-Macmillan series on Language and Globalization. 11 Cowie, Claire and Lalita Murty (2010) "Researching and understanding accent shifts in Indian call centre agents".Globalization, Communication and the Workplace: Talking Across the World. eds. Gail Forey and Jane Lockwood. Continuum. Crowley, Terry (1990) From Beach-la-Mar to Bislama: The emergence of a national language. Oxford: Clarendon Press. Crystal, David (1988) The English Language. Harmondsworth: Penguin Crystal, David (2003) English as a Global Language. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2nd ed. [1st ed. 1997] [available as an e-book!] Cui Xiaoxia (2006). An understanding of ‘China English’ and the learning and use of the English language in China. English Today, , pp 40-43. Dalton-Puffer, Kaltenboeck and Smit (1997) ‘Learner attitudes and L2 pronunciation in Austria’. World Englishes 16/1 Davies, Alan (2003) The Native Speaker: Myth and Reality. Clevedon: Multilingual Matters Davies, A., Hamp‐Lyons, L., & Kemp, C. (2003). Whose norms? International proficiency tests in English. World Englishes, 22(4), 571-584. M. Derwing and Murray J. Munro (1997). ACCENT, INTELLIGIBILITY, AND COMPREHENSIBILITY. Studies in Second Language Acquisition, , pp 1-16. Deterding, David The pronunciation of English by speakers from China (2006) English World-Wide 27:2. 175-198 Deterding, David (2007) Singapore English. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press Deterding, David (2013) Brunei English. A new variety in a multilingual society. Springer Deterding, David, Ee Ling Low and Adam Brown, eds. (2003) English in Singapore: Research on Grammar. Singapore: McGraw-Hill. Deterding, David, Ee Ling Low and Adam Brown, eds. (2005) English in Singapore: Phonetic Research on a Corpus. Singapore: McGraw-Hill. Deterding, David and Andy Kirkpatrick (2006) Emerging South-East Asian Englishes and intelligibility. World Englishes 25: 391-409. Deterding, David, Jennie Wong and Andy Kirkpatrick (2008) ‘The pronunciation of Hong Kong English’ English World-Wide, Volume 29, Number 2, pp. 148-175. Dewey, Martin and Alessio Cogo (2012) Analysing English as a Lingua Franca: A Corpusdriven Investigation. Continuum Dougill, John (1987) “English as a decorative language” English Today, 3, pp 33-35 Dudrah, Rajinder Kumar (2006) Bollywood: Sociology Goes to the Movies. New Delhi: Sage. Eckert, P. (2008). Where do ethnolects stop?. International Journal of Bilingualism, 12(1-2), 25-42. Ellis, R. (2008). The Study of Second Language Acquisition (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. Erling, Elizabeth J. (2002) ’I learn English since ten years’: The Global English debate and the German university classroom’ English Today 18/2: 8-13 Erling, Elizabeth J. (2004) Globalization, English and the German University Classroom: A sociolinguistic profile of students of English at the Freie Universität Berlin. PhD diss. University of Edinburgh. [in library, special collections] Faraclas, N. (1996) Nigerian Pidgin, London: Routledge Filppula, Marko, Juhani Klemola & Heli Paulasto “Vernacular Universals and Language Contacts: An Overview” in Filppula, Marko, Juhani Klemola & Heli Paulasto (eds.) (2009) Vernacular universals and language contacts: Evidence from varieties of English and beyond. New York & London: Routledge. Finlayson, Rosalie, Karen Calteaux, and Carol Myers-Scotton (1998) ‘Orderly mixing and accommodation in South African codeswitching’. Journal of Sociolinguistics 2/3: 395-420. Forde, K. 1995. A study of learner attitudes towards accents of English. Hong Kong Polytechnic University Working Paper in ELT & Applied Linguistics 1, 59-76. Friedman, T. L. (2005) The World is Flat: a brief history of the twenty-first century. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. 