CECS-478 Introduction to Computer Security
advertisement

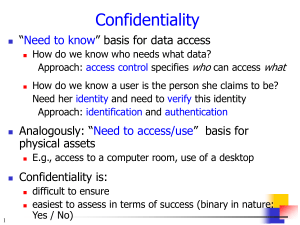
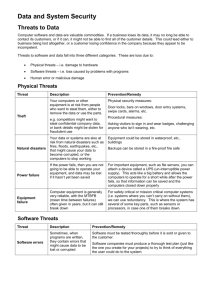
Course Outline CECS 478 Introduction to Computer Security (3) Prerequisites: CECS 323, 328, 474. Controlling the risk of computer security: Security threats and vulnerabilities in the development and use of computer systems. Tools and controls that can reduce or block these threats. Law, privacy and ethics. (Lecture 2 hours, laboratory 3 hours.) Traditional grading only. Textbook(s) Title: Security in Computing, Third Edition 2003 Author: Charles P. Pfleeger, Shari Lawrence Pfleeger Publisher: Prentice Hall ISBN: 0-13-035548-8 Course Objectives Awareness and understanding of the following issues and the ability to apply this understanding to develop a computing style - as a user, developer, manager, consumer and voter - that balances security and risk: Security problems in Computing o The risks involved in computing. o The goals of secure computing: confidentiality, integrity, availability o The threats to security: interception, interruption, modification, fabrication. o Controls available to address these threats: encryption, programming controls, operating systems, network controls, administrative controls, law and ethics. Elementary Cryptography o Concepts of Encryption o Cryptanalysis o Symmetric (secret key) encryption - DES, AES algorithms o Asymmetric (public) encryption - RSA algorithm. o Digital Signatures Program Security o Programming errors with security implications o Malicious code - viruses, worms, Trojan horses o Program development controls against malicious code and vulnerabilities software engineering principles o Controls to protect against program flaws in execution Protection in general-purpose Operating Systems o Protection features provided by general purpose operating systems o Controlled access to objects o User authentication Designing Trusted Operating Systems Database Security o Integrity for databases o Security for databases: access control, inference and aggregation Security in Networks o Threats against networked applications: denial of service, web site defacements, malicious mobile code, and protocol attacks. o Controls against network attacks o Firewalls: design, capabilities, limitations o Intrusion detection systems o Private email: PGP and S/MIME Administering Security o Security planning o Risk analysis o Security policies o Physical security Legal, Privacy, and Ethical Issues in Computer Security o Patents, Copyrights and Trademarks o Computer crime o Privacy o Codes of professional ethics Topics Introduction: Computer Security vulnerabilities and controls. Elementary cryptography Program Security. Protection in general-purpose operating systems Designing trusted operating systems. Database Security Security in Networks Administering Security Legal and Ethical Issues in Computer Security Bibliography Matt Bishop, Computer Security - Art and Science, Addison Wesley, 2003. Kirk Hausman, Diane Barrett, Martin Weiss, Security+ CompTIA SYO-101 Study Guide, Que Certification 2003. Allan Liska, The Practice of Network Security, Prentice Hall, 2003. Donald L. Pipkin, Halting the hacker, Second Edition, Prentice Hall, 2003.