Earth Science Reference Table pg. 12 and 13
advertisement

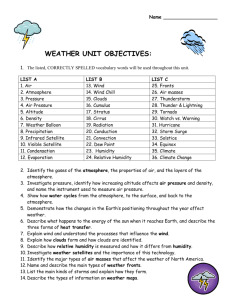
CURRICULUM TOOL: METEOROLOGY WEATHER VARIABLES NYS Earth Science Core Curriculum Performance Indicator 2.1 Use the concepts of density and heat energy to explain observations of weather patterns, seasonal changes, and the movements of Earth’s plates. 2.1b The transfer of heat energy within the atmosphere, the hydrosphere, and Earth’s interior results in the formation of regions of different densities. These density differences result in motion. 2.1c Weather patterns become evident when weather variables are observed, measured, and recorded. These variables include air temperature, air pressure, moisture (relative humidity and dewpoint), precipitation (rain, snow, hail, sleet, etc.), wind speed and direction, and cloud cover. 2.1d Weather variables are measured using instruments such as thermometers, barometers, psychrometers, precipitation gauges, anemometers, and wind vanes. 2.1e Weather variables are interrelated. For example: • temperature and humidity affect air pressure and probability of precipitation • air pressure gradient controls wind velocity 2.1f Air temperature, dewpoint, cloud formation, and precipitation are affected by the expansion and contraction of air due to vertical atmospheric movement. Performance Indicator 2.2 Explain how incoming solar radiation, ocean currents, and land masses affect weather and climate. 2.2d Temperature and precipitation patterns are altered by: • natural events such as El Niño and volcanic eruptions • human influences including deforestation, urbanization, and the production of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. Some Past Part A Questions 1. Which weather variable generally decreases when wind speed is increasing, clouds are thickening, and visibility drops? (1) relative humidity (3) precipitation (2) dewpoint (4) air pressure High School of Language and Innovation 2012 (draft) Curriculum-Based Questions How are each of the weather variables measured? How do high and low pressure systems compare? How do weather variables influence weather patterns? What is the relationship between relative humidity, dewpoint, and condensation? How does the expansion and contraction of air due to vertical atmospheric movement affect air temperature, dewpoint, cloud formation, and precipitation? Complete one Weather Variable activity from the green Meteorology binder. Earth Science Reference Table pg. 12 and 13 Some Past Part B-1, B-2, C Questions January 2013 Question 41-43, 74-77 August 2012 Question 47 June 2012 Questions 83 *Released Regents Tests: http://www.nysedregents.org/earthscience/ CURRICULUM TOOL: METEOROLOGY WEATHER VARIABLES 2. The diagram to the right shows a weather instrument found at most weather stations. The main function of this instrument is to measure which variable? (1) wind speed (3) air pressure (2) wind direction (4) relative humidity 3. What is the approximate dewpoint temperature if the dry-bulb temperature is 10°C and the wet-bulb temperature is 8°C? (1) 1°C (3) 6°C (2) -13°C (4) 3°C Resources for Learning Readings Websites Videos Holt (yellow book) pg. 550-551 (pressure), 577-580 (humidity), 581-583 (clouds), 587-590 (precipitation), 611-612 (measurement) Meteorology: Weather Variables http://hmxearthscience.com/weather_variables.html Atmospheric Science http://weather.about.com/od/weathertutorials/u/atm ospherebasics.htm Atmospheric Pressure http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Atmosphere/ atm_press.html Weather http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Atmosphere/ atm_press.html Wind http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Atmosphere/ wind.html Regents Review Materials http://reviewearthscience.com/ http://regentsearth.com/ How do Clouds Form? http://video.about.com/weather/How-Do-Clouds-Form.htm#vdTrn Relative Humidity and Dewpoint http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5EbDKEAy5tw&feature=plcp Weather Relationships http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PssZKFILOeM&feature=plcp Air Pressure http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LYeQLA1eI0s&feature=plcp Glencoe (big blue book) pg. 285-286 (clouds), 310-313 (pressure) McGuire (little blue book) pg. 439-450, 476-486 (humidity), 486-488 (clouds) Unison Reading Binder: Meteorology At home: Weather Instruments http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JNQoBWHlJbU&list=UUrh1E Zmf6fLmpKqsDyWg4HA&index=10 Pressure Demos http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m1jmpGZUEJA&list=UUrh1E Zmf6fLmpKqsDyWg4HA&index=3 Foreign Language: Sling Pschrometer Aire en Movimiento http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QbcaCxuA1LI&list=UUrh1EZ http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Atmosphere/ mf6fLmpKqsDyWg4HA&index=4 wind.html&lang=sp High School of Language and Innovation 2012 (draft) In-Class Activities Meteorology Binder Weather Variable Vocabulary Weather Instrument Memory CURRICULUM TOOL: METEOROLOGY WEATHER VARIABLES High School of Language and Innovation 2012 (draft)