Abstract Template - 5th International Conference on
advertisement

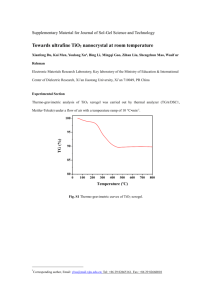
OPTOFLUIDICS2015 CONFERENCE SAMPLE ABSTRACT AND INSTRUCTIONS FOR ABSTRACT PREPARATION Author name1,* and Author name2 Address1 includes Institute, City, Country 2 Addresss2 includes Institute, City, Country 1 * Email: aaa@bbb.edu; Tel.: +86-(20) 3931-4813 The 5th International Conference on Optofluidics (Optofluidics2015) will be held in Taipei, Taiwan on July 26-29, 2015. Authors are invited to contribute original presentations on advances in optofluidics, microfluidics and related research areas. The Optofluidics2015 Conference Committee encourages submission of original work for either oral or poster presentation. Submitted abstracts should be two-pages: one text page (500 words or less, 11 point Times New Roman font) and one page of figures and tables on A4 Standard (21 cm x 29.7 cm) paper. The title, authors, affiliations and all text must fit on the first page. The second page should contain any figures or tables. References may go on either page. All other style formatting is up to the authors. The Abstract should be converted into a PDF file before uploading. Abstracts in other document formats will not be accepted. The purpose of an Abstract is to tell what new results you propose to present. Therefore, it is important within the first few sentences to state what your primary result is. For example: “This paper reports a new design of optofluidic cell sorting chip that ….” It is also important to identify how the new work differs from previous work from your own group and from other groups, especially work presented at recent and upcoming international meetings. For example: “The fabrication process for the optofluidic chip was reported at Optofluidics2012 [1], and an analysis of the optical field pattern which is essential for the sorting function was reported at Transducers 2011 [2]. Our method differs from that of group X [3] in the structural design, and of group Y [4] in the working principles.” After an introduction of the basic ideas and how the work relates to other work, present detailed descriptions of methods, device structures, and examples of specific results, whether experimental or theoretical. Figures and Tables can support these results. For example: “A schematic view of the device design is illustrated in Figure 1, and the simulated fluidic velocity distribution is shown in Figure 2. Table I shows the device geometries using the analysis procedure in [2].” After presentation of results, it is useful to compare specific results with related work, and also to comment on the broader impact of the results. Please make sure that all the figures/photographs are clearly visible. If the program committee cannot clearly see and understand the role of these visual aids, it will be viewed negatively. All submitted abstracts would be considered for both Oral and Poster Sessions unless the submitting author specifically requests a Poster. The deadline for abstract submission is March 30, 2015 (Hawaii Time). Word Count: <= 500 1 PL intensity (a.u.) M-BVO M-BVO+TiO2 450 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the microfluidic planar reactor and structures of the catalyst film and the tree-shaped microchannels for inlet and outlet. 500 20 (224) (204) (116) (220) (215) (004) (200) (105) (211) (100) (121) M-BiVO4 30 (112) (051) (132) (042) (202) (161) (013) (152) (002) 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 (040) (011) Intensity(a.u.) Anatase-TiO2 40 2(degree) 50 60 Fig. 3 Characteristics of the photocatalytic films: XRD patterns of the layers of BVOand TiO2(inset). The BVO layer shows a monoclinic structure and the TiO2 is in pure anatase phase. 600 Fig. 4Characteristics of the photocatalytic films: Photoluminescence of M-BVO and BVO/TiO2. Table 1. Fig. 2Photograph of the microfluidic planar reactor integrated with the inlet and the outlet. 550 Wavelength (nm) Sample of a Table Format REFERENCES: [1] L. Lei, N. Wang, X. M. Zhang, Q. D. Tai, D. P. Tsai and Helen L.W. Chan, “Optofluidic planar reactors for photocatalytic water treatment using solar energy,” Biomicrofluidics (in press) [2] A. Kudo, K. Omori, and H. Kato, “A novel aqueous process for preparation of crystal form controlled and highly crystalline bivo4 powder from layered vanadates at room temperature and its photocatalytic and photophysical properties,” J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 11459-11467. [3] M. Long, W. Cai and H. Kisch “Visible light induced photoelectrochemical properties of n-BiVO4 and n-BiVO4/p-Co3O4,” J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 548-554. 2