Cloud Formation Graphing Lab
advertisement
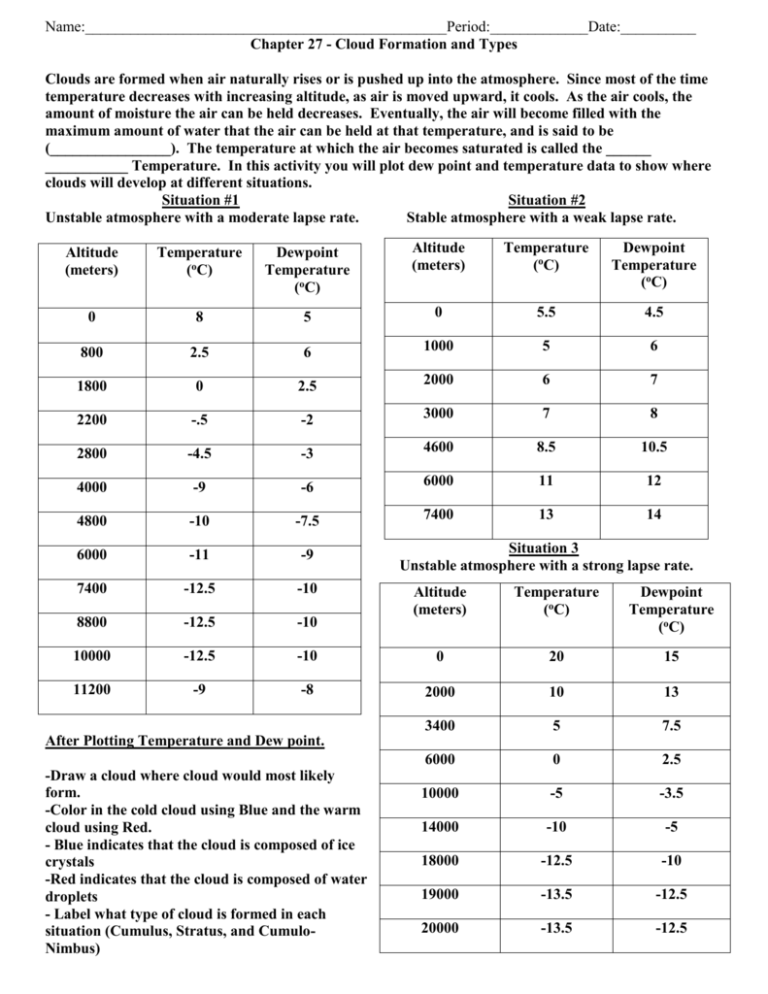
Name:________________________________________________Period:_____________Date:__________ Chapter 27 - Cloud Formation and Types Clouds are formed when air naturally rises or is pushed up into the atmosphere. Since most of the time temperature decreases with increasing altitude, as air is moved upward, it cools. As the air cools, the amount of moisture the air can be held decreases. Eventually, the air will become filled with the maximum amount of water that the air can be held at that temperature, and is said to be (________________). The temperature at which the air becomes saturated is called the ______ ___________ Temperature. In this activity you will plot dew point and temperature data to show where clouds will develop at different situations. Situation #1 Situation #2 Unstable atmosphere with a moderate lapse rate. Stable atmosphere with a weak lapse rate. Altitude (meters) Temperature (oC) Dewpoint Temperature (oC) Altitude (meters) Temperature (oC) Dewpoint Temperature (oC) 0 8 5 0 5.5 4.5 800 2.5 6 1000 5 6 1800 0 2.5 2000 6 7 2200 -.5 -2 3000 7 8 2800 -4.5 -3 4600 8.5 10.5 4000 -9 -6 6000 11 12 4800 -10 -7.5 7400 13 14 6000 -11 -9 7400 -12.5 -10 8800 -12.5 -10 10000 -12.5 11200 -9 Situation 3 Unstable atmosphere with a strong lapse rate. Altitude (meters) Temperature (oC) Dewpoint Temperature (oC) -10 0 20 15 -8 2000 10 13 3400 5 7.5 6000 0 2.5 10000 -5 -3.5 14000 -10 -5 18000 -12.5 -10 19000 -13.5 -12.5 20000 -13.5 -12.5 After Plotting Temperature and Dew point. -Draw a cloud where cloud would most likely form. -Color in the cold cloud using Blue and the warm cloud using Red. - Blue indicates that the cloud is composed of ice crystals -Red indicates that the cloud is composed of water droplets - Label what type of cloud is formed in each situation (Cumulus, Stratus, and CumuloNimbus) Questions 1. Situation 1’s clouds are both caused by vertically rising air. Which one of the three main types of clouds are being formed here? 2. The warm cloud closest to the ground would be called what? 3. The mid level cold cloud would be given what name? 4. What layer of the atmosphere might you enter at about 10,000 meters? 5. Compare situation 1 and 2. What is the major difference between these two graphs? (Look at the lines) 6. When air is allowed to rise, we call the atmosphere unstable. When air is not allowed to rise, we call the atmosphere stable. Situation 1 is an example of what kind of atmosphere? Situation 2 is an example of what kind of atmosphere? 7. What type of cloud would most likely form at the lowest level of situation 2? 8. Looking at situation 3, what type of cloud is forming here? Look at the lines of Dew point and Temperature. Where do you think the cloud would be the widest? Skinniest? 9. Precipitation is formed when the particles of clouds coalesce (come together) into larger droplets. Which cloud situation would have the greatest chance of creating precipitation? 10. Use table 27.15 on page 514. What are the 4 major types of precipitation? What are the NWS symbols for each?








