Third Grade Timeline - Airport Community Schools
advertisement

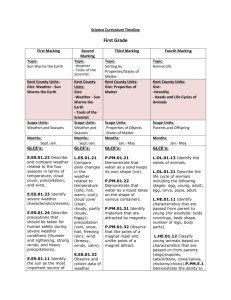
Science Curriculum Timeline Third Grade First Marking Topic: Life Science Second Marking Topic: Life Science Third Marking Topic: Earth Science Kent County Units: Gist: -Plants - Animals Kent County Units: Gist: -Animals - Adaptation Kent County Units: Gist: -Earth Materials - Surface Changes - Natural Resources Scope Units: -Plant Exploration -Animal Characteristics and Adaptations Scope Units: -Plant Exploration -Animal Characteristics and Adaptations Months: September, October, and November Months: November, December and January Scope Units: -Earth’s Surface -Using Natural Resources -Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle Months: GLCE’s: GLCE’s: January, February, and March GLCE’s: - Describe the function of the - Describe the function of the - Identify natural resources following plant parts: flower, following plant parts: flower, (metals, fuels, fresh water, soil, stem, root, and leaf. (L.OL.03.31) stem, root, and leaf. (L.OL.03.31) and forests). (E.ES.03.41) - Identify and compare structures in animals used for controlling body temperature, support, movement, food-getting, and protection (fur, wings, teeth, claws, scales). (L.OL.03.32) - Identify and compare structures in animals used for controlling body temperature, support, movement, food-getting, and protection (fur, wings, teeth, claws, scales). (L.OL.03.32) - Classify renewable (fresh water, forests) and nonrenewable (fuels, metals) resources. (E.ES.03.42) - Describe ways humans are protecting, extending and - Classify plants on the basis of - Classify plants on the basis of restoring resources (recycle, observable physical characteristics observable physical characteristics reuse, reduce, renewal). (roots, leaves, stems, and (roots, leaves, stems, and (E.ES.03.43) flowers). (L.OL.03.41) flowers). (L.OL.03.41) - Recognize that paper, metal, - Classify animals on the basis - Classify animals on the basis glass, and some plastics can be of observable physical of observable physical recycled. (E.ES.03.44) characteristics (backbone, body characteristics (backbone, body covering, limbs). (L.OL.03.42) covering, limbs). (L.OL.03.42) - Describe ways humans are dependent on the natural - Relate characteristics and - Relate characteristics and environment (forests, water, functions of observable parts in functions of observable parts in clean air, Earth materials) and Fourth Marking Topic: -Physical Science -Science Processes Kent County Units: Gist: - Force and Motion - Light and Sound - Measurement and Gravity Scope Units: -Light Energy -Sound Energy -Forces and Motion Months: March, April, and May GLCE’s: - Identify light and sound as forms of energy. (P.EN.03.11) - Demonstrate that light travels in a straight line and that shadows are made by placing an object in a path of light. (P.EN.03.21) - Describe what happens to light when it travels from water to air (a straw half in water and half in the air looks bent). (P.EN.03.22) - Relate sounds to their sources of vibrations (for example: a musical note produced by a vibrating guitar string, the sounds of a drum made by the vibrating drum head). (P.EN.03.31) a variety of plants that allow them to live in their environment (for example: leaf shape, thorns, odor, color). (L.EV.03.11) a variety of plants that allow them to live in their environment (for example: leaf shape, thorns, odor, color). (L.EV.03.11) constructed environments (homes, - Distinguish the effect of fast neighborhoods, shopping malls, or slow vibrations as pitch. factories, and industry). (P.EN.03.32) (E.ES.03.51) - Describe helpful or harmful - Relate characteristics and - Relate characteristics and effects of humans on the functions of observable body functions of observable body environment (garbage, habitat parts to the ability of animals to parts to the ability of animals to destruction, land management, live in their environment (for live in their environment (for renewable and non-renewable example: sharp teeth, claws, example: sharp teeth, claws, resources). (E.ES.03.52) odor, body coverings). odor, body coverings). (L.EV.03.12) (L.EV.03.12) - Recognize and describe different types of Earth materials (mineral, rock, clay, boulder, gravel, sand, soil). (E.SE.03.13) - Recognize that rocks are made up of minerals. (E.SE.03.14) - Identify and describe natural causes of change in the Earth’s surface (erosion, glaciers, volcanoes, landslides, and earthquakes). (E.SE.03.22) - Identify Earth materials used to construct some common objects (for example: bricks, buildings, roads, glass). (E.SE. 03.31) - Describe how materials taken from the Earth can be used as fuels for heating and transportation. (E.SE.03.32) - Demonstrate how some materials are heated more than others by light that shines on them. (P.PM.03.51) - Explain how we need light to see objects: light from a source reflects off objects and enters our eyes. (P.PM.03.52) - Identify the force that pulls objects towards the Earth. (P.FM.03.22) - Describe how a push or a pull is a force. (P.FM.03.35) - Relate a change in motion of an object to the force that caused the change in motion. (P.FM.03.36) - Demonstrate how the change in motion of an object is related to the strength of the force acting upon the object and to the weight of the object. (P.FM.03.37) - Demonstrate when an object does not move in response to a force, it is because another force is acting on it. (P.FM.03.38) - Describe the motion of objects in terms of the path and direction. (P.FM.03.41) - Identify changes in motion (change direction, speeding up, slowing down). (P.FM.03.42) - Relate the speed of an object to the distance it travels in standard amount of time. (P.FM.03.43) Kent County Vocabulary: Kent County Vocabulary: Kent County Vocabulary: Kent County Vocabulary: Prerequisite Vocabulary: air compare leaf (plural leaves) plant centimeter flower leaf shape seed characteristic flowering plant light survive classify fruit living temperature color investigation observation water (See Animal Vocabulary from First Quarter) Prerequisite Vocabulary: Prerequisite Vocabulary: Prerequisite Vocabulary: animal color leaf shape size body covering compare observation survive characteristic flower plant temperature classify fruit seed Earth Materials: Earth materials physical property sand sort fresh water rock soil texture Force and Motion: above between object slower away from direction position speed behind faster pull toward below mass push New Vocabulary: function physical characteristic structure survival of organism minerals plant root support thermometer organism stem Enrichment Vocabulary: branching root habitat pollinators New Vocabulary: animal features food getting physical characteristic survival of organism claws odor protection thorns environment organism structure Surface Changes: hill rain snow valley ice river soil water mountain rock surface wind precipitation Natural Resources: Earth materials fresh water water New Vocabulary: Enrichment Vocabulary: animal adaptations growth mimicry prey Earth Materials: boulder crude oil metal oil Light and Sound: color light sound Measurement and Gravity: balance investigation meter (m) temperature centimeter (cm) length observation tool compare measure pull volume trunk broad-leafed plants living organism sapling woody stems evergreen tap root pollination camouflage habitat omnivore producer consumer herbivore plant adaptations protective adaptations decomposer interdependence predator reproduction environmental change migration clay fuel minerals soil color coal gravel natural gas soil texture Surface Changes: change in Earth's surface glacier landslide volcano earthquake harmful change rock breakage weathered rock erosion helpful change volcanic eruption weathering Natural Resources: cause and effect habitat metal recycle constructed environment habitat destruction minerals reduce environment harmful change natural environment renewable resource forest helpful change natural resource renewal fuel land management nonrenewable resource reuse garbage data measurement push New Vocabulary: Force and Motion: around force path stop cause and effect force strength slowing down through change in motion gravity speeding up weight change of direction motion start Light and Sound: absorption light source reflection thermometer energy path of light shadow vibrations forms of energy pitch sound source Measurement and Gravity: clock with a second hand gravity measuring tape stopwatch contrast hour minute timer force Enrichment Vocabulary: Earth Materials: brick gasoline natural resource pebble building glass nutrients roads Earth materials' ability to hold water heating ore silt farmland loam particle size transportation fossil fuel manufactured Surface Changes: Earth materials' ability to hold water magma rock cycle silt fault molten