Electron - Wyckoff School District
advertisement
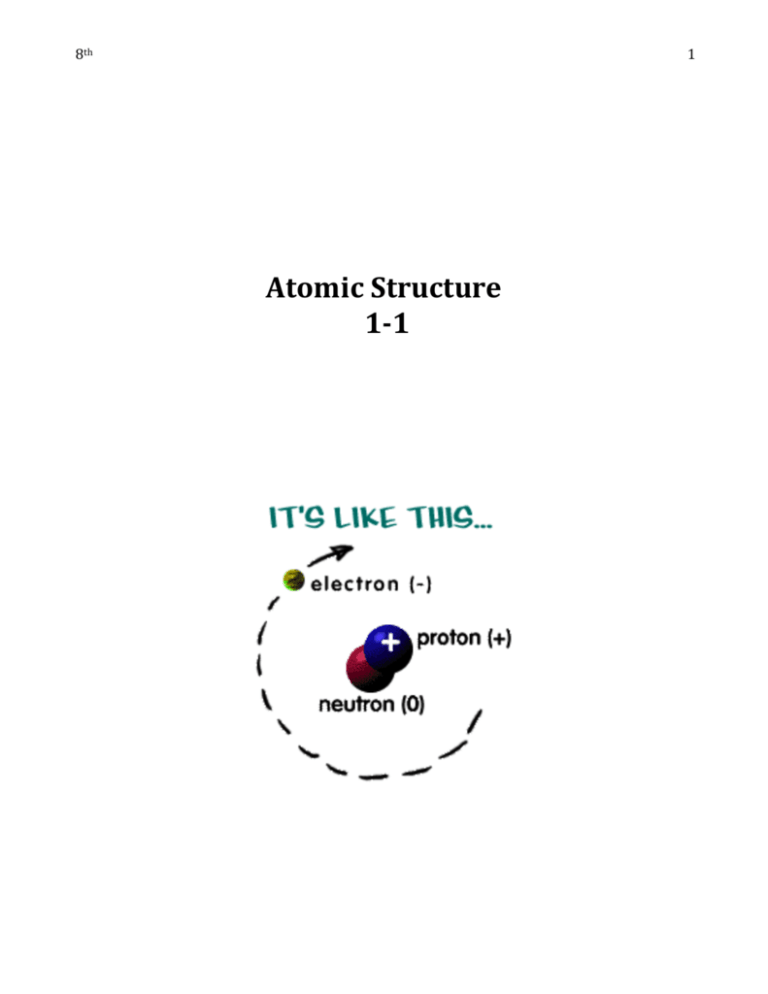
1 8th Atomic Structure 1-1 Date 2 Atomic Theory and Organizing the Elements What you need to know: Atoms are the smallest complete particle of matter. Atoms have central core called the nucleus. The atomic nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive charge (+). Neutrons have a neutral charge (0). Neutrons and protons are made of smaller particles called quarks. A cloud of electrons surrounds the nucleus. Electrons have a negative charge (-). Elements can be arranged in a periodic table based on atomic number. Elements in a column (group or family) have similar properties The three main types of elements are metals, metalloids, and nonmetals. Nuclear reactions involve changes in the nucleus. Modern Atomic Theory 1. Atoms are the smallest complete unit of matter. 2. Atoms can be broken down into three main component particles: electrons, protons, and neutrons. Protons and neutrons can be further broken down into quarks. 3. In any element, all the atoms have the same number of protons. Atoms with a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. 4. Atoms of different elements are different. 5. Atoms of two or more elements can combine to form compounds. 6. The average atomic weight (mass) of an element reflects the average of all its isotopic forms, but is unique to the element. 7. Atoms of elements in a compound combine in a constant ratio. Date 3 A Brief History of Modern Atomic Theory Early 1800’s John Dalton reviews research of other scientists and proposes the theory that all matter is composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 1897 Joseph John (J.J.) Thomson discovers the electron, a negative subatomic particle. 1909 Ernest Rutherford discovers that most of the volume of the atom is empty space. 1915 Niels Bohr proposes a model of the atom in which electrons move in orbitals around a dense core called the nucleus. 1919 Ernest Rutherford discovers the proton, a positive subatomic particle. 1932 James Chadwick discovers the neutron, a neutral subatomic particle. 1935 Hideki Yukawa proposes the idea that neutrons and protons are composed of smaller particles. 1973 Murray Gell-Mann leads the development of the quark theory that explains the charges of protons and neutrons. Chemist Facebook Page Project Total 30 Points: Directions: Together we will put together a history of chemist time line, starting with the discovery of the atom. You will be working by your self to complete this project. Use the internet to research information about your chemist. Below are the Criteria for Your Chemist Facebook Page. Fill out the graphic organizer below before you move on to the LARGE FACEBOOK PAGE!! 1. Information that must be on the page (10 points) Date of Discovery _____________ Full Name of Scientist:________________________________ Nickname if they had one___________________ Born __________________ Where they lived for the majority of their Life:____________________________ Education (college, high school, grade school?) ____________________ Died: ____________________ Date 4 Discoveries major discoveries: _______________________________________ Hobbies or Interests___________________ Books written, if any _________________________ 2. Pictures (10 points) -Pictures of your chemists -Picture of his discoveries or books written 3. Neatness (10 points) - color information written or typed neatly creative presentation Date 5 Structure of the Atom Definitions Nucleus central core of the atom composed of protons and usually neutrons Proton a small particle in the nucleus of the atom with a positive charge Neutron a small particle in the nucleus of the atom with no electrical charge Orbital energy shell around the nucleus where electrons are found Electron a tiny particle with a negative charge that moves around the nucleus of an atom Valence the outer orbital of an atom; valence electrons are the farthest from the nucleus and are involved in chemical reactions between atoms How many protons are in the atom shown above? How many neutrons are in the atom shown above? How many electrons are in the atom shown above? Complete the Statement: An atom has a neutral charge when the number of electrons is the same as the number of . NOTE: Only two electrons may occupy the first orbital. Date Structure of the Atom 6 Definitions Atomic number the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Atomic mass the average mass of one atom of an element Atomic mass unit a unit used to measure the mass of particles in atoms; the proton and neutron each have a mass of 1 amu; an electron has a mass of 1/2000 amu Atomic mass number the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus Isotope atoms with the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons and different atomic mass number Use the definitions to follow the instructions. The dotted lines represent electron orbitals. The shaded center circle represents the nucleus. Fill in 4 protons, 5 neutrons, and 4 orbital electrons for element 4 of the periodic table. Show the charges for the protons and electrons. If the atomic number is the number of protons, what is the atomic number of this element? _____________ If the atomic mass number is the total of the number of protons and number of neutrons, what is the atomic mass number of this element? _________________ Isotopes have the same number of protons and different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass of element 4 Is 9.012 amu. Does this element have isotopes? ______________ Date Structure of the Atom Word Bank (use as often as needed) 1 amu positive about 1/2000 amu neutral Part of the Atom 7 Mass negative Charge inside the nucleus outside the nucleus Location Electron Proton Neutron Check Your Understanding Atom A has ____ protons, ___ neutrons, and ____ Atom B has ____ protons, ___ neutrons, and electrons. ____ electrons. The atomic number is _____. The atomic number is _____. The atomic mass number is ______. The atomic mass number is _____. The outermost ring of electrons is called the valence. The electrons are called the valence electrons. Filling Rules for Orbitals 1-3 Period Number of Maximum Number (Row) Orbitals of Electrons 1 1 2 2 2 2, 8 3 3 2, 8, 8 NOTE: Rules for filling orbitals after 3 are more complicated, especially the transition metal elements. In general, the last orbital, or valence, may never have more than 8 electrons. Date 8 IONS Directions: use the word box to fill out the following information about ions. Cross out the word once you use it. You can use a word more then once. Electrons Negative Electron Positive Ion (Net Lost Charge) Gained Positive Negative In a neutral atom the # number of protons = the # of ________________________ The ________________________ charges of the protons and the negative charges of the ________________equal each other for a net charge of zero. A ______________________ is an atom that has gained or lost __________________________________ Ions have a ______________ ____________________, either positive or negative. Why aren’t protons lost or gained?








