Chapter 5 Section 1

“Trouble on the Frontier”
* * * * * * * * * * * *
Focus Question: How did the British gain French territory in North America?
*Between 1650 and 1700, American colonists developed a large degree of self-government, were proud of their hard-won rights, and were loyal to the king.
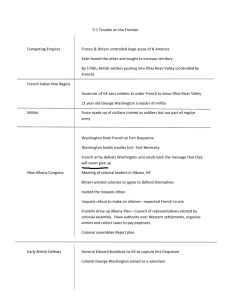
Competing Empire
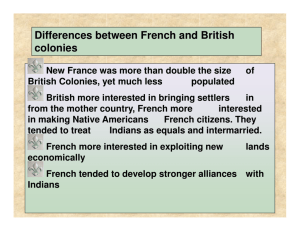
*By mid-1700s, Britain and France controlled bordering large areas of North America; each sought to increase the size of land under its control.
*Native Americans lived on most of territory claimed by Britain and France. There were few
French settlers so they did not threaten to seize
Native American lands, but British settlers wanted for farming.
*By 1740s, British settlers were pushing into Ohio
River valley lands claimed by French.
The French and Indian War Begins
*1753 – French built forts to protect land between
Lake Erie and Ohio River (Virginia Company also claimed Ohio River Valley)
*Governor of VA sent soldiers to order French to leave (21-yr-old surveyor of VA militia, George
Washington, led them). Militia – force made up of civilians trained as soldiers but not part of the
regular army.
*French rejected Washington’s warning.
*Next year, Washington traveled again with orders to build fort where Allegheny and
Monongahela River meet to form Ohio River.
*French had already built Fort Duquesne there.
Washington built Fort Necessity about 50 miles south.
*Although Washington’s troops defeated a small
French force, they eventually had to surrender
Fort Necessity. They had to return home to VA with news that French would never give up Ohio
River Valley.
Albany Congress
*Expecting war, British government met with colonial leaders in Albany, NY (wanted colonies to agree to cooperate in defending themselves against
French)
*Iroquois invited to meeting, hoping to form alliance, an agreement between countries to help
each other against other countries, against French
*Iroquois refused to attend (thinking French would win war)
*Colonial leaders tried to work out plan for defense.
*Ben Franklin of PA believed colonies had to succeed, published picture of chopped up snake with warning “Join or Die”.
*Franklin drew up Albany Plan of Union which called for council of representatives elected by colonial assemblies; council would have
~authority over western settlements
~relations with Native Americans
~organize armies
~collect taxes to pay its expenses
*Albany Congress approved plan but colonial assemblies did not (colonies wanted to control own taxes and armies).
Early British Defeats
*1755 – British sent General Edward Braddock to
VA with order to capture Fort Duquesne;
Braddock brought large force of regular British troops and VA militia (Washington joined as volunteer)
Disaster at Fort Duquesne
*Braddock accustomed to European military tactics (fight in formation in open fields)
*Braddock warned by soldiers against marching down narrow road through dense forest in red coats; Braddock did not listen
*As they approached Fort Duquesne, Braddock’s force ambushed by French and Native Americans
(Huron and Algonquin); more than half were killed or wounded (Braddock died)
More British Defeats
*1755 – army led by governor of MA failed to take
Fort Niagara on Lake Ontario
*Further east, army of British colonists and
Native Americans were ambushed near Lake
George
*Defeats may have strengthened Iroquois decision not to ally with Britain
*May 1756 – Britain declared war on France in
Europe (beginning of Seven Years’ War)
*French troops led by General Louis de Montcalm captured and destroyed Britain’s Fort Oswego on
Lake Ontario and captured Fort William Henry on Lake George in 1757
The British Turn the Tide
*1757 – William Pitt became prime minister in
Britain and sought top generals
*Summer of 1758 – Britain scored first major victory – captured fort at Louisbourg.
*Fall of 1758 – British took Fort Duquesne and renamed it Fort Pitt (later became Pittsburgh)
*Iroquois now sided with British
*Quebec (capital of New France) on high cliff overlooking St. Lawrence River matched French
General Montcalm vs. British General James
Wolfe
*British found unguarded trail that allowed them to climb cliffs; Sept. 1757 – 4,000 British defeated
4,500 French (more than 2,000 killed or wounded)
*French lost Quebec and could not defend rest of its North American territory (Montreal fell in
1760)
*Feb. 1763 – Treaty of Paris signed:
~France lost almost all of North American possessions
~France ceded, or surrendered, French
Canada to Great Britain
~Britain gained all other French territories east of Mississippi, except New Orleans
~Britain received Spanish Florida.
~Spain received New Orleans and all French territory west of Mississippi
*Without French help, the Native Americans could not stop British settlers from moving on their lands.
Review Questions:
1.) Why were the British concerned about French activity in the Ohio River valley?
The British also claimed the Ohio River valley.
2.) What fatal errors did General Edward
Braddock make?
He tried to fight using tactics that worked in
Europe and did not adapt to North American conditions.
3.) What was the outcome of the Battle of Quebec?
The British defeated the French, who were no longer able to defend the rest of its North
American territory.