Key Concepts - Cloudfront.net
advertisement
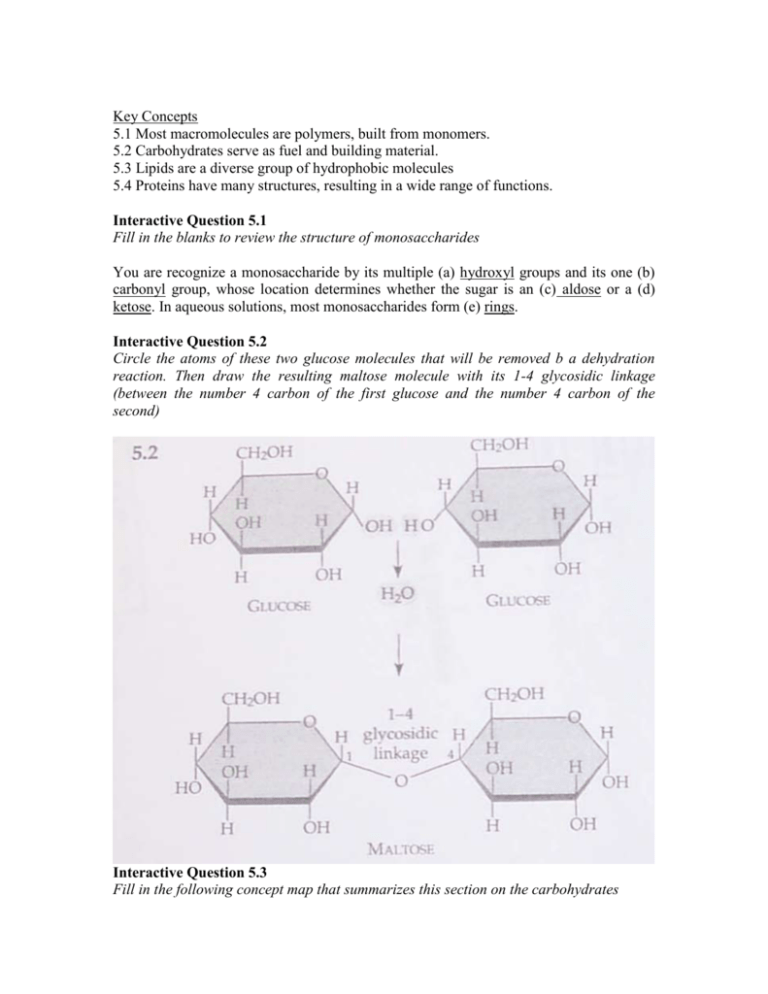
Key Concepts 5.1 Most macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers. 5.2 Carbohydrates serve as fuel and building material. 5.3 Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules 5.4 Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions. Interactive Question 5.1 Fill in the blanks to review the structure of monosaccharides You are recognize a monosaccharide by its multiple (a) hydroxyl groups and its one (b) carbonyl group, whose location determines whether the sugar is an (c) aldose or a (d) ketose. In aqueous solutions, most monosaccharides form (e) rings. Interactive Question 5.2 Circle the atoms of these two glucose molecules that will be removed b a dehydration reaction. Then draw the resulting maltose molecule with its 1-4 glycosidic linkage (between the number 4 carbon of the first glucose and the number 4 carbon of the second) Interactive Question 5.3 Fill in the following concept map that summarizes this section on the carbohydrates Carbohydrates Include a. monosaccharides b. (CH2O)n i.animals are hydrophobic and insoluble in water composed of composed of molecules with c. energy compounds d. fatty acids g. phosphate group 4 carbon rings is a store are forms a may functions as 3-C alcohol energy long charged, hydrophilic j Starch in C-H bonds hydrocarbon head chain with carboxyl group may be forms a e. polysaccharides f. disaccharides hydrophobic tail oils: kinks keep liquid solid at room temperature bilayer forms at room temperature h. glycogen Interactive Question 5.4 Sketch a section of a phospholipids bilayer of a membrane, and label the hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail of one of the phospholipids. Interactive Question 5.5 Fill in this concept map to help you organize your understanding of lipids. Interactive Question 5.6 a. Draw the amino acids alanine (R-group-CH) and serine (R-group-CH2OH) and then show how a dehydration reaction will form a peptide bon between the two. b. Which of these amino acids has a polar R group ( Serine) and which has a nonpolar R group? (Alanine) c. What does this molecule segment represent? Note the N-C-C-N-C-C sequence. A polypeptide backbone. Interactive Question 5.7 In the following diagram of a portion of a polypeptide, label the types of interactions that are shown. What level of structure are these interactions producing? a. b. c. d. hydrogen bond hydrophobic and van derWaals interaction disulfide bridge ionic bond Tertiary Structure. Interactive Question 5.8 a. Why would a change in pH cause a protein to denature? A change in pH alters the availability of H+, OH, or other ions, thereby disrupting the hydrogen bonding and ionic bonds that maintain protein shape. b. Why would transfer to a nonpolar organic solvent (such as ether) cause denaturation A protein in an organic solvent would turn inside out as the hydrophobic regions became clustered on the inside of the molecule and the hydrophobic regions interacted with the nonpolar solvent. c. A denatured protein may re-form to its fictional shape when returned to its normal environment. What does that indicate about protein’s conformation? The return to its functional shape indicates that a protein’s conformation is