Individual - spellingfireworks
advertisement

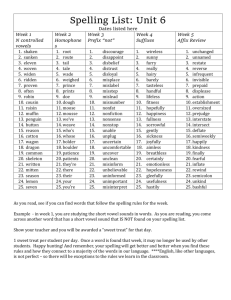
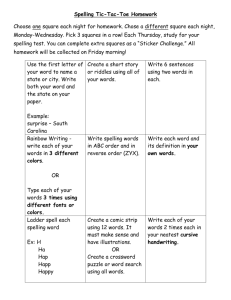
Table 1. Individual Spelling Activities. Individual Visual Practical Ideas Look, cover, write check Why? A strategy to support visual knowledge. Variation 1. Look at the word. Say- make sure you know how to pronounce the word. Break the word into syllables. Write the word without copying. Check what you have written. Revise. Variation 2. AusVELS standards: (ACELA1779), (ACELA1526), (ACELA1485). The Look, Cover, Write strategy is particularly useful for lower and middle primary students and struggling spellers. It is also useful for spelling irregular words. Select the word you wish to spell. Pronounce the word clearly. Say each syllable of the word. Name the letters in the word. Write the word, naming each letter as you write. Writing spelling words out in colourful and creative ways (i.e. bubble writing, different coloured letters). Helps create a different way of visualising spelling words. Self-correction Encourage students in their writing to “Have a go” in their spelling rather than asking you for the correct spelling. Encourage students to use their spelling strategies such as sounding the word out, what words do they know that sound similar? Encourage students to use words they are not confident in spelling instead of using easy or simple words and assure students that they will be able to correct their spelling once their writing is finished. Once students have finished their written work, have students circle or box words they feel they have misspelt. Then students can investigate through various strategies to find the correct spelling. This can be through a spell checker, dictionary, asking a friend etc. The types of investigations is up to the teacher and students. Once the student has corrected their work (The teacher can check the final draft) they then rewrite their final piece. 1 Encouraging students to “Have a go” in their writing enables the student to write in a more fluent manner rather than stopping to get assistance from the teacher. It also encourages students to use alternative words to the words they are confident in spelling which will increase their vocabulary and confidence in learning to spell. Having an investigative approach to learning to spell gives the students a sense of ownership over their learning. The teacher is not there crossing out misspelled words and providing the correct Table 1. Individual Spelling Activities. For upper primary students, etymological knowledge (Word origin), morphemic word families and homophones in context can be investigated. spellings but rather there to help students if they get stuck in their investigations by encouraging them to use an alternative methods. Students will have a better chance at absorbing the correct spelling of a word if they have investigated it and rewritten it in their writing. AusVELS Standards: (ACELY1684), (ACELA1780), (ACELY1683), (ACELA1485), (ACELA1779), (ACELY1697), (ACELY1695), (ACELA1513), (ACELA1498), (ACELA1780), (ACELA 1526). Homonyms (Leading on from whole class and paired activities) Construct a proofreading activity with a focus on: correct spelling of homonyms and correct spelling of high frequency words. Students circle the mistakes and write the corrections above. Demonstrate proof reading to students: read for meaning, track with a pointer and follow each word as it is read, re-read for spelling errors. When re-reading for spelling errors ask: Does it look right? Can I see letters for all the sounds I can hear when I say the word? Is the word made from a word or group of words I know? What resources can I use to check? Phonology Word sort activities can be useful when investigating blends, syllables, diagraphs and diphthongs. Write a selection of words onto cards and have students arrange the cards into groups (Depending on content explored i.e. blends students would group all the bl, st, cr etc. words). Encourage students to sound out words as they categorise them. 2 Reinforces the whole class and group/paired activities (See tables for each) for homonyms. Incorporates spelling practice in high frequency words. AusVELS standards: (ACELA1780), (ACELA1485), (ACELA1500). Word sort activities are an effective strategy for teaching students to look closely at words AusVELS standards: (ACELA1485) Table 1. Individual Spelling Activities. Also give the students the opportunity to sort out their words without a category, students can study the words carefully and make their own relationships and group accordingly. Promotes individual, strategic thinking. Morphemes Morphemes explored could include: Plurals, i.e. s. es (You may Comparatives i.e. er, est find you Verb ending, i.e. ing, ed need to Prefixes, i.e. un, mis, pre, dis start off Suffixes, i.e. ment, ness, ly, able, ful, less. with whole class You could have students create a word web instruction around a morpheme i.e. ing. Have ing in the before middle of the page then have students write their moving words (Create a list of words that are experienced onto in student’s reading and writing i.e. run, go, read, individual eat, have, come) with the ing morpheme added. work) Base word work: select a base word to which prefixes and suffixes can be added. Students use a list of prefixes and suffixes and the dictionary to generate as many words as possible. Students explore morphemic knowledge. Aids in extending the range of words students can spell. Create a word wheel: where a base word is positioned in the middle of the wheel i.e. play with its associated suffixes and compound words written around the movable outer wheel i.e. ground, s, ing, ful, time, ed. So students can move the outer wheel and position it so that they can make new words i.e. played. Computer activities encourage motivation, practice and give immediate feedback. Please see the digital links provided in the activities section on the spelling fireworks website for online games, apps and online spelling programs. Have students create an individual word web. Allocate a different word to each student and have them put this word in the centre of their page, then have the students research the meaning of their word through the dictionary and exploring the internet. 3 AusVELS standards: (ACELA1526), (ACELA1485), (ACELA1779) To help build the student’s knowledge of base word and its associated suffixes and compound words. Table 1. Individual Spelling Activities. Etymology Have students break the word into parts of meaning i.e. Tele – from the Greek meaning far and phone-sound. Students could add words around their word web with words containing tele or phone i.e. Telescope, phonics. To assist students in both spelling and vocabulary by helping them see why some words have their present spelling. AusVELS standards: (ACELA1513), (ACELA1500). At home practice If the classroom you are placed in has a weekly spelling test and therefor a list of weekly spelling words to be learnt students will be encouraged to practice their spelling at home in a spelling book. Some useful and interesting techniques is for students to do a different activity involving their spelling words each day (Or at least three times a week). Such as writing each of their spelling words in fancy, colourful writing three times. Writing their spelling words in alphabetical order, word disappear and reappear i.e. the word friend frien frie fri fr f Finding their spelling words in books, newspapers and magazines. Practice spelling words at home is a good way for family members to become involved and help students learn their words. By mixing up activities students learn their words in context and it motivates learning. Students are not just memorising how to spell their words which doesn’t work with all students and the ability to spell those words in context even if spelled correctly in the spelling test may be absent. Look for words within words i.e. capacity-city, it, cap. References NSW State Literacy and Numeracy Plan (2007). Writing and Spelling Strategies: Assisting students who have additional learning support needs. NSW Department of Education and Training. State Literacy Plan (2007). Programming and Strategies Handbook: Assisting year 3 and year 5 Students who need additional support in literacy. NSW Department of Education and Training. VCAA (2014). AusVELS Curriculum. Retrieved from http://ausvels.vcaa.vic.edu.au/ Winch, G., Ross Johnston, R., March, P., Ljungdahl, L., & Holliday, M. (2010). Literacy: reading, writing and children’s literature (4th ed.) South Melbourne, VIC: Oxford University Press. 4 Table 1. Individual Spelling Activities. 5