FIND THE ORGANS AND FUNCTIONS OF THE 11 ORGAN
advertisement

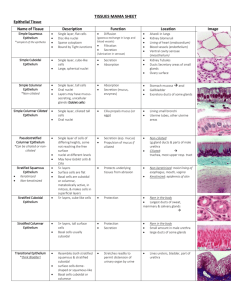
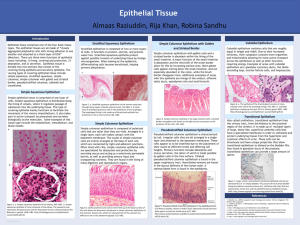
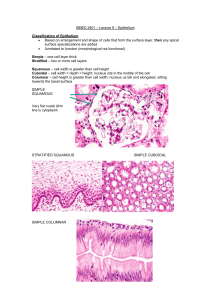
Anatomy & Physiology HISTOLOGY SCRAMBLE FIND THE LOCATION AND FUNCTIONS OF THE FOLLOWING TISSUES OF THE BODY. REWRITE INTO TABLE FORM. DRAW DIAGRAMS OF Tissues. TISSUE Description Function Location Free surface and basement membrane, avascular and Protection, absorption, Covering of mitotic diffusion, secretion, organs , lining of Epithelial filtration cavities Matrix, mitotic, most are Support, protection, connective vascular storage, inflammatory response Throughout body Ability to lengthen and shorten, amitotic after attached to puberty, vascular Movement of bones, bones, in hollow muscular materials and blood organs, heart Cell processes, amitotic after 2, avascular Brain and spinal nervous conduct electrical signals cord Haversian rings, lacunae, caniculi, central canal, hard matrix, mitotic and vascular support, storage of calcium, bone protection skeleton Single layer with goblet cells and cilia, nuclei at Pseudostratified different heights Respiratory ciliated columnar Mucus secretion passageways Mast cells, elastin and collagen fibers, liquid Areolar matrix Inflammatory response, Around organs, water reservoir, packing under skin Many layers with top layer flattened. Nuclei decrease away from basement membrane, avascular, Epidermis mitotic Esophagus, stratified squamous protection mouth Long cylindrical cells, many Skeletal muscle nuclei, striations Movement of bones Attached to bones Support and friction Joints, end of ribs, Hyaline cartilage Lacunae, gel matrix reduction nose Tall cells, nuclei found close to basement Digestive tract membrane, goblet cells Produce mucus, absorb from stomach to columnar nutrients anus Uninucleate, branching cells with striations and Contraction and relaxation Cardiac muscle intercalated disks of heart heart Anatomy & Physiology HISTOLOGY SCRAMBLE Match the functions on the left with the tissue on the right. Choices can be used more than once. 1. Consists of many layer of cells E A) Simple squamous epithelium 2. Nuclei located at different levels in cell D B) Simple cuboidal epithelium 3. Forms the walls of capillaries A C) Simple columnar epithelium 4. Forms linings of respiratory passages.D D) Pseudostratified columnar 5. Have centrally located spherical nuclei B E) Stratified squamous epithelium 6. Forms lining of digestive tract.C 7. Nuclei located near basement membrane C 8. Top layer is thin like floor tiles E 9. Forms the lining of the mouth. E 10. Forms the lining of the ducts in glands. B Which one doesn’t belong? Choose the word or phrase that is different from the others. 11. A) squamous B). cartilage 12. A) goblet cell 13. A) Mouth B) abuse C) stratified squamous D) absorption 14. A) simple B) one layer C) stratified D) diffusion 15. A) hyaline B) Adipose C) fat D) buttock, breast 16. A) smooth muscle 17 A) connective tissue B) matrix 18 A) blood B) solid matrix 19 A) kidneys B) stratified B) cilia C) columnar C) stratified squamous B) hollow organs D). transitional D) pseudostratified C) multinucleate C) areolar C) anucleate C) filtration columnar D) involuntary D) apical surface D) extracellular substance D) cuboidal Complete the sentence by filling in the blank: 20. All epithelial tissue types have CLOSELY PACKED cells, are AVASCULAR and are highly MITOTIC. 21. Connective tissue has the general function of SUPPORT. 22. One characteristic that all connective tissue types share is extracellular material called MATRIX. Match the prefix with the word or phrase that defines it: 23. adip- h a. bone 24. pseudo-d b. without 25. squam-g c. cartilage 26. strat-e d. false 27. chondr-c e. layers 28. os- a f. cell 29. –cyte f g. flat 30. a- b h. fat