THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - Hamburg Central School District
advertisement

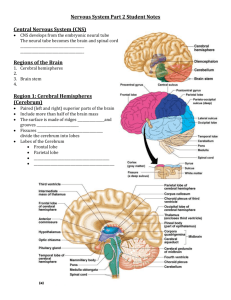
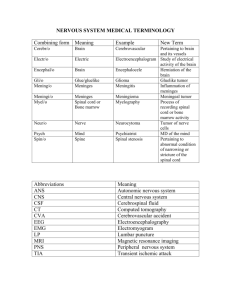
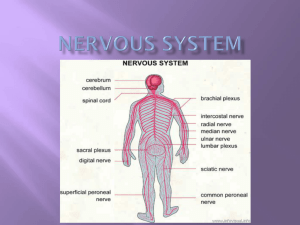
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Your nervous system receives, processes, and sends out information, and it also monitors and responds to change in the environment. Some activities your nervous system does automatically are blinking, blood pressure, breathing, temperature, digestion, shivering, and heart beats. Changes occurring in the environment around you are called stimulus or stimuli. An example of this would be when a bug comes near your eye, it causes you to blink. The basic unit of structure in the nervous system is called a neuron (nerve cells). CELL BODY NUCLEUS DENTRITE AXON SYNAPSE CNS ~ contains nucleus (houses it) ~ controls all activities of the cell ~ carries messages to the cell body ~ carries messages away from the cell body ~ space between two nerve cells ~ central nervous system TYPES OF NEURONS: SENSORY NEURONS ~ carries messages to the brain & spinal cord INTERNEURONS ~ “middle man” relays messages between sensory and motor MOTOR NEURONS ~ carry messages from CNS to body Receptor cells detect changes in your surroundings. While effectors (basically muscles) carry out the instruction of your CNS to the body. A nerve impulse is an electro, a chemical message in the nervous system. A nerve impulse can travel 120m/sec. A nerve impulse can “jump” a synapse by getting a message which becomes a chemical and flows across the synapse. THE CNS & PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The major parts of the CNS are the brain and the spinal cord. The brain is the main control center. The spinal cord is the link between the brain and the body. THE BRAIN The brain weighs 1.4kg (~3 pounds). The skull is protects the brain along with 3 layers of tissue (that forms a pillow like coating) and fluid. The three parts of the brain are the cerebrum (separates humans from animals), medulla and the cerebellum. THE CEREBRUM (pink part of the brain ~ on a model) The cerebrum is the largest and arguably most important part of the human brain. Important tasks that the cerebrum is in charge of are the voluntary muscles, emotions, attitude, higher thinking and your speech. The term hemisphere means that it is divided into two halves, the right and left. The right hemisphere is responsible for your creativity, you are artistic. It also controls the left side of your brain. The left hemisphere is responsible for your math ability, logic, analytical thinking. It controls the right side of your brain. THE CEREBELLUM (brownish part of the brain ~ on a model) The cerebellum coordinates muscle movement and balance. THE MEDULLA (at the base of the brain stem) The medulla connects the brain to the spinal cord. It controls involuntary actions such as breathing, sweating, hear beat, digestion… Autonomic processes refer to those that are involuntary or automatic. THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is approximately 43cm long. The vertebra or backbones protect the spinal cord. The spinal cord connects the brain to the body and it controls reflexes. Reflex is a quick response to a stimulus, an automatic reaction. THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The peripheral nervous system links between the CNS and the rest of your body.