Mr. Brascia Semester II Exam Review Poster: Biology 1
advertisement

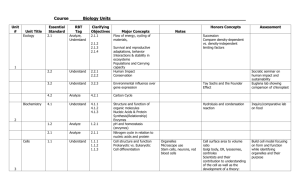
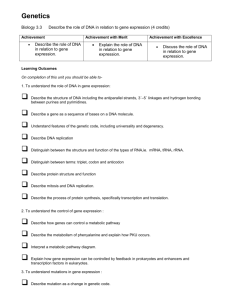
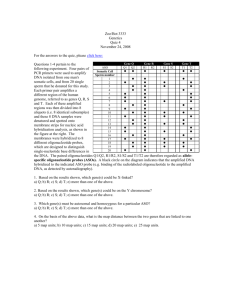
Name: __________________________ Pd: ___ Mr. Brascia Semester II Exam Review Poster: Due: _______ Biology 1 Procedure 1. Using two pieces of blank typing paper, divide your papers into six parts by folding the paper or drawing on it. You may use both sides of the paper. 2. Label the divided areas according to the units given below. 3. Then place your answers to those questions within the proper divided section of your poster. - Be sure that your answers are in complete sentences and numbered. 4. This activity is due the day of your Semester Exam and is your final grade for the fourth quarter, worth 50 points. You will be able to use it for the exam. Chapter 10: DNA 1. What is the purpose of DNA? 2. Where is it found? 3. What is its structure? 4. Draw and label a nucleotide. 5. Explain complementary base pairing. 6. Explain protein synthesis. Chapter 11: 1. Explain why cells regulate gene expression. 2. Discuss the role of operons in prokaryotic gene expression. 3. Determine how repressor proteins and inducers affect transcription in prokaryotes. 4. Describe the structure of a eukaryotic gene. 5. Compare the two ways gene expression is controlled in eukaryotes. Chapter 12: 1. Distinguish between sex chromosomes and autosomes. 2. Explain the role of sex chromosomes in sex determination. 3. Describe how an X- or Y-linked gene affects the inheritance of traits. 4. Explain the effect of crossing-over on the inheritance of genes in linkage groups. 5. Distinguish between chromosome mutations and gene mutations. Chapter 13: 1. Explain the significance of noncoding DNA to DNA identification. 2. Describe four major steps commonly used in DNA identification. 3. Explain the use of restriction enzymes, cloning vectors, and probes in making recombinant DNA. 4. Summarize several applications of DNA identification. Chapter 14-15: Evolution 1. How old is the earth? What evidence is used to determine the age of rocks and fossils? 2. Define radiometric dating and half-life. 3. Describe the Miller-Urey experiment: what was its purpose and what did it show? 4. What were the earliest cells like? (pro- or eukaryotic, autotrophs or heterotrophs) 5. Define “uniformitarianism”, whose theory it was, and explain how it relates to evolution. 6. What is “inheritance of acquired characteristics”, whose idea was it, and how is it wrong? 7. Where did Darwin travel and how? 8. List and describe the 4 parts of Natural Selection 9. Contrast “Evolution” with “Natural Selection” 10. What lines of evidence support the Theory of Evolution? 11. Define and contrast analogous and homologous structures. 12. What are vestigial structures (and give examples)? 13. Contrast gradualism and punctuated equilibrium. 14. What is coevolution and when does it occur? Chapter 16-17 1. Identify/explain traits that vary in populations and that may be studied and the importance of the bell curve to population genetics. 2. Compare three causes of genetic variation in a population and calculate allele frequency and phenotype frequency/ explain Hardy-Weinberg-equilibrium. 3. Relate biodiversity to biological classification. 4. Explain why naturalists replaced Aristotle’s classification system. 5. Identify the main criterion that Linnaeus used to classify organisms. 6. List the common levels of modern classification from general to specific. Chapter 18-21: Ecology 1. Sketch and label the following cycles: a. Carbon b. Nitrogen c. Water 2. Explain a food chain and how it is different from a food web. 3. Draw an energy transfer diagram and label the different trophic levels 4. What are the differences between producers and consumers? 5. Create and fill in a table to organize information about relationships between organisms. 6. Compare and contrast primary and secondary succession. 7. What are the 8 major biomes and what are their characteristics? 8. Explain differences between photic zone and aphotic zone of aquatic ecosystems. Chapter 45: 1. Describe four types of tissues that make up the human body. 2. Explain how tissues, organs, and organ systems are organized. 3. Summarize the functions of the primary organ systems in the human body. 4. Identify the five human body cavities and the organs that each contains. Chapter 46: 1. Describe the structure and function of the human heart. 2. Trace the flow of blood through the heart and body. 3. Distinguish between arteries, veins, and capillaries in terms of their structure and function. 4. Distinguish between pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation. Chapter 47: 1. Describe how the skin and mucous membranes protect the body against pathogens. 2. Describe the steps of the inflammatory response. 3. Analyze the roles of white blood cells in fighting pathogens. 4. Explain the functions of fever and proteins in fighting pathogens. Chapter 48: 1. Relate the role of each of the six classes of nutrients in maintaining a healthy body. 2. Describe each of the parts of the USDA Food Guide Pyramid. 3. Identify foods containing each of the organic nutrients. 4. Explain the importance of vitamins, minerals, and water in maintaining the body’s functions. 5. Identify three disorders associated with improper nutrition. Chapter 49: 1. Describe the structure of a neuron. 2. Summarize the electrical and chemical conditions that characterize a resting potential. 3. Outline the electrical and chemical changes that occur during an action potential. 4. Explain the role of neurotransmitters in transmitting a signal across a synapse. Good Luck on Your Final Exams! Be life-long learners, don’t procrastinate or wait until it’s too late for anything!!! Use this class and your experiences this year as a reference guide to build upon, help make decisions, what to do and what not to do. Create and compose from the good things, learn from the bad things don’t repeat the same mistakes; and always remember…THINK---DO---SUCCEED. Congratulations on the completion of one year of Biology I!