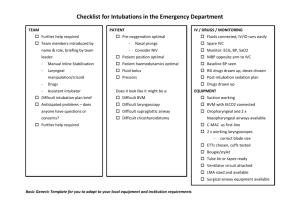
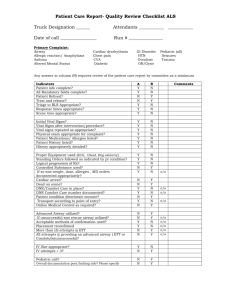
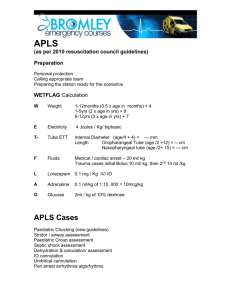
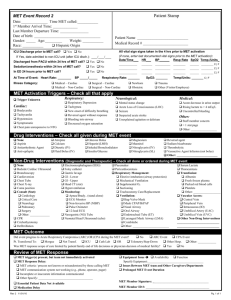
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
advertisement

PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST Cardiac dysfunction in children is more likely to respond to effective oxygenation and ventilation than fluid administration and medications. Defibrillation alone is rarely successful. USE BROSELOW TAPE! FIRST RESPONDER 1. CPR 2. Ventilate with BVM / 100% O2. Consider airway adjunct if no chest rise with BVM 3. If foreign body suspected see PINK 7-PEDIATRIC AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION 4. AED if 6 years old or above 5. Request ALS EMT-BASIC 6. Pulse oximeter PARAMEDIC 7. Advanced airway (consider possibility of PEDIATRIC AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION: PINK 7) 8. Cardiac monitor / IV/IO 9. Blood glucose check. If blood glucose check <60mg in child or <40 in newborn a. >2 years: D50W at 1ml/kg b. <2 years: D25W at 2ml/kg c. <1 month: D10W at 5ml/kg d. Glucagon 1mg IM if no IV/IO 10. Treat dysrhythmias according to protocol using pediatric dosages listed below 11. If hypovolemia suspected (trauma, sepsis, dehydration, spinal injury) IV/IO bolus of 20 ml/kg NS may be repeated a total of three times 12. Bilateral chest decompressions for traumatic arrest (GREEN 3) 13. Consider OG / NG if abdominal distention PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST DOSAGES Medications: o Atropine IV/IO 0.02 mg/kg: Minimum dose: 0.1 mg Maximum single dose: 1 mg o Epinephrine IV/IO: 0.01 mg/kg (1:10,000, 0.1 ml/kg) ET: 0.1 mg/kg (1:1,000, 0.1 ml/kg) Repeat every 3-5 minutes o Lidocaine IV/IO: 1 mg/kg o Magnesium 25-50mg/kg IV/IO (max 2gm) for Torsades Electricity o Cardioversion: 0.5 J/kg (initial); 1.0 J/kg (subsequent) o Defibrillation: 2.0 J/kg (initial); 4.0 J/kg (subsequent) USE BROSELOW TAPE! PINK 4