1 - Aboutculture
advertisement

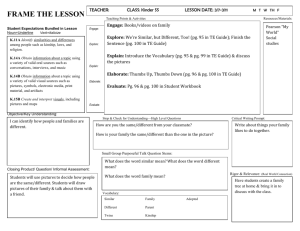
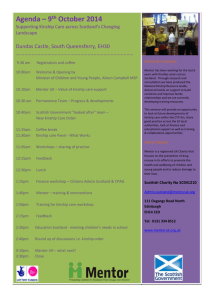
Quiz 2 study guide Cultural Anthropology, spring 2012 Quiz is scheduled for May 21 1. What is the difference between sex and gender? (lecture and ‘Humanity’ ch. 11) 2. According to Michael Kimmel, is gender inequality learned or biological? (lecture) 3. What is the general rule connected with women, economic contribution and level of power and influence in a culture or group? (lecture) 4. Why have many anthropologists concluded that gender inequalities in several places of the world were often created or exacerbated by Western, European and EuroAmerican influences during and after colonialism? How is the case of the Igbo women in Nigeria an example? (lecture) 5. What did anthropologist Helen Fisher (TED video) say concerning the sex drive, romantic love, and deep attachment? 6. What did Signithia Fordham show in her study of a predominantly black high school in Washington D.C? What did Fordham learn about the paradox that Euro-American women experienced in the 1990s compared with the double paradox that African American women experienced? What were mainstream assumptions about women and the reality for African American women? Why? (lecture) 7. How do plow agriculture and horticulture often figure into historic and current patterns of male and female relationships? 8. How does Fordham’s study relate to Maltz and Borker’s study results about ‘mainstream’ male and female differences in communication and the reasons for those differences? (handout) 9. How does the Malagasy example of men and women’s speech patterns and beliefs about gender compare with typical North American assumptions about men and women’s speech patterns and beliefs about gender? (lecture) 10. According to the biological anthropologist authors of Why Sex Matters, what are the reproductive imperatives of males compared with females and what might those differences have to do with patterns of gender dominance? (lecture) 11. Why have there been no apparent matriarchies? (lecture/Why Sex Matters, ‘Humanity’) 12. What are some of the main points that evolutionary psychology scientists make concerning sexual double standards? (‘Humanity’, pgs. 240 to 241) 13. What is significant about the Hua of Papua New Guinea and their concepts concerning gender? (‘Humanity’ pg. 242) 14. Be prepared to discuss multiple gender identities discussed in your book Humanity, pgs. 244-249, and the article The Berdache Tradition in AEA. According to the article The Berdache Tradition, why is the Western debate about homosexuality less applicable to more traditional Native American philosophy and cosmology? How are more traditional Native American understandings about spirituality and nature different from many Western traditions, and how do philosophies about human relationships with spirituality and nature influence interpretations of sexuality? 15. Consider some of the scientific examples concerning homosexuality that are outlined on the handout and that were discussed in the videos. (You can review the videos on the wiki, week 7) 16. Understand the main points of the articles Where Fat is a Mark of Feminine Beauty and … what if it’s a girl? 17. What were the main points in the video Missrepresentation. When the social order of a society is undergoing change, people often work (often subconsciously) to bring back the status quo. They may try to do so indirectly. How does this tendency connect with the observations made in the video? (See video trailer for review. If you have forgotten some of the main points, a few notes concerning the video have been provided on the wiki, week 5.) Kinship Section (see study cards for some of these concepts, the lectures and chapters 8 and 9 in ‘Humanity’) 18. What is the importance of kinship to social organization? 19. Vertical function of kinship 20. Horizontal function of kinship 21. Define types of kinship descent: bilateral, patrilineal, matrilineal 22. Define common types of residence after marriage: patrilocal, matrilocal, neolocal 23. Bride wealth, bride service and their functions 24. Dowry and its function 25. Polygamy 26. Polygyny and reasons for … (‘Humanity’ pgs. 174 – 179) 27. Polyandry and reasons for … (‘Humanity’ pgs. 179 – 180) 28. In reference to the exercise you did as a class to arrange the marriages of your children: be able to explain what you learned about the economic and social functions and ideologies connected with arranged marriage in many Arab cultures. 29. What is the theory of cultural materialism? (see lecture notes) What are infrastructure, social structure, and super structure and their relation to each other? 30. How might the theory of cultural materialism help explain some of the reasons for kinship systems and marriage practices such as polyandry in Tibet (article), the Awlad ‘Ali Bedouins (lecture and class exercise), Kyrgyzstan bride kidnapping (video) and arranged marriages in India (article). Consider the basic infrastructure (economic system, technology, environment, ways of making a living etc.) for each group and be able to point to how the kinship system and marriage rules (social structure) support the infrastructure. Discuss what you know about the ideologies and beliefs (super structure) that motivate people in these groups to follow their kinship rules and marriage practices.