Biology 300 - Mrs. GM Biology 200
advertisement

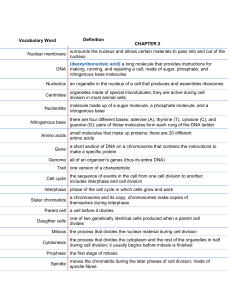
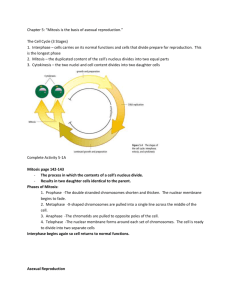
Name ___KEY_________ Date ___________ Mrs. Geithner-Marron (Biology 200) Period _________ Asexual Reproduction Quiz REVIEW 1. Define/describe the following types of asexual reproduction: o binary fission DNA copied & organism divides in 2 prokaryotes w/ NO nucleus (ex. bacteria)… chromosome copied, cell grows, divides in 2 eukaryotes w/ nucleus (ex. protists)... mitosis must happen before cell division b/c nucleus must be copied, not just DNA parent & offspring genetically the same & generally the same size o budding offspring begins to develop on the parent’s body & then breaks off ex. yeast, Hydra offspring smaller than parent, but still genetically identical o vegetative propagation budding… in plants ex. strawberries, potatoes What is a runner (creeper)? a horizontal stem that grows from the parent plant which forms roots and new plants; once runner is rooted, it separates from original plant & grows independently o fragmentation fragment (piece) grows into new organism (by mitosis) ex. sponges, sea stars (1 leg new organism) o regeneration regrowth of missing body parts (by mitosis) ex. Planaria, sea stars (leg cut off grows new leg), salamander o spores contain DNA, cytoplasm & tough outer wall (coat)...grow into multicellular organisms w/o fertilization ex. mushrooms, mold, mosses, ferns coat protects spore until conditions are favorable & keeps spore from drying out (adaptation for life on land) o parthenogenesis unfertilized egg develops into adult (drone) ex. Daphnia, aphids, honey bees How is binary fission in Protists such as the Amoeba and Paramecium (which are eukaryotic) different from binary fission in bacteria (which are prokaryotic)? Why is it different? Binary fission in Protists is different from bacteria b/c in Protists it involves mitosis and then cell division b/c Protists have nucleus (are eukaryotic) & bacteria don’t have a nucleus (prokaryotic). 2. In asexual reproduction, how do the offspring compare to the parent genetically? The parent & offspring are genetically identical (as well as the offspring genetically identical to each other).