rock rock layer solid rock gully particle size sand dune water cycle lava Natural Resources: building materials drinking water fossil fuels preservation compost farmland pollution kilometer (km) second weight Enrichment Vocabulary: Force and Motion: block and tackle inclined plane north up change of speed left pulley wedge complex machine lever relative position west down machine right wheel and axle east measurement of motion screw work friction Newton simple machine work fulcrum Newtons South Light and Sound: auditory nerve eye opaque transmit bright guitar optic nerve transparent dim heat sustainability conservation reflex tuning fork drumhead intensity refract volume (sound) ear light rays translucent white light eardrum Measurement and Gravity: cause and effect graduated cylinder metric measurement scientific method conclusion graph procedure table (data) control hypothesis purpose theory design inference scientific experiment thermometer generalization journal scientific law variable Scope Vocabulary: air animal features color plant backbone/no backbone environment nutrients organism plant root flowers stem leaf survival of organisms Scope Vocabulary: air animal features color plant backbone/no backbone environment nutrients organism plant root flowers stem leaf survival of organisms Scope Vocabulary: Scope Vocabulary: boulder Earth materials rock clay sand gravel soil soil texture soil color water wind Iie helpful change force force strength push pull gravity weight motion position speed speeding up slowing down faster slower temperature Celsius thermometer centimeter support movement food getting protection structure function physical characteristics compare classify temperature Celsius thermometer centimeter support movement food getting protection structure function physical characteristics compare classify changes in the Earth’s surface harmful change earthquake erosion landslide glacier metal mineral oil stop start change of motion change of direction moving away from toward around above below behind between through centimeters meters kilometers seconds minutes hours compare and contrast cause stop watches timers clocks with a second hand meter sticks rulers measuring tapes light path of light sound sound source light source forms of energy vibrations thermometer degrees Celsius light absorption light reflection shadow pitch sun as a source of energy effect Trade Books: Trade Books: Trade Books: Trade Books: Aloian, Molly. Wetland Habitats. Aloian, Molly. Wetland Habitats. Cole, Joanna. The Magic School Bus: Inside the Bailey, Gerry. Light and Color: Discover New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2007. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2007. Kalman, Bobbie. The ABC’s of Animals. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2008. Kalman, Bobbie. The ABC’s of Animals. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2008. ---. Animals Called Mammals. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2005. ---. Animals Called Mammals. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2005. ---. Animals Without Backbones. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2009. ---. Animals Without Backbones. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2009. ---. Camouflage: Changing to Hide. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2005. ---. Camouflage: Changing to Hide. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2005. Morganelli, Adrianna. Minerals. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2004. ---. How Do Animals Find Food? New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2001. ---. How Do Animals Find Food? New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2001. Morris, Neil. Rocks and Minerals. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 1998. ---. Land Habitats. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2007. ---. Land Habitats. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2007. ---. What are Camouflage and Mimicry? New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2001. ---. What are Camouflage and Mimicry? New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2001. ---. What is a Mammal? New York: Crabtree Publishing, 1998. ---. What is a Mammal? New York: Crabtree Publishing, 1998. ---. What is a Vertebrate? New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2008. ---. What is a Vertebrate? New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2008. Rauzon, Mark. Feet, Flippers, Hooves, and Hands. New York: Lothrop, Lee, and Shepard, 1994. Rauzon, Mark. Feet, Flippers, Hooves, and Hands. New York: Lothrop, Lee, and Shepard, 1994. Earth. New York: Scholastic, 1996. Kalman, Bobbie. Volcanoes on Earth. