Gulf Coast Community College
advertisement

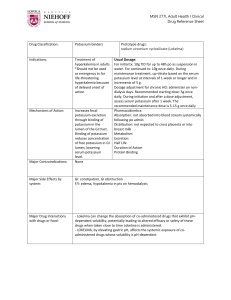
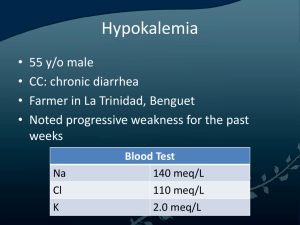
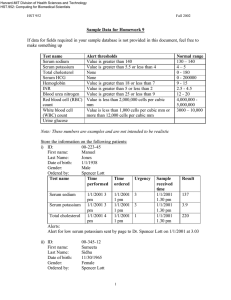
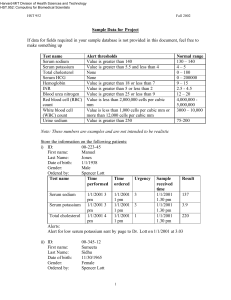
Gulf Coast Community College- Associate degree Nursing NUR 1260C – Gerontological Nursing Medication Cards Student Name: _ ___________ Name of Drug: Generic: Hydrochlorothiazide Trade: Hydrochlorothiazide and Hydralazine Classification: antihypertensives, diuretics, thiazide diuretics Usual Dose: 12.5-100 mg/day in 1-2 divided doses (up to 200 mg/day); not to exceed 50 mg/day for hypertension; daily doses above 25 mg are associated with greater likelihood of electrolyte abnormalities. Resident/Client/ Patient Dose: Action: Increases excretion of sodium and water by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule. Promotes excretion of chloride, potassium, magnesium, and bicarbonate. May produce arteriolar dilation. Lowering of blood pressure in hypertensive patients and diuresis with mobilization of edema. Side Effects & Toxic Effects: dizziness, drowsiness, lethargy, weakness, hypotension, anorexia, cramping, hepatitis, nausea, pancreatitis, vomiting, photosensitivity, rashes, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, dehydration, hypercalcemia, hypochloremic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, hyponatremia, hypophosphatemia, Hypovolemia, thrombocytopenia hypercholesterolemia, hyperuricemia, muscle cramps. Drug Interactions: Additive hypotension with other antihypertensives, acute ingestion of alcohol, or nitrates. Additive hypokalemia with corticosteroids, amphotericin B, piperacillin, or ticarcillin. decrease excretion of lithium. Cholestyramine or colestipol decrease absorption. Hypokalemia increase risk of digoxin toxicity. NSAIDs may decrease effectiveness. Nursing Implications: Monitor blood pressure, intake, output, and daily weight and assess feet, legs, and sacral area for edema daily. Assess patient, especially if taking digoxin, for anorexia, nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, paresthesia, and confusion. Notify health care professional if these signs of electrolyte imbalance occur. Patients taking digoxin are at risk of digoxin toxicity because of the potassium-depleting effect of the diuretic. If hypokalemia occurs, consideration may be given to potassium supplements or decreasing dose of diuretic. Assess patient for allergy to sulfonamides. Monitor blood pressure before and periodically during therapy. Monitor frequency of prescription refills to determine compliance. Laboratory Considerations: Monitor electrolytes (especially potassium), blood glucose, BUN, serum creatinine, and uric acid levels before and periodically throughout therapy. May cause increase in serum and urine glucose in diabetic patients. May cause increase in serum bilirubin, calcium, creatinine, and uric acid, and decrease in serum magnesium, potassium, sodium, and urinary calcium concentrations. May cause increased serum cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein, and triglyceride concentrations.