THREE MODELS OF URBAN STRUCTURE
advertisement

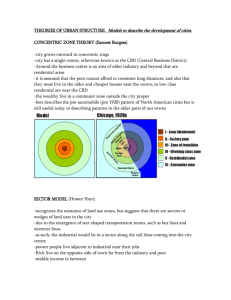
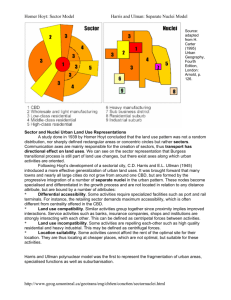
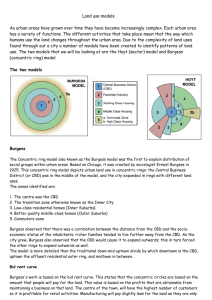
THREE MODELS OF URBAN STRUCTURE Urban structure is the arrangement of land use in urban areas. Sociologists, economists, and geographers have developed several models, explaining where different types of people and businesses tend to exist within the urban setting. Three models are described in this article. Urban structure can also refer to the urban spatial structure, which concerns the arrangement of public and private space in cities and the degree of connectivity and accessibility. The three models we will be looking at for CAPE level are: Burgess Concentric Zone Model Hoyt Sector Model Ullman and Harris Nuclei Model All three models were developed in Chicago. Other than Lake Michigan on the east, few physical features have inhibited Chicago's growth. Chicago includes a Central Business District (CBD), known as the Loop because of the elevated railway lines around it. Residential suburbs go to the north, west, and south. 1. Concentric Zone Model - created in 1923 by sociologist E. W. Burgess. -According to this model, the city grows outward beginning with the Central Business District in the middle. -The second ring is the zone in transition where industry and poorer-quality housing is. Usually new immigrants to the city live in this zone in small quarters. Rooming houses for single individuals are located here, too. -The third ring is the zone of independent workers' homes. These are modest older houses occupied by the working class. -The fourth ring is the zone of better residences where more spacious houses for middleclass families. -Finally, the fifth zone is the commuter's zone. People who work in the center choose to live in the suburbs. 2. Sector Model - developed in 1939 by land economist Homer Hoyt. -According to this model, the city develops in a series of sectors, not rings. Certain areas are more attractive for different activities. -In the center is the Central Business District. As the city grows, activities expand in a wedge, or sector, from the center. Once a district with "high-class" housing is established, the most expensive houses is built on the outer edge of that district further from the center. -Industrial and retailing activities develop in other sectors, as well as low-class and middle-class residential sectors. -As for Chicago, Hoyt argued that the best housing is developed north from the CBD along Lake Michigan, while industry was located along the major rail lines and roads to the northwest, south, and southwest. 3. Multiple Nuclei Model - developed in 1945 by geographers C.D. Harris and E.L. Ullman . -According to this model, a city includes more than one center that activities revolve. Examples of these nodes include: ports, neighborhood business center, university, airport, and parks. -Some activities go with particular nodes while others do not. For example, a university node may attract well-educated residents, bookstores, and copy places. Or, the airport may attract hotels and warehouses. Likewise, incompatible land use activities will not be clustered together. For example, industries will not be placed near high-class housing.