intrinsically determined by its primary structure—the sequence of its amino acids. Interactive Question 5.11 Interactive Question 5.9 Interactive Question 5.10 Show the flow of genetic information in a cell. DNA => RNA => Protein Interactive Question 5.11 a. Label the three parts of this nucleotide Indicate with an arrow where the phosphate group of the next nucleotide would attach t build a polynucleotide. Number the carbons of the pentose sugar. b. Is this a purine or a pyrimidine? pyrimidine c. Is this a DNA or RNA nucleotide? DNA Interactive Question 5.12 Structure Your Knowledge 1. Describe the four structural levels in the conformation of a protein: 2. Identify the type of monomer or group shown by the formulas shown on the right Then match the chemical formulae with their description. Answers may be used more than once. 1. Molecules that would combine to form a fat. Fatty Acid/Glycerol- B, D 2. Molecule that would be attached to other monomers b a peptide bond. A, Amino Acid 3. Molecules or groups that would combine to form a nucleotide. C, E, F 4. Molecules that are carbohydrates. F, G 5. Molecules that is a purine. C 6. Monomer of a protein. A 7. Groups that would be joined b phosphodeister bonds. E, F 8. Most nonpolar (hydrophobic) molecule. B a. amino acid b. fatty acid c. nitrogenous base (Purine) d. Glycerol e. Phosphate f. Pentose g. Triose (sugar) Test Your Knowledge 1. Glycogen (Carbohydrate) 2. Cholesterol (Lipid) 3. RNA (Nucleic Acid) 4. Collagen (Protein) 5. Hemoglobin (Protein) 6. A gene (Nucleic Acid) 7. Triacylglycerol (Lipid) 8. Enzyme (Protein) 9. Cellulose (Carbohydrate) 10. Chitin (Carbohydrate) Multiple Choice 1. Polymerization is a process that e. may involve all of the above 391 2. Which of the following is not true of a pentose? C. it has the formula CH12O5 b70f 3. Disaccharides can differ from each other in all of the following was except in the number of their monosaccharides. 70 4. Which of the following is not true of cellulose? E. its monomers are glucose with nitrogen containing appendages. 52, 72, 106, 558 5. Plants store most of their energy as c. starch 71 6. What happens when a protein denatures b. it loses its secondary and tertiary structures. 84-85 7. c. stabilized by hydrogen bonds and commonly found in fibrous proteins. 47-48 8. a. saturated 75-76 9. d. C51H98O6 75 10. c. folds stabilized by hydrogen bonds between segments of the polypeptide backbone. 82, 85f 11. c. one of their stomachs contains bacteria that can hydrolyze the bonds of cellulose. 74f 12. d. fat 859, 861f 13. b. the sequence of nucleotides in RNA, which was determine by the sequence of nucleotides in the gene for that protein. 79f 14. c. C12H2O11 70, 71f 15. d. covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next. 88 16. a. cholesterol. 77f 17. c. polypeptide (tripeptide) 78-81 18. b. 2 80 19. c. CGGATT 89 20. b. the two groups share a relatively recent common ancestor 398-402 21. d. phospholipids. 99 22. a. proteins. 84-85 23. d. fats that contain trans double bonds and may contribute to arteriosclerosis. 75f 24. e. primary component of cell membranes. 84-85 Fill in the blanks 1. F Sanger 2. Guanine 3. Purine 4. Nucleotide 5. 1st structure 6. quaternary 7. glycogen 8. phospholipids 9. cellulose 10. chaperonins (Amino acid sequences)