Unit 5: DNA and Genetics Review
advertisement

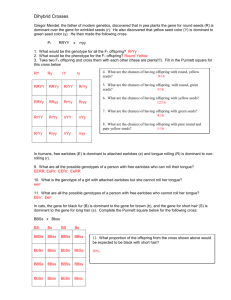
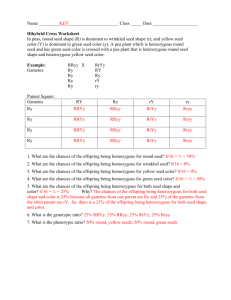
Unit 5: DNA and Genetics Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. Offspring that result from crosses between true-breeding parents with different traits a. are true-breeding. c. make up the parental generation. b. make up the F2 generation. d. are called hybrids. 2. Mendel concluded that traits are a. not inherited by offspring. b. inherited through the passing of factors from parents to offspring. c. determined by dominant factors only. d. determined by recessive factors only. 3. When Mendel crossed true-breeding tall plants with true-breeding short plants, all the offspring were tall because a. the allele for tall plants is recessive. b. the allele for short plants is dominant. c. the allele for tall plants is dominant. d. they were true-breeding like their parents. 4. In the P generation, a tall plant was crossed with a short plant. Short plants reappeared in the F2 generation because a. some of the F2 plants produced gametes that carried the allele for shortness. b. the allele for shortness is dominant. c. the allele for shortness and the allele for tallness segregated when the F1 plants produced gametes. d. they inherited an allele for shortness from one parent and an allele for tallness from the other parent. 5. The principles of probability can be used to a. predict the traits of the offspring produced by genetic crosses. b. determine the actual outcomes of genetic crosses. c. predict the traits of the parents used in genetic crosses. d. decide which organisms are best to use in genetic crosses. 6. A Punnett square shows all of the following EXCEPT a. all possible results of a genetic cross. b. the genotypes of the offspring. c. the alleles in the gametes of each parent. d. the actual results of a genetic cross. 7. How many different allele combinations would be found in the gametes produced by a pea plant whose genotype was RrYy? a. 2 c. 8 b. 4 d. 16 8. A cross of a white hen with a black rooster produces grey-color offspring. This type of inheritance is known as a. incomplete dominance. c. codominance. b. polygenic inheritance. d. multiple alleles. 9. If an organism’s diploid number is 12, its haploid number is a. 12. c. 24. b. 6. d. 3. ____ 10. What is shown in Figure 11-1? Figure 11–1 ____ 11. ____ 12. ____ 13. ____ 14. ____ 15. ____ 16. ____ 17. a. independent assortment c. crossing-over b. anaphase I of meiosis d. incomplete dominance Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in the formation of a. two genetically identical diploid cells. b. four genetically different haploid cells. c. four genetically identical haploid cells. d. two genetically different diploid cells. What did Griffith observe when he injected into mice a mixture of heat-killed disease-causing bacteria and live harmless bacteria? a. The disease-causing bacteria changed into harmless bacteria. b. The mice developed pneumonia. c. The harmless bacteria died. d. The mice were unaffected. Which of the following is a nucleotide found in DNA? a. ribose + phosphate group + thymine b. ribose + phosphate group + uracil c. deoxyribose + phosphate group + uracil d. deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine Unlike DNA, RNA contains a. adenine. c. phosphate groups. b. uracil. d. thymine. Which type(s) of RNA is(are) involved in protein synthesis? a. transfer RNA only b. messenger RNA only c. ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA only d. messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA During transcription, an RNA molecule is formed a. that is complementary to both strands of DNA. b. that is complementary to neither strand of DNA. c. that is double-stranded. d. inside the nucleus. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? a. 3 c. 9 b. 6 d. 12 ____ 18. Which type of RNA functions as a blueprint of the genetic code? a. rRNA c. mRNA b. tRNA d. RNA polymerase ____ 19. Selective breeding produces a. more offspring. c. desired traits in offspring. b. fewer offspring. d. transgenic organisms. ____ 20. The crossing of buffalo and cattle to produce beefalo is an example of a. inbreeding. c. genetic engineering. b. hybridization. d. transformation. ____ 21. Genetic engineering involves a. reading a DNA sequence. b. editing a DNA sequence. c. reinserting DNA into living organisms. d. all of the above ____ 22. What kind of cell or cells were used to make Dolly? a. body cell only c. egg cell and sperm cell b. egg cell only d. body cell and egg cell Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 23. The plants that Mendel crossed to produce the F1 generation made up the ____________________ generation. 24. A pea plant that has two different alleles for the same trait is said to be ____________________. 25. Pea plants that are TT, ____________________, or tt have different genotypes. 26. An organism’s gametes have ____________________ the number of chromosomes found in the organism’s body cells. 27. The structure labeled X in Figure 12-1 is a(an) ____________________. Figure 12–1 28. The mutations that breeders induce in organisms are passed on to the organisms’ ____________________. Short Answer 29. How many recessive alleles for a trait must an organism inherit in order to show that trait? 30. What is the phenotype ratio of the offspring in the Punnett square shown in Figure 11-3? RrYy RY Ry rY ry RY RRYY RRYy RrYY RrYy Ry RRYy RRyy RrYy Rryy RrYy rY RrYY RrYy rrYY rrYy ry RrYy Rryy rrYy rryy Figure 11–3 31. Contrast the cells produced by mitosis with those produced by meiosis. 32. In Figure 12-2, which molecule is tRNA, and what is its function? Figure 12–2 33. According to the figure, what codons specify the amino acid arginine? Seed Shape R = Round r = Wrinkled Seed Color Y = Yellow y = Green