12 Friginal, Eric (2007) ‘Outsourced call centers and English in the Phillipines’ World Englishes 26/3: 331-345 Gardner-Chloros, Penelope (2009) Code-switching. Cambridge: CUP. Giddens, Anthony (1999) Runaway World: How Globalization is Reshaping Our Lives. London : Profile. Görlach, Manfred (1991) Englishes: Studies in Varieties of English 1984-1988. Amsterdam: Benjamins. Görlach, Manfred (1995) More Englishes: New Studies in Varieties of English 1988-1994. Amsterdam: Benjamins. Görlach, Manfred and John Holm (ed.) (1986). Varieties of English around the World: Focus on the Caribbean. Amsterdam: Benjamins Gotz, Sandra (2013) Fluency in Native and Nonnative English Speech. John Benjamins Graddol, D., D. Leith and J. Swann eds. (1996) English: history, diversity and change. London: Routledge Graddol, D. (1997) The future of English? British Council. Graddol, David (2006) English Next: Why global English may mean the end of ‘English as a foreign language’?. British Council www.britishcouncil.org/learning-researchenglishnext.htm Graddol, David (2010) English Next India http://www.britishcouncil.org/learning-english-next-india-2010-book.htm Gut, Ulrike (2007) ‘First language influence and final consonant clusters in the new Englishes of Singapore and Nigeria’ World Englishes 26/3: 346-359 Gupta, Anthea Fraser & Tan Chor Hiang (1992) Post-vocalic /r/ in Singapore English. York Papers in Linguistics 16, 139-152. Gupta, A.F. (1992) The pragmatic particles of Singapore Colloquial English. Journal of Pragmatics 18:31-57. Gut, U. and Fuchs, R. (2013). Progressive Aspect in Nigerian English. Journal of English Linguistics. 40(3): 243-267. Hansen, Jette (2006) Acquiring a Non-Native Phonology: Linguistic Constraints and Social Barriers. Continuum. Hansen, Jette and M.L. Zampini eds. (2008) Phonology and Second Language Acquisition. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company. Hickey, Raymond ed. (2004) Legacies of Colonial English: Studies in Transported Dialects. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press Ho, Mian Lian and John Platt (1993) Dynamics of a contact continuum: Singaporean English. Oxford: Clarendon Press Holm, John (1991) An Introduction to Pidgins and Creoles. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Hu, G. (2003) English Language Teaching in China: Regional Differences and Contributing Factors. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development. Vol. 24, No. 4. Hu, Xiaoqiong (2004) Why China English should stand alongside British, American and the other World Englishes. English Today 20:26-33 Hu Xiaoqiong (2005). China English, at home and in the world. English Today, , pp 27-38. Hu, Guiling & Stephanie Lindemann (2009) Stereotypes of Cantonese English, apparent native/nonnative status, and their effect on nonnative English speakers’ perception. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development 30(3), 253-269. Hung, Tony T.N. (2003) ‘Towards a phonology of Hong Kong English’ World Englishes 19/3: 337-356 Igboanusi, H. (2008) Empowering Nigerian Pidgin: a challenge for status planning?, World Englishes, Vol. 27, No. 1, pp. 68-82 13 Jenkins (1998) ‘Which pronunciation norms and models for English as an International Language?’ ELT Journal 52/2:119-26. Jenkins, Jennifer (2000) The phonology of English as an international language : new models, new norms, new goals. Oxford : Oxford University Press Jenkins, Jennifer (2002) ‘A sociolinguistically based, empirically researched pronunciation syllabus for English as an International Language’ Applied Linguistics 23/1: 83-103. Jenkins, Jennifer (2003) World Englishes: a resource book for students. London: Routledge Jenkins, Jennifer (2007) English as a Lingua Franca: Attitude and Identity. Oxford: OUP Joseph, John E. (2004) Language and Identity: National, Ethnic, Religious. Palgrave Macmillan. Kachru, Braj. B. (1990) The Alchemy of English: The spread, Function and Models of NonNative Englishes. Urbana: University of Illinois Press. Kachru, Braj B (1991) ‘Liberation linguistics and the Quirk concern’ English