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2008. ---. What Shapes the Land? New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2009. Malin, Stuart. Story of the Earth. Mahwah, NJ: Troll Associates, 1991. Parker, Steve. Rocks and Minerals. New York: Dorling Kindersley Publishing, 1997. Bang, Molly Garrett. Common Ground: The Water, Earth, and Air We Share. New York: Scholastic, 1997. Lauber, Patricia. Be a Friend to Trees. New York: HarperCollins, 1994. Bang, Molly Garrett. Common Ground: The Water, Earth, and Air We Share. New York: Scholastic, 1997. Science Through Facts and Fun. Strongsville, OH: Gareth Stevens Publishing, 2008. Broekel, Ray. Experiments with Light. New York: Children’s Press, 1986. Cooper, Jason. Science Secrets: LIGHT. Vero Beach, FL: Rourke Corporation, 1992. Davies, Kay, and Wendy Oldfield. Light. Austin, TX: Steck-Vaughn Library, 1992. Gardner, Robert. Experiments with Light and Mirrors. Berkeley, NJ: Enslow Publishers, 2006. Hewitt, Sally. Amazing Light. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2008. Johnstone, Leslie, and Shar Levine. The Optics Book of Fun Experiments with Light, Vision, and Color. New York: Sterling Publishing Company, 1998. Lauw, Darlene. Light. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2002. Lynette, Rachel. Experiments with Light. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann, 2008. Lauber, Patricia. Be a Friend to Trees. New York: HarperCollins, 1994. ---. Horns, Antlers, Fangs, and Tusks. New York: Lothrop, Lee, and Shepard, 1993. ---. Horns, Antlers, Fangs, and Tusks. New York: Lothrop, Lee, and Shepard, 1993. ---. Skin, Scales, Feathers, and Fur. New York: Lothrop, Lee, and Shepard, 1993. ---. Skin, Scales, Feathers, and Fur. New York: Lothrop, Lee, and Shepard, 1993. Walker, Niki. How Do Animals Move? New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2000. Walker, Niki. How Do Animals Move? New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2000. Heller, Ruth. The Reason for a Flower. New York: Penguin Putnam Publishing Group, 1999. Heller, Ruth. The Reason for a Flower. New York: Penguin Putnam Publishing Group, 1999. ---. Your Local Environment (Green Team). New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2008. Pallotta, Jerry. The Flower Alphabet Book. Watertown, MA: Charlesbridge, 1998. Pallotta, Jerry. The Flower Alphabet Book. Watertown, MA: Charlesbridge, 1998. Robinson, Fay. Recycle That. Danbury, CT: Grolier Publications, 1995. Technology: Technology: Lab Kits: Lab Kits: Hewitt, Sally. Reduce and Reuse (Green Team). New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2008. ---. Waste and Recycling (Green Team). New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2008. Suid, Annalisa. Learn to Recycle. Palo Alto, CA: Monday Morning Press, 1993. Williams, Rozanne, and Neena Chawla. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle. Fresno, CA: Creative Teaching Press, 1995. Technology: Lab Kits: Rosinsky. Light: Shadows, Mirrors, and Rainbows. Mankato, MN: Picture Window Books, 2004. Taylor, Barbara. Light, Color, and Art Activities. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2002. Cole, Joanna. Magic School Bus in the Haunted Museum: A Book About Sound. New York: Scholastic, 1995. A First Look: Sound. Cochran. 2001. Discovery Education. 15 July 2009 Hewitt, Sally. Amazing Sound. New York: Crabtree Publishing, 2008. Martin, Bill. Polar Bear, Polar Bear, What Do You Hear? New York: Henry Holt Company, 1997. Pfeffer, Wendy. Sounds All Around. New York: HarperCollins, 1999. Seuss, Dr. Mr. Brown Can Moo! Can You? Dr. Seuss’s Book of Wonderful Noises. New York: Random House, 1987. Cole, Joanna. The Magic School Bus Plays Ball: A Book About Forces. New York: Scholastic, 1998. DePinna, Simon. Forces and Motion. Austin, TX: Raintree/SteckVaughn, 1998. Hockett, Ad. Red Herrings Science Mysteries. Pacific Grove, CA: Critical Thinking Books, 1996. Marshall, John. Motion and Speed. Vero Beach, FL: Rourke Book Company, 1995. Oxlade, Chris. Science Magic with Forces. New York: Barrons Educational Series, 1995. Riley, Peter. Forces and Movement. New York: Franklin Watts, 1998. Technology: Lab Kits: