AY 2013-2014 (doc)
advertisement

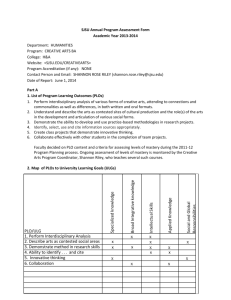
SJSU Annual Program Assessment Form Academic Year 2013-2014 Department: Computer Science Program: BS in Computer Science (BSCS) and MS in Computer Science(MSCS) College: Science Website: http://cs.sjsu.edu/ x Check here if your website addresses the University Learning Goals. http://www.sjsu.edu/cs/assessment/bscs/ugoal/ Program Accreditation (if any): ABET accredited Contact Person and Email: Chris Tseng, chris.tseng@sjsu.edu Date of Report: May 31, 2014 Part A 1. List of Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) List of PLOs for BSCS (a) An ability to apply knowledge of computing and mathematics to solve problems (b) An ability to analyze a problem, and identify and define the computing requirements appropriate to its solution (c) An ability to design, implement, and evaluate a computer-based system, process, component, or program to meet desired needs (d) An ability to function effectively on teams to accomplish a common goal (e) An understanding of professional, ethical, legal, security and social issues and responsibilities (f) An ability to communicate effectively with a range of audiences (g) An ability to analyze the local and global impact of computing on individuals, organizations, and society (h) Recognition of the need for and an ability to engage in continuing professional development (i) An ability to use current techniques, skills, and tools necessary for computing practice (j) An ability to apply mathematical foundations, algorithmic principles, and computer science theory in the modeling and design of computer-based systems in a way that demonstrates comprehension of the tradeoffs involved in design choices (k) An ability to apply design and development principles in the construction of software systems of varying complexity List of PLOs for MSCS: http://www.sjsu.edu/cs/assessment/mscs/objectives/index.html Outcomes Upon graduation a student should have acquired: MSCS.OC1 Breadth of knowledge in computer science MSCS.OC2 Depth of knowledge in an advanced topic in computer science MSCS.OC3 Technical communication skills Decision on PLO content The department faculty proposed and approved the standard PLOs recommended by ABET. Criteria for assessing levels of mastery Each PLO is assessed by a set of related courses. Each course is designed to achieve a set of performance indicators. Each performance indicator supports progress towards one or more PLOs. A set of rubrics is established for the assessment of each performance indicator. Each rubric consists of 3 achievement levels. Thus, a set of rubrics defines the criteria for assessing levels of mastery of each PLO. 2. Map of PLOs to University Learning Goals (ULGs) PLO/ULG Specialized Knowledge BSCS PLOs to ULGs map Broad Integrative Intellectual Knowledge Skills Applied Knowledge (a) X X (b) (c) (d) X X X X X (e) X Social and Global Responsibilities X (f) (g) X (h) (i) (j) (k) X X X X X X X X X X X PLO/ULG Specialized Knowledge Broad Integrative Knowledge MSCS.OC1 Intellectual Skills Applied Knowledge X MSCS.OC2 MSCS.OC3 Social and Global Responsibilities X X X X X MSCS PLOs to ULGs map 3. Alignment – Matrix of PLOs to Courses BSCS Outcomes Courses Support Courses Math (a) 1 Physics 1 Science 1 (b) 1 (c) CS 100W (d) 2 Phil 134 (f) (g) 3 3 1 C 2 (h) (i) (j) (k) 1 3 A 2 D 1 2 1 E 1 2 1 R 1 2 2 S 1 2 2 1 V CS 46A 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 CS 46B 1 1 1 1 1 1 CS 146 3 2 2 2 3 2 CS 151 2 3 3 2 2 3 CS 47 1 1 1 1 1 CS 49C/J 1 1 1 1 1 CS 147 2 2 2 2 2 CS 149 2 2 2 2 2 2 CS 152 2 3 3 2 2 3 CS 154 3 2 2 3 CS 160 3 3 3 3 3 3 DEEP 3 3 3 3 3 3 GE Courses Required CS Courses (e) 3 3 3 3 1 4 Electives CS X E E E E E E Matrix of PLOs to Courses in BSCS 1: Indicating Beginner level, 2: Intermediate level, 3: Advanced level x: not assessed in this report 4. Planning – Assessment Schedule Course CS 100W CS 146 CS 151 CS 160 Course OC1 OC2 OC3 S12 F12 S13 X Assessment Semester F13 S14 F14 X S15 X X X F12 X X S16 X X X BSCS Assessment Schedule S12 F15 Assessment Semester F13 S14 F14 X X X MSCS Assessment Schedule S13 X S15 F15 X S16 X 5. Student Experience University Learning Goal for BS and MS can be found under the following website: http://www.sjsu.edu/cs/assessment/bscs/ugoal/ BSCS PLOs and ULGs are posted at the website: http://www.sjsu.edu/cs/assessment/bscs/outcomes/ http://www.sjsu.edu/cs/assessment/bscs/ugoal/matrix/ PLOs are included in syllabi Annual alumni survey is used to provide feedback to PLOs for the consideration of enhancements MSCS PLOs are ULGs are posted at the website: http://www.sjsu.edu/cs/assessment/mscs/objectives/index.html MCSC Outcomes: Upon graduation a student should have acquired: MSCS.OC1 E Breadth of knowledge in computer science MSCS.OC2 Depth of knowledge in an advanced topic in computer science MSCS.OC3 Technical communication skills Part B 6. Graduation Rates for Total, Non URM and URM students (per program and degree) The following table summarizes the graduate rate based on 6 years of data for those who started in Fall 2007. 6 Yr All URM Total 42.2% 0.0% First-time Freshmen Non-URM 42.5% 6 Yr Total All URM Non-URM 55.8% 66.7% 63.6% Transfers 7. Headcounts of program majors and new students (per program and degree) Headcount of majors by major and concentration in recent semesters is as summarized below. Headcount Fall 2013 Spring 2014 F M Total F M Total Computer 4 48 52 0 1 1 Science Total 4 48 52 0 1 1 The number of students entering the program under Applied, Admitted, and Enrolled for recent semesters is summarized below. Headcount Fall 2013 Applied Admitted Enrolled Indicator Indicator Indicator First-time Freshman 741 425 51 New Undergraduate 410 125 44 Transfer First-time Graduate 872 114 52 Total 2,023 664 147 Headcount Spring 2014 Applied Admitted Enrolled First-time Freshman New Undergraduate Transfer First-time Graduate Total Indicator 18 140 527 685 Indicator 4 74 120 198 Indicator 1 41 76 118 Our enrollment trend shows a matching demand for our major as tied to the hi-tech industry economy. After the decline in the last few years during the economic down turn, both our undergraduate and graduate enrollment have been holding steady or improving. This is evidenced by the enrollment trend figures as shown below. 60 90 60 40 30 20 0 0 Fall 2009 Fall 2010 Fall 2011 Fall 2012 Fall 2009 Fall 2013 First-time Freshman Fall 2009 – 2013 Fall 2010 Fall 2011 Fall 2012 Fall 2013 New Undergraduate Transfer Fall 2009 – 2013 200 60 150 40 100 20 50 0 Fall 2009 Fall 2010 Fall 2011 Fall 2012 0 Fall 2013 Fall 2009 First-time Graduate Fall 2009 – 2013 Fall 2010 Fall 2011 Fall 2012 Fall 2013 Total headcount Fall 2009 – 2013 The enrolled Full Time Equivalent Graduate (MSCS) Students in recent years is as shown below. Graduates (MSCS) Fall 2009 96.75 Fall 2010 103.67 Fall 2011 70.92 Fall 2012 75.08 120.00 90.00 60.00 30.00 0.00 Fall 2009 Fall 2010 Fall 2011 Fall 2012 Fall 2013 Fall 2013 76.50 8. SFR and average section size (per program) SFR Fall 2013 Lower Division 46.0 Upper Division 24.6 Graduate Division 8.8 Total 21.1 Student to Faculty Ratio (SFR) Average Section Size Lower Division Upper Division Graduate Division All Level Average section sizes Fall 2013 54.6 23.5 6.9 19.6 The SFR and average headcount of our program as compared to other departments in the same college and that in College of Engineering are summarized in the 2 tables below. Department Lower Division Upper Division Graduate Total CS 46 24.6 8.8 54.8 CMPE 23.1 25.8 46.2 95.1 ENGR (college) 26.6 16.4 15.2 58.2 EE 45.4 22.9 31.5 99.8 Student to Faculty Ratio (SFR) as compared with other departments and college Student College Lower Division Upper Division Graduate Total CS 54.6 23.5 6.9 85 CMPE 45.2 31.2 33.5 109.9 ENGR 51.8 21.8 13.7 87.3 EE 39.4 37.8 32 109.2 Average headcount as compared with other departments and college 9. Percentage of tenured/tenure-track instructional faculty (per department) The percentage of tenured/tenure-track instructional faculty in Fall 2013 is 64% and in Spring 2014 is 57% FTEF 2013/2014 Fall 2013 Spring 2014 Avg Tenured 10.5 (56%) 8.7(47%) 9.6 (52%) Probationary 1.5(8%) 1.8 (10%) 1.7(10%) Temp Lecturer 6.7(36%) 8.1 (43%) 7.4 (38%) Total 18.6 18.7 18.6 Part C Closing the Loop/Recommended Actions Outcomes a, b, and j were re-assessed in Spring 2013 to determine if changes recommended by earlier OARs were effective. Closing the Loop: Outcome b Outcome b states that graduates should have the ability to analyze a problem, and identify and define the computing requirements appropriate to its solution. According to the assessment matrix in section 3, this outcome is enabled by several courses at various levels. CS151, Object-Oriented Design, enables the outcome at the advanced level and is assessed every two years. The enablement was assessed in the Fall 2012 semester. The Fall 2012 OAR (Outcome Assessment Report) raised concerns over the percentage of students who performed below the satisfactory level on both indicators (26.6% for indicator 1 and 33.3% for indicator 2). The OAR concurred with the analysis and recommendations made by the CS 151 course coordinator (who is also the instructor) in the corresponding CAR. The course coordinator proposed more practice selecting patterns without a list of choices. The recommended pedagogical changes were made and the enablement was reassessed in the Spring 2013 semester. The Spring 2013 OAR indicates that the percentage of students performing below the satisfactory level in both indicators has dropped to 13%. Closing the Loop: Outcomes a and j According to the assessment matrix in section 3, these outcomes are enabled by several courses at various levels. CS146, Algorithms and Data Structures, enables both outcomes at the advanced level and is assessed every two years. Both enablements were assessed in the Spring 2012 semester. The Spring 2012 OAR (Outcome Assessment Report) raised several concerns: The report concurred with the analyses and recommendations made by the course coordinator in the corresponding CAR. The recommended pedagogical changes were made and the enablement was reassessed in the Spring 2013 semester. 10. Assessment Data Each of PLO is assessed by one upper division course. Each of these assessed courses defines a set of Course Learning Objectives (CLOs) or performance indicators. A set of rubrics is established for the assessment of each CLO. According to the assessment schedule in Section 4, the course instructor generates a Course Assessment Report (CAR). The rubrics, the associated CLOs and PLOs are presented in CARs. The data presented in CARs for each course are used to produce the Outcome Assessment Report (OAR) every two years. The OARs collectively address achievement of PLOs and also recommend actions. The CARs generated for the latest assessment cycle are attached as appendices. 11. Analysis Based on the data and summary of the CARs, all 11 PLOs have been achieved. As shown in Section 10, the majority of the actions recommended during last assessment cycle have been implemented. The changes proposed during the last assessment cycle are listed in Section 13. These proposed changes will be evaluated and prioritized for the implementation in the coming academic year. 12. Proposed changes and goals (if any) In order to enhance students to achieve PLOs and improve the assessment process, changes have been proposed at the course level. The changes were summarized as follows. In the assessment of Outcome J in CS 146, Performance Indicator 2 was proposed to be changed from "Given pseudocode of two algorithms (eg. sort), describe most suitable data structure to use" to "Given pseudocode of two algorithms (eg. sort), analyze which is more efficient." This change was made by consensus among the instructors and Course Coordinator of CS 146, as well as the Assessment Coordinator, who all believe that the original statement was confusing, and the new statement makes much better sense.