Today 25 Kachru, Braj. B (1992) The Other Tongue: English across Cultures, 2nd edition. Urbana: University of Illinois Press. Kachru, Braj B. (1983) The Indianization of English : the English language in India . Delhi ; New York : Oxford Kachru, Braj B.ed. (2005) Asian Englishes beyond the canon. Hong Kong University Press. Kachru, Braj,. B., Yamuna Kachru and Cecil. L. Nelson. Eds. (2006) The Handbook of World Englishes Oxford: Blackwell Kang, O., & Rubin, D.L. (2009). Reverse linguistic stereotyping: Measuring the effect of listener expectations on speech evaluation. Journal of Language and Social Psychology, 28:4, 441-456. Kirkpatrick, Andy (2010). The Routledge Handbook of World Englishes. Routledge Handbooks in Applied Linguistics. London: Routledge. Kirkpatrick, Andy, Deterding, David and Jennie Wong (2008) ‘The international intelligibility of Hong Kong English’ World Englishes 27: 359–377 Kortmann, B., Schneider, E.W., Burridge, K., Mesthrie, R. and Upton, C. eds. (2004) A handbook of varieties of English : a multimedia reference tool. Berlin; New York : Mouton de Gruyter Szmrecsanyi, Benedikt and Bernd Kortmann (2009) “Vernacular Universals and Angloversals in a Typological Perspective” in Filppula, Marko, Juhani Klemola & Heli Paulasto (eds.) (2009) Vernacular universals and language contacts: Evidence from varieties of English and beyond. New York & London: Routledge. Krishnaswamy, N. and Burde, Archana S. (1998) The Politics of Indians' English: Linguistic Colonialism and the Expanding English Empire. Delhi, Oxford: Oxford University Press Kubota, Ryuko (1998) ‘Ideologies of English in Japan’ in World Englishes 17:3 Lai, Eva (2001) Teaching English as a private enterprise in China. English Today. Vol 17: 3236 Lange, Claudia (2007) Focus marking in Indian English. English World Wide 28:1. 89-118 Lange, Claudia (2012) The Syntax of Spoken Indian English. Amsterdam/Philadelphia: Benjamins. Leith, Dick (1996) ‘English – colonial to postcolonial’ in Goodman, Sharon and David Graddol. eds. Redesigning English: new texts, new identities. London: Routledge. Lim, Lisa ed. (2004) Singapore English. A Grammatical Description. Amsterdam: John Benjamins 14 Lim, Lisa and Ee-ling Low eds.(2004) Multilingual, Globalizing Asia: Implications for policy and education. AILA Review, Volume 22, Lindemann, Stephanie (2011) Who’s “unintelligible”? The perceiver’s role. Issues in Applied Linguistics 18(2) 223-232. Lindemann, Stephanie (2005) Who speaks 'broken English'? US undergraduates' perceptions of non-native English. International Journal of Applied Linguistics 15(2), 187-212. Lindemann, Stephanie (2003) Koreans, Chinese, or Indians? Attitudes and ideologies about non-native English speakers in the United States. Journal of Sociolinguistics 7(3), 348-364. Lo Bianco, Joseph, Jane Orton and Gao Yihong (eds.) (2009) China and English: Globalisation and the Dilemmas of Identity. Multilingual Matters. Machan, Tim William (2013) What is English? And why should we care? Oxford: OUP Maybin, Janet and Neil Mercer (1996) Using English: from conversation to canon. London: Routledge McArthur, Tom (1998) The English Languages. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. McArthur, Tom (2003) The Oxford guide to world English. Oxford, Eng. ; New York, NY : Oxford University Press McKenzie, Robert M. (2010) The Social Psychology of English as a Global Language: Attitudes, Awareness and Identity in the Japanese Context. Educational Lingustics series. Springer. [e-book] McLaughlin, Fiona ed. (2009) The Languages of Urban Africa. Continuum Meierkord, Christiane (2009) It’s kuloo tu: recent developments in Kenya’s Englishes: On identity construction in multilingual environments English today 25:3-11 Melchers, Gunnel and Philip Shaw (2003) World Englishes. Oxford: Oxford University Press Mendoza-Denton, N. (2008). Homegirls: Language and cultural practice among Latina youth gangs. John Wiley & Sons. Mesthrie, Rajend and Rakesh M. Bhatt (2008) World Englishes: The Study of New Linguistic Varieties. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Mesthrie, Rajend (2010) Socio-phonetics and social change: Deracialisation of the GOOSE vowel in South African English. Journal of Sociolinguistics 14:1. 3-33 Mesthrie, Rajend (2007) “Deracialising the GOOSE vowel in South African English: accelerated linguistic change amongst young, middle class females in post-apartheid South Africa” in World Englishes -- problems, properties and prospects, selected papers from the 13th IAWE conference. Eds. Thomas Hoffmann, Lucia Stiebers. Mesthrie, Rajend (2008) “I’ve been speaking Tsotsitaal all my life without knowing it: Towards a unified account of tsotsitaals in South Africa” in Meyerhoff, Miriam and Naomi Nagy (eds.) 2008 Social Lives in Language: Sociolinguistic studies of multilingual communities. Amsterdam: John Benjamins. Meyerhoff, Miriam 2008. Bequia (is/Ø) sweet: Syntactic variation in a lesser-known variety of Caribbean English. English Today 93, 24. 31-37 Modiano, Marco (1996) ‘The Americanization of Euro-English’. World Englishes 15:2 Mufwene, Salikoko (2001) The Ecology of Language Evolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press Munro, M. J. and Derwing, T. M. (1995), Foreign Accent, Comprehensibility, and Intelligibility in the Speech of Second Language Learners. Language Learning, 45: 73–97. Munshi, Kaivan with Mark Rosenzweig “Traditional Institutions Meet the Modern World: Caste, Gender, and Schooling Choice in a Globalizing Economy." 2006. American Economic Review 96(4):1225-1252,. 15 Myers-Scotton, C. (1990) Codeswitching with English: types of switching, types of communities. World Englishes 6, 33-48. Myers-Scotton, Carol (ed.) (1998). Codes and consequences: Choosing linguistic varieties. New York: Oxford University Press. Niu Qiang and Martin Wolff (2003). China and Chinese, or Chingland and Chinglish?. English Today, Omoniyi, T. (2006) Hip-hop through the World Englishes lens: a response to globalization. World Englishes 25/2:195-208 Ostler, Nicholas (2010) The Last Lingua Franca: English Until the Return of Babel. Allen Lane Patrick, Peter L. Patrick (1999) Urban Jamaican Creole: Variation in the Mesolect. Varieties of English Around the World, No. G17. Amsterdam & Philadelphia: John Benjamins Publishing Co. Patrick, Peter (2004) “Jamaican Creole: Morphology and syntax.” In A Handbook of Varieties of English. Vol 2: Morphology and Syntax, ed. Bernd Kortmann, Edgar W Schneider, Clive Upton, Rajend Mesthrie & Kate Burridge. Berlin, New York: Mouton de Gruyter, 407-438. Pennycook, Alistair (1994) The Cultural Politics of English as an International Language. London: Longman. Pennycook A. D. (2003) Global Englishes, rip slime, and performativity. Journal of Sociolinguistics 7/4: 513-33. Phillipson, Robert (1992) Linguistic Imperialism. Oxford: Oxford University Press Phillipson, R. (1998). Globalizing English: Are linguistic human rights an alternative to linguistic imperialism?. Language Sciences, 20(1), 101-112. Phillipson, R. (2003). English-only Europe?: Challenging language policy. Routledge. Patrick, Peter L. (1999) Urban Jamaican Creole: Variation in the Mesolect. (Varieties of English Around the World, No. G17.) Amsterdam & Philadelphia: John Benjamins Publishers Platt, J.T (1975) The Singapore English speech continuum and its basilect ‘Singlish’ as a creoloid. Anthropological Linguistics 17: 363-74 Platt, J.T and M.L Ho (1989) Discourse particles in Singaporean English: substratum influence and universals. World Englishes 8: 215-21. Platt, John T., Weber, Heidi and Mian Lian Ho (1984) The New Englishes. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul. Platt, John, Heidi Weber and Mian Lian Ho (1983) Singapore and Malaysia. Amsterdam: Benjamins Poplack, Shana and Natalie Dion (2012) Myths and facts about loanword development. Language Variation and Change, 24 (2012), 279–315. Poppi, Franca (2013) Global Interactions in English as a Lingua Franca: How written communication is changing under the influence of electronic media and new contexts of use. Peter Lang Prodromou, Luke (2008) English as a Lingua Franca: A Corpus-based Analysis. Continuum Qiong, Hu Xiao (2004) Why China English should stand alongside British, American, and the other ‘world Englishes’ English Today. Vol 20: 26-33 Quirk. R. (1990) Language varieties and standard language. English Today 21: 3-10 Robertson, Roland. "Glocalization: Time-space and homogeneity-heterogeneity." Global modernities (1995): 25-44. Rampton, B. (1995). Crossing: Language and ethnicity among adolescents. London: Longman. Rampton, B. (1999). Crossing. Journal of Linguistic Anthropology, 9(1‐2), 54-56. Römer, U. (2005). Progressives, patterns, pedagogy: A corpus-driven approach to English progressive forms, functions, contexts and didactics (Vol. 18). John Benjamins Publishing. Rubdy, Rani (2001) Creative destruction: Singapore’s Speak Good English Movement. World Englishes 20:3. 341-355 16 Rubdy, R. & Saraceni, M. (EDS.). (2006). English in the World: Global Rules, Global Roles (PP. 218). London, New York: Continuum. Sahgal, A., & Agnihotri, R. K. (1988). Indian English Phonology: a sociolinguistic perspective. English World-Wide, 9, 51-64. Salbrina, Sharbawi and David Deterding (2010) Rhoticity in Brunei English English WorldWide 31:2. 121-137 Samy, Alim, H. (2009). Translocal style communities: Hip hop youth as cultural theorists of style, language, and globalization. Pragmatics 19(1). 103-128. Sand, A. (2004) Shared morpho-syntactic features in contact varieties of English: article use. World Englishes 23: 281-98. Schmied, Josef J. (1991) English in Africa: an introduction. London: Longman Schneider, E.W. ed. (1997). Englishes around the World, Volumes 1 & 2. Amsterdam: Benjamins. Schneider, E. W. (2003) The dynamics of New Englishes: from identity construction to dialect birth. Language 79/2: 233- 81 Schneider, E.W. (2006) Postcolonial Englishes. Cambridge: CUP. Schneider, Edgar W. (2011) English Around the World: An Introduction. Cambridge: CUP Schreier, D. & M. Hundt (eds.), English as a contact language. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press Seargeant, Philip (2012). Exploring World Englishes: Language in a Global Context. Routledge Introductions to Applied Linguistics. Abingdon: Routledge. Seargeant, Philip and Erling, Elizabeth (2011). The discourse of English as a language for international development: policy assumptions and practical challenges. In: Coleman, Hywel ed. Dreams and Realities: Developing Countries and the English Language. London: British Council, pp. 248- 267. Seargeant, Philip (2009). The idea of English in Japan: ideology and the evolution of a global language. Bristol: Multilingual Matters. Sebba, M., & Tate, S. (2002). “Global” and “Local” identities in the discourses of Britishborn Caribbeans. International Journal of Bilingualism, 6(1), 75-89. Sebba, Mark (1997) Contact Languages: Pidgins and Creoles. London: Macmillan Press Ltd. Sebba, M. (1993). London Jamaican. London: Longman. Sebba, M. (1986). London Jamaican and Black London English. The Language of the Black Experience, Oxford: Blackwell, 149-167. Seidlhofer, Barbara (1999) ‘Double standards: teacher education in the Expanding Circle’. World Englishes 18/2: 233-45 Seidlhofer, B. (2005) ‘English as a Lingua Franca’. ELT Journal 59/4:339-41. Seidlhofer, Barbara. 2011. Understanding English as a Lingua Franca. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Siegel, J. (2010). Second dialect acquisition. Cambridge University Press. Siegel, J. (2003). Substrate influence in creoles and the role of transfer in second language acquisition. Studies in Second Language Acquisition, 25(2), 185-209. Setter, J. (2008) Consonant clusters in Hong Kong English. World Englishes 23/3-4: 502-515. Setter, J., C. S. P. Wong and B. H. S. Chan. (2010). Hong Kong English. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. Silver, Lubna, Christine CM Goh and Rita Elaine Asaoff (2009) Language Learning in New English Contexts: Studies of Acquisition and Development. Continuum Singh, Ishtla (2000) Pidgins and Creoles: An Introduction. London: Arnold Shao, X. Z (2005). practising my english in china. English Today, , pp 48-54. Sharma, D (2011) Cognitive and social forces in dialect shift: Gradual change in London Asian Speech. Language Variation and Change 23: 399-428 Sharma, Devyani and Lavanya Sankaran (2011). Style repertoire and social change in British Asian English. Journal of Sociolinguistics, 15(4), 464-492. 17 Sharma, Devyani (2009) “Typological diversity in New Englishes, English World-Wide, Volume 30, Number 2, 2009 , pp. 170-195 Sharma, Devyani and John Rickford (2009) “AAVE / creole copula absence: A critique of the Imperfect Learning Hypothesis”. Journal of Pidgin and Creole Languages 24(1): 53– 90. Sharma, D (2005) Language Transfer and Discourse Universals in Indian English article use. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 27: 535-566 Sharma, Devyani (2005) ‘Dialect stabilization and speaker awareness in non-native varieties of English’. Journal of Sociolinguistics 9/2 Si, Aung (2010) A Diachronic Investigation of Hindi-English code-switching, using Bollywood film scripts. International Journal of Bilingualism XX(X):1-20 Steger, Manfred B.(2009) Globalization: A very short introduction. Oxford: OUP Swann, Joan (1996) ‘English Voices’ in Goodman, Sharon and David Graddol. eds. Tan, P. K.W. & Rubdy, R. (EDS.). (2008). Language as Commodity: Global Structures, Local Marketplaces (PP. 228). London, New York: Continuum. Tan, Ying Ying (2012) To r or not to r: social correlates of /ɹ/ in Singapore English International Journal of the Sociology of Language vol. 218 Terkourafi, Marina ed. (2012) The languages of global hip hop. Bloomsbury. Tsui, Amy B. M. and David Bunton (2003) The discourse and attitudes of English language teachers in Hong Kong. World Englishes 19/3: 287-303 Thomason, Sarah G. (2001) Language contact: an introduction. Washington, DC: Georgetown University Press. Thompson, Roger M. (2003) Filipino English and Taglish: Language switching from multiple perspectives. Amsterdam/Philadelphia: John Benjamins Thorniley, Tessa (2010) Battle intensifies for $2bn English-teaching business in China (http://www.guardian.co.uk/education/2010/jul/13/china-english-schools) Tian bo Li and Gillian Moreira (2009). Learning English in corporate China. English Today, 25, pp 41-48. Vaish, Viniti ed. (2010) Globalization of Language and Culture in Asia: The Impact of Globalization Processes on Language. Bloomsbury. Lionel Wee, Robbie B.H. Goh and Lisa Lim eds. (2013) The Politics of English: South Asia, Southeast Asia and the Asia Pacific. Benjamins. Williams, Jessica. (1987) ‘Non-native varieties of English: a special case of language acquisition’. English World-Wide 8:2 Wiltshire, Caroline R. and James D. Harnsberger (2006) “The influence of Gujarati and Tamil L1s on Indian English: a preliminary study”. World Englishes 25/1: 91-104 Winford, Donald (2003) Introduction to Contact Linguistics. Oxford: Blackwell. the Pacific, Asia and the Americas. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. Winford, Donald (2013) Substrate influence and universals in the emergence of contact Englishes: Re- evaluating the evidence. In D. Schreier & M. Hundt (eds.), English as a contact language, pp. 222-241. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Wu, Y. (2001) English Language Teaching in China: Trends and Challenges. TESOL Quarterly. vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 191-194(4). Zhang, Wei & Lijuan Ding (2011) A preliminary study on Chinese EFL learners’ attitude towards their accent. ICPhS XVII Hong Kong 18