Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Review
advertisement
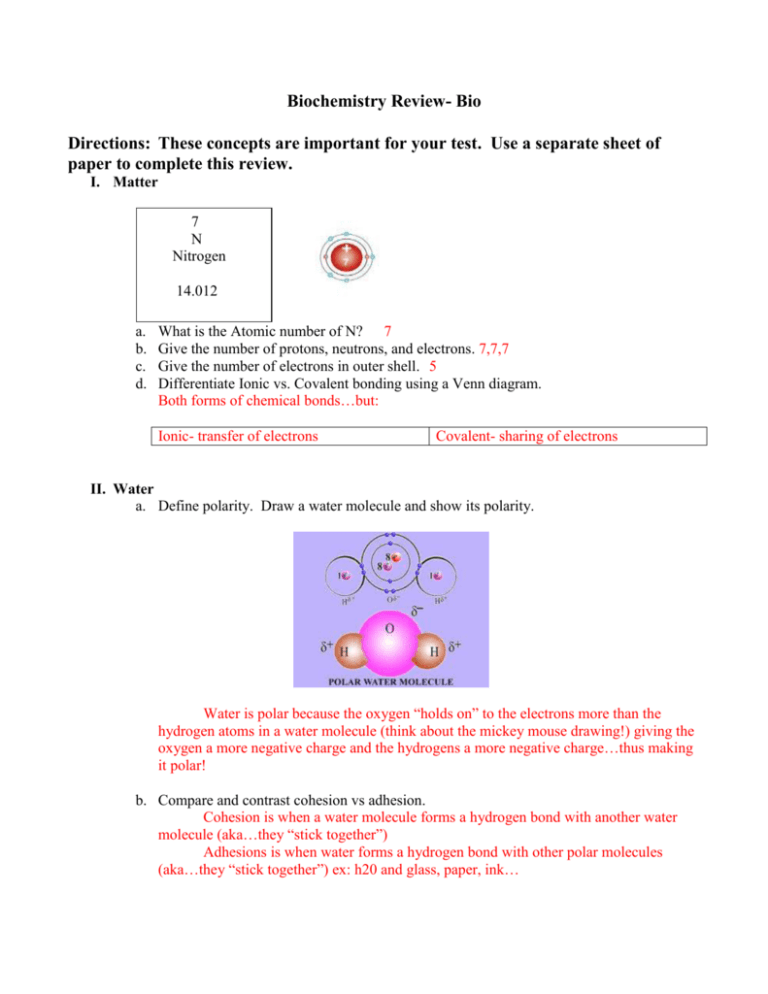
Biochemistry Review- Bio Directions: These concepts are important for your test. Use a separate sheet of paper to complete this review. I. Matter 7 N Nitrogen 14.012 a. b. c. d. What is the Atomic number of N? 7 Give the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 7,7,7 Give the number of electrons in outer shell. 5 Differentiate Ionic vs. Covalent bonding using a Venn diagram. Both forms of chemical bonds…but: Ionic- transfer of electrons Covalent- sharing of electrons II. Water a. Define polarity. Draw a water molecule and show its polarity. Water is polar because the oxygen “holds on” to the electrons more than the hydrogen atoms in a water molecule (think about the mickey mouse drawing!) giving the oxygen a more negative charge and the hydrogens a more negative charge…thus making it polar! b. Compare and contrast cohesion vs adhesion. Cohesion is when a water molecule forms a hydrogen bond with another water molecule (aka…they “stick together”) Adhesions is when water forms a hydrogen bond with other polar molecules (aka…they “stick together”) ex: h20 and glass, paper, ink… c. Compare and contrast capillary action and transpiration Transpiration is when a plant loses water from their leaves by evaporation. The water moves up the plant by the process of capillary action (cohesion and adhesion) d. List 3 unique properties of water and describe how they allow for life. Temperature moderation, density of ICE, universal solvent III. pH a. Differentiate between acids and bases. a. What type of ions are in each? Acids= more H+ ions (hydrogen) Base (alkaline)= more OH- ions (hydroxide) b. pH scale- What does it go from and how much is each step? As you move from one number to the next, there is a 10x increase or decrease in acidity c. Define buffers. Substances that change the pH of a substance. Can occur naturally in the body to regulate pH IV. Macromolecules- name the building blocks (monomers) as well as any special properties a. Carbohydrates b. Lipids c. Proteins d. Nucleic acids e. Vocab: glucose, amino acids, saturated, nonsaturated, fatty acid chains, glycerol, nucleotides. **See chart from class** V. Enzymes a. What is the difference between “catalyst” and “enzyme”? Enzymes are organic catalysts. They increase the rate of chemical reactions by decreasing the amount of activation energy needed to start the reaction b. Describe enzyme specificity. c. What are enzymes made of? Enzymes are Proteins (which are made from amino acids) d. Why does form and function matter in enzymes? If the enzyme does not have the correct shape, it will not react with the substrate and the chemical reaction will not work. i. What happens to enzymes if they are heated or if the pH is changed? They will work to a certain point, then will change shape and ultimately become denatured and not work at all!









![Paper ID [C2008]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008826590_1-1dd50f6f840af6fb83a867d42efaca34-300x300.png)