Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry Practice Test Answer Section
advertisement

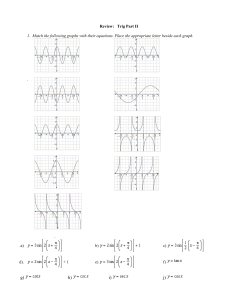
Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. What does the 4 in represent? a. the mass number b. the atomic number c. the number of protons d. the number of neutrons 2. What does the 101 in a. the mass number b. the atomic number c. the nuclide number d. the number of neutrons represent? 3. Balance the following equation: ____ a. c. b. d. 4. Balance the following equation: a. b. ____ + c. d. ____ 5. The spontaneous disintegration of a nucleus into a slightly lighter and more stable nucleus, accompanied by emission of particles, electromagnetic radiation, or both, is a. nuclear fusion. c. radioactive decay. b. nuclear radiation. d. nuclear fission. ____ 6. Which of the following forms of radiation has the greatest penetrating power? a. alpha particles c. gamma rays b. beta particles d. positrons ____ 7. Alpha particles are a. electrons. b. helium nuclei. c. electromagnetic waves. d. neutrons. 8. Beta particles are a. electrons. b. helium nuclei. c. electromagnetic waves. d. neutrons. ____ ____ 9. Which of the illustrations below represents a fission reaction? a. A b. B c. C d. D ____ 10. The energy as heat produced by a reactor is used to a. boil water for steam turbines. c. produce graphite. b. melt metal. d. produce coal. ____ 11. At present, fusion reactions a. cannot be used to produce energy in reactors. b. produce the energy in some nuclear power plants. c. produce the energy in most nuclear power plants. d. produce the energy in all recent nuclear power plants. ____ 12. What is the product of -ray emission from a radioactive isotope of lead? a. Thallium c. Bismuth b. Mercury d. Lead ____ 13. What is the reason for the decay of naturally radioactive elements? a. To reduce the number of neutrons as the elements lie above the band of stability. b. To reduce the number of protons as the elements lie below the band of stability. c. To reduce the number of either neutrons or protons to lie in the band of stability. d. To release the energy from nucleus in the form of gamma radiation. ____ 14. How does a positron differ from an electron? a. A positron has no electrical charge, unlike an electron. b. A positron has a charge opposite that of an electron. c. A positron has less mass than an electron. d. A positron has greater mass than an electron. ____ 15. What is the main product of the fusion reactions in our sun? a. b. c. d. hydrogen-2 hydrogen-3 helium-3 helium-4 ____ 16. What is the product of this radioactive decay? Mn ____ + e a. Co b. Mn c. Fe d. Cr ____ 17. A transmutation reaction must always involve a(n) ____. a. change in the number of electrons in the atom b. decrease in the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom c. increase in the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom d. change in the number of protons in a nucleus of an atom ____ 18. A reaction in which small nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus is a ____. a. fission reaction b. chemical reaction c. background reaction d. fusion reaction Short Answer 19. Calculate the remaining amount of 100.0 grams of cobalt-60 after 1600 years. The half life of cobalt-60 is 5272 years. 20. If the half-life of sodium-24 is 15 hours, how much remains from a 10.0-g sample after 60 hours? Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry Practice Test Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: I REF: 1 OBJ: 1 STA: SC.A.2.4.3 2. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: I REF: 1 OBJ: 1 STA: SC.A.2.4.3 3. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: II REF: 1 OBJ: 4 STA: SC.A.2.4.3 4. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: II REF: 1 OBJ: 4 STA: SC.A.2.4.3 5. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: I REF: 2 OBJ: 1 STA: SC.A.2.4.3 | SC.C.2.4.4 6. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: I REF: 2 OBJ: 2 STA: SC.A.2.4.3 7. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: I REF: 2 OBJ: 2 STA: SC.A.2.4.3 8. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: I REF: 2 OBJ: 2 STA: SC.A.2.4.3 9. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: II REF: 4 OBJ: 1 STA: SC.A.2.4.3 | SC.A.2.4.4 | SC.C.2.4.4 10. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: I REF: 4 OBJ: 2 STA: SC.B.1.4.5 11. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: I REF: 4 OBJ: 3 STA: SC.A.2.4.4 | SC.B.1.4.5 12. ANS: C On emission of beta radiation, the atomic number of the product will increase by one, and Bismuth-83 will be formed. Feedback A B C D The atomic number of thallium is one less than lead, which should have been one more after the beta radiation. Mercury is the product of an alpha emission. Correct! After beta radiation, the product will be different from the parent element. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1|DOK 1 NAT: B.2 | B.6 STA: SC.A.2.4.3 TOP: Identify alpha, beta, and gamma radiation in terms of composition and key properties. KEY: Radioactive isotope MSC: 2 13. ANS: C A radioisotope with an atomic number above 83 attains stability by reducing the number of either neutrons or protons, thereby positioning the element within the band of stability. Feedback A B C D 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. A reduction in the number of neutrons alone will not give stability to any atom with atomic number above 83. A reduction in the number of protons alone will not give stability to any element having atomic number above 83. Correct! Gamma emission will not bring an element with atomic number above 83 to the band of stability. PTS: STA: KEY: ANS: OBJ: STA: ANS: OBJ: STA: ANS: OBJ: STA: ANS: OBJ: MSC: ANS: OBJ: STA: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2|DOK 1 NAT: UCP.3 | B.1 SC.A.2.4.3 TOP: Apply your knowledge of radioactive decay to write balanced nuclear equations. Radioactive decay MSC: 2 B PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 881 25.2.1 Describe the type of decay a radioisotope undergoes. SC.912.P.10.11 | SC.912.P.10.12 MSC: knowledge D PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 891 25.3.3 Distinguish fission reactions from fusion reactions. SC.912.P.10.11 | SC.912.P.10.12 | LA.910.2.2.3 MSC: knowledge C PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 878 25.1.2 Describe the three main types of nuclear radiation. SC.912.P.10.11 | SC.912.P.10.12 MSC: application D PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 885 25.2.3 Identify the two ways transmutations can occur. STA: SC.912.P.10.11 | SC.912.P.10.12 comprehension D PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 891 25.3.3 Distinguish fission reactions from fusion reactions. SC.912.P.10.11 | SC.912.P.10.12 | LA.910.2.2.3 MSC: knowledge SHORT ANSWER 19. ANS: 81.03 grams PTS: 1 STA: SC.C.2.4.4 20. ANS: 0.63 g DIF: Bloom's Level 3|DOK 2 PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: p. 883 OBJ: 25.2.2 Solve problems that involve half-life. MSC: analysis NAT: UCP.3 | E.2 STA: SC.912.P.10.11 | SC.912.P.10.12