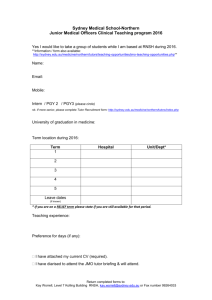
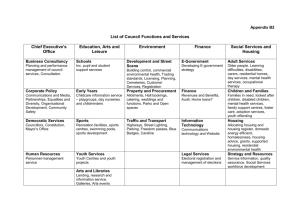
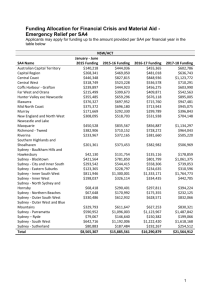
Dominance and dependence

The relationship of dominance and dependence could be said to belong to the interaction between world cities and the other urban centres in proximity to them. World cities, whether they be characterised as dominant, major or secondary, are sites of world accumulation.
Technological dominance and innovation.
Financial dominance in the production and distribution of goods and services on a global scale.
The cultural influence that arises from world cities is widespread, as is the level of strategic decision making.
Urban centres on the other hand, have functions that show dependence on the world cities.
Accumulation and the production and distribution is only on the national scale.
Technology is often adopted, as there is a relatively lower degree of research and development.
A limited cultural influence with some political control.
Eg Perth’s financial system is dependent on Sydney Head Offices.
The hierarchy of world cities indicates that there is a level of dominance emulating from New York, London, Paris and Tokyo over the other world cities.
They have a disproportionate concentration of top-level headquarters of the financial, industrial, commercial and producer service sectors. large industrial TNCs that account for nearly 70% of the international trade are headquartered in these cities.
The massive expansion of the global financial industry over the last 20 years has greatly increased the global significance of London, New York and Tokyo. The main financial transactions in shares, bonds, loans and foreign currency are dominated by these three cities. Together with Los Angeles, Frankfurt and
Hong Kong they provide a 24-hours-a-day global coverage of financial transactions.
Dominance and dependence also exists between world cities and other urban centres. An example of this is Sydney’s role in contrast to the other Australian cities. Sydney, as a major world city has 27 head office locations for Australia’s
50 largest corporations. Melbourne comprises 16 of these, while Brisbane,
Perth and Adelaide have less than three in their respective cities. Sydney is the
principal centre for smaller, Australian-controlled businesses. Nearly half of these have grown through national mergers and takeovers. Sydney is the principal financial centre as countries like Japan prefer to locate trading, marketing and financial companies there. Although Melbourne dominates in the areas of manufacturing and mining, Sydney is the dominant link to the global economy as it represents a more recent period of capital accumulation associated with economic globalisation, especially in the financial sector.
The other urban centres that are also state capitals only play minor roles in national production let alone global accumulation. Cities like Brisbane, Darwin,
Adelaide, Hobart, and Perth have functions that have been largely absorbed into
Sydney and to a lesser extent Melbourne through corporate takeovers. These urban centres operate at an intrastate level of networking within Australia’s federal administrative structure. Further dominance would be exerted from
Sydney over nearby urban centres like Newcastle and Wollongong. These relationships of dominance and dependence occur on a global scale and these roles are even more pronounced when the country has a greater number of urban centres and world cities that surround a dominant world city.
The United States presents clear trends of dominance and dependence whereby
New York, with a group of world cities dependent on it, especially for financial transactions. Major world cities include Chicago, San Francisco, Miami, Boston and Los Angeles. Clustered around these world cities are the urban centres that have dependent relationships with their nearby world cities.
Chicago, dependent urban places in close proximity include Minneapolis,
Milwaukee, Indianapolis, St. Louis and Kansas City.
The United Kingdom: London acts as a centre of dependence for other major cities across the nation especially for financial transactions. Cities such as
Birmingham, Newcastle and Manchester rely on London for a variety of needs and allow them to subsequently be linked into the global network. Clustered around these major cities are the urban centers that have dependent relationship with their closest major city. Eg Manchester - dependent urban places in close proximity include Liverpool, Chester, Preston and Stockport.
Rural trends There have been changes in the relative significance of settlements in rural areas at a regional and local level. Overall, countries like Canada, the
United States and Australia have witnessed the growth of regional centres with a corresponding decline in population and economic activity throughout the surrounding small towns. Urban systems / metropolitan areas Urban systems comprise of the national city (eg. Sydney, Brisbane and Melbourne) that have a complex set of functions. These include wholesaling, retailing, manufacturing, finance and corporate management, education, entertainment and health services. Metropolitan areas perform these functions for smaller urban places and rural areas in their general vicinity. These metropolitan hinterlands vary greatly in size and shape depending on the type of services provided.