Language Standards Note on range and content of student
advertisement
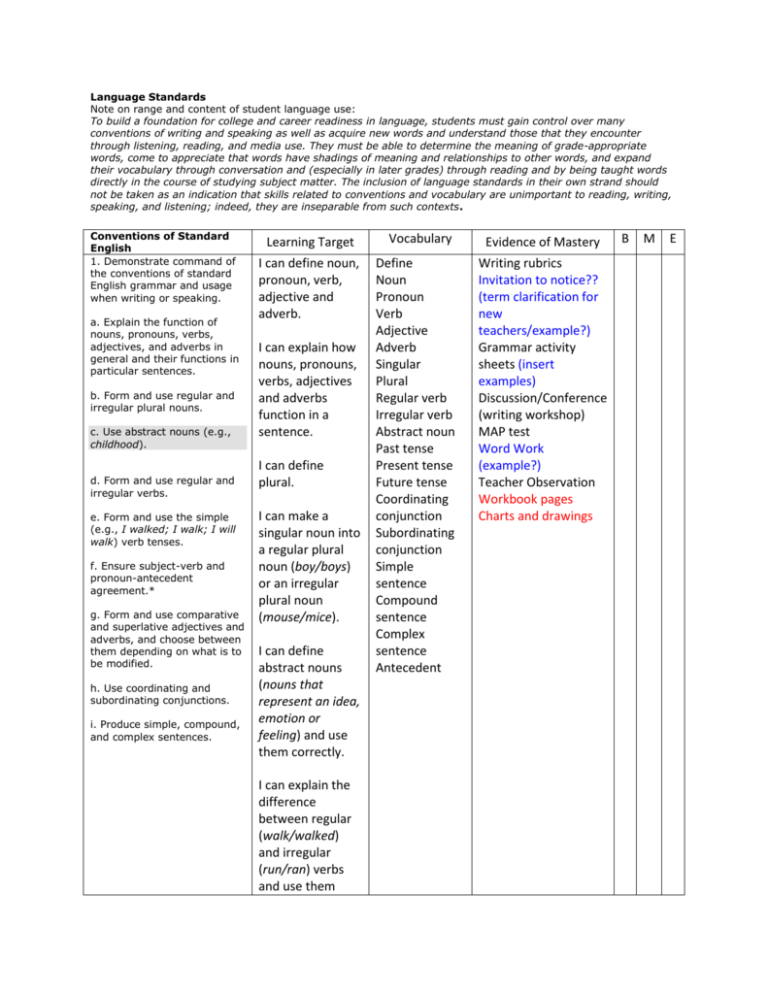
Language Standards Note on range and content of student language use: To build a foundation for college and career readiness in language, students must gain control over many conventions of writing and speaking as well as acquire new words and understand those that they encounter through listening, reading, and media use. They must be able to determine the meaning of grade-appropriate words, come to appreciate that words have shadings of meaning and relationships to other words, and expand their vocabulary through conversation and (especially in later grades) through reading and by being taught words directly in the course of studying subject matter. The inclusion of language standards in their own strand should not be taken as an indication that skills related to conventions and vocabulary are unimportant to reading, writing, speaking, and listening; indeed, they are inseparable from such contexts. Conventions of Standard English 1. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. a. Explain the function of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in general and their functions in particular sentences. b. Form and use regular and irregular plural nouns. c. Use abstract nouns (e.g., childhood). d. Form and use regular and irregular verbs. e. Form and use the simple (e.g., I walked; I walk; I will walk) verb tenses. f. Ensure subject-verb and pronoun-antecedent agreement.* g. Form and use comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs, and choose between them depending on what is to be modified. h. Use coordinating and subordinating conjunctions. i. Produce simple, compound, and complex sentences. Learning Target I can define noun, pronoun, verb, adjective and adverb. I can explain how nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs function in a sentence. I can define plural. I can make a singular noun into a regular plural noun (boy/boys) or an irregular plural noun (mouse/mice). I can define abstract nouns (nouns that represent an idea, emotion or feeling) and use them correctly. I can explain the difference between regular (walk/walked) and irregular (run/ran) verbs and use them Vocabulary Define Noun Pronoun Verb Adjective Adverb Singular Plural Regular verb Irregular verb Abstract noun Past tense Present tense Future tense Coordinating conjunction Subordinating conjunction Simple sentence Compound sentence Complex sentence Antecedent Evidence of Mastery Writing rubrics Invitation to notice?? (term clarification for new teachers/example?) Grammar activity sheets (insert examples) Discussion/Conference (writing workshop) MAP test Word Work (example?) Teacher Observation Workbook pages Charts and drawings B M E correctly. I can explain the difference between simple verb tenses (past, present and future) and use them correctly. I can define subject and verb and explain that a singular subject needs a singular verb and a plural subject needs a plural verb. I can define antecedent (the word or group of words a pronoun replaces) and make sure a pronoun agrees with its antecedent (the girl/her; the group/them) I can choose the correct form of an adjective, its –er form and its -est form when writing or speaking. I can identify coordinating conjunctions (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) and subordinating conjunctions (after, because, if, since, while) and use them correctly. 2. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. a. Capitalize appropriate words in titles. W.GR.02.01 b. Use commas in addresses. c. Use commas and quotation marks in dialogue. d. Form and use possessives. e. Use conventional spelling for high-frequency and other studied words and for adding suffixes to base words (e.g., sitting, smiled, cries, happiness). f. Use spelling patterns and generalizations (e.g., word families, position-based spellings, syllable patterns, ending rules, meaningful word parts) in writing words. g. Consult reference materials, including beginning dictionaries, as needed to check and correct spellings. I can identify and create simple sentences (Emma walks to school.), compound sentences (Emma walks to school, and her dog follows her.), and complex sentences (Because Emma took the dog back home, she was late for school.). I can identify words in a title that should be capitalized. Capitalize Comma Quotation Marks Dialogue I can identify Apostrophe words in a title Suffix that should not be Prefix capitalized. Singular possessive I can use a Plural comma to possessive separate the city and state in an address. I can use commas and quotations marks correctly in dialogue. I can identify possessives (nouns that own something) and form singular possessives (‘s) and plural possessives (s’). DOL Writing rubrics Invitation to notice Grammar activity sheets (examples) Discusion/Conference (writing workshop) Small Group Teacher Observation Peer Editing Letters/Envelopes (address) MAP test Spelling tests Quick word Vocabulary activity sheets (examples) Word Work (example) I can spell sight words and spelling words correctly, and I know the spelling rules to use when I add suffixes. I can write words correctly using common spelling patterns. I can identify misspelled words and use resources to help me in spelling correctly. Knowledge of Language 3. Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening. a. Choose words and phrases for effect.* b. Recognize and observe differences between the conventions of spoken and written standard English. I can identify words or phrases in a story that bring it to life. I can choose words and phrases when writing or speaking to bring my story to life. I can explain the difference between written and spoken language and when it is appropriate to use formal or informal language conventions? I can follow standard English rules when writing. Vocabulary Acquisition and Written language Spoken language Standard English rules Formal language Informal language Writing Rubrics Discussion/Conference Invitation to Notice Teacher observation Writer’s workshop Student presentations Peer evaluation Use 4. Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning word and phrases based on grade 3 reading and content, choosing flexibly from a range of strategies. a. Use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. b. Determine the meaning of the new word formed when a known affix is added to a known word (e.g., agreeable/disagreeable, comfortable/uncomfortable, care/careless, heat/preheat). c. Use a known root word as a clue to the meaning of an unknown word with the same root (e.g., company, companion). d. Use glossaries or beginning dictionaries, both print and digital, to determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases. I can use context clues in a sentence to help me understand the meaning of an unknown word. Context clues Affixes Root word Base word Reference materials I can recognize and define (use understand??) common affixes (un, dis, able, less). I can break down unknown words into units of meaning (affix, root) to understand a word. Teacher Observation T.O.C. Rigby Dibels Vocabulary activities (example??) DOL Word Work activities (examples??) Phonics workbook?? Small Group Discussion/Conference Lexile DORF Lexia Workbook MAP I can find the meaning of a word using references materials (dictionaries, glossaries, QuickWord, etc.) 5. Demonstrate understanding of word relationships and nuances in word meanings. a. Distinguish the literal and non-literal meanings of words and phrases in context (e.g., take steps). b. Identify real-life connections between words I can explain the difference between literal meaning (means exactly what it says) and nonliteral meaning (what it says is not exactly Literal meaning Nonliteral meaning Figurative language Connection Mood Correct retell of text Vocabulary activities (various per teacher) AR Vocab. quizzes DOL Writing rubrics (does this fit??) Discussion/Conference Small Group and their use (e.g., describe people who are friendly or helpful). c. Distinguish shades of meaning among related words that describe states of mind or degrees of certainty (e.g., knew, believed, suspected, heard, wondered). what it means) of words and phrases. I can tell when a word or phrase means something other than what it says. I can make reallife connections to words I hear and read. 6. Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic, and domainspecific words and phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner that night we went looking for them). I can recognize words that have similar meaning and choose the word that best describes the mood. I can learn and use new vocabulary correctly. I can recognize the difference between words used in general and vocabulary words used in certain subjects. Vocabulary activities (example??) Rigby Dibels AR Vocab quizzes Subject specific assessments that contain vocabulary Writing rubrics Correct retell of text Discussion/Conference Small Group **Reading log example included as an option formatted to align with Reader’s Workshop. **Spoken evidence of mastery includes discussion, small group, book clubs, one-on-one conferencing, pair share, etc. **Written retells may include written sentences/paragraphs, reflections, graphic organizer, etc.