Trinity Day School Preschool Curriculum
advertisement

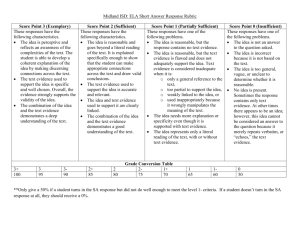
Trinity Day School Preschool Curriculum Our goal is to create a secure, nurturing environment where children are accepted for their individuality and respected as curious learners. With understanding, facilitation and a clear knowledge of child development we will expose our students to a variety of age-appropriate activities while empowering them to make independent decisions and choices in their exploration. We will provide experiences that promote self-reliance and build self-esteem. Guiding Principles are as follows: Positive interactions and relationships with adults provide a critical foundation for successful learning. Social-emotional competence is a significant factor in school success. Constructive, purposeful play supports essential learning. The physical environment affects the type and quality of learning interactions. Teacher-family partnerships promote development and learning. Program Goals and Content Standards: Our curriculum objectives for learning and development are divided into nine areas of child growth and development. The first four describe major areas of child growth and development: social-emotional, physical, language and cognitive. The other five areas are described as outcomes in early learning standards; Literacy, Mathematics, Science and Technology, Social Studies, and The Arts. Attention is given to the different needs, interests and developmental levels of the individual children and each child’s family and community cultures when planning curriculum. Social-Emotional Development Young children’s social-emotional development involves learning how to understand their own and other’s feelings, regulate and express their emotions appropriately, build relationships with others, and interact in groups. Social-Emotional Development Objectives (3): 1. Regulates own emotions and behaviors a. Manages feelings b. Follows limits and expectations c. Takes care of own needs appropriately 2. Establishes and sustains positive relationships a. Forms relationships with adults b. Responds to emotional cues c. Interacts with peers d. Makes friends 3. Participates cooperatively and constructively in group situations a. Balances needs and rights of self and others b. Solves social problems Physical Development Physical development includes children’s gross (large muscle) and fine (small muscle) motor skills. Balance; coordination; and locomotion, or traveling, are part of gross-motor development. Grabbing an object; picking up a small object; cutting; drawing; and writing, are part of finemotor development. Physical Development Objectives (4): 4. Demonstrates traveling skills 5. Demonstrates balancing skills 6. Demonstrates gross-motor manipulative skills 7. Demonstrates fine-motor strength and coordination a. Uses fingers and hands b. Uses writing and drawing tools Language Development Language is the principal tool for establishing and maintaining relationships with adults and other children. Children’s desire to communicate their thoughts, ideas, needs, and feelings with others motivates them to develop language. Language also involves learning about the structure and sequence of speech sounds, vocabulary, grammar, and the rules for engaging in appropriate and effective conversation. Language Development Objectives (3): 8. Listens to and understand increasingly complex language a. Comprehends language b. Follows directions 9. Uses language to express thoughts and needs a. Uses an expanding expressive vocabulary b. Speaks clearly c. Uses conventional grammar d. Tells about another time or place 10. Uses appropriate conversational and other communication skills a. Engages in conversations b. Uses social rules of language Cognitive Development Cognitive development, also called intellectual development, is influenced by the child’s approaches to learning as well as his or her biological makeup and the environment. Cognitive skills include information processing, memory, classification, problem solving, language acquisition, and reading and mathematics learning. Cognitive Development Objectives (4): 11. Demonstrates positive approaches to learning a. Attends and engages b. Persists c. Solves problems d. Shows curiosity and motivation e. Shows flexibility and inventiveness in thinking 12. Remembers and connects experiences a. Recognizes and recalls b. Makes connections 13. Uses classification skills 14. Uses symbols and images to represent something not present a. Thinks symbolically b. Engages in sociodramatic play Literacy Objectives (5): 15. Demonstrates phonological awareness a. Notices and discriminates rhyme b. Notices and discriminates alliteration c. Notices and discriminates smaller and smaller units of sound 16. Demonstrates knowledge of the alphabet a. Identifies and names letters b. Uses letter-sound knowledge 17. Demonstrates knowledge of print and its uses a. Uses and appreciates books b. Uses print concepts 18. Comprehends and responds to books and other texts a. Interacts during read-alouds and book conversations b. Uses emergent reading skills c. Retells stories 19. Demonstrates emergent writing skills a. Writes name b. Writes to convey meaning Mathematics Objectives (4): 20. Uses number concepts and operations a. Counts b. Quantifies c. Connects numerals with their quantities 21. Explores and describes spatial relationships and shapes a. Understand spatial relationships b. Understands shapes 22. Compares and measures 23. Demonstrates knowledge of patterns Science and Technology Objectives (5): 24. Uses scientific inquiry skills 25. Demonstrates knowledge of the characteristics of living things 26. Demonstrates knowledge of the physical properties of objects and materials 27. Demonstrates knowledge of Earth’s environment 28. Uses tools and other technology to perform tasks Social Studies (4): 29. Demonstrates knowledge about self 30. Shows basic understanding of people and how they live 31. Explores changes related to familiar people or places 32. Demonstrates simple geographic knowledge The Arts (4): 33. Explores the visual arts 34. Explores musical concepts and expression 35. Explores dance and movement concepts 36. Explores drama through actions and language Assessment: Teachers will use ongoing assessments to plan and implement developmentally appropriate curriculum that addresses specific learning outcomes. They will observe, record and document children’s progress and use these assessments as a basis for a variety of educational decisions that affect the child. Communication: Written reports will be given to parents at least twice per year (in the fall and in the spring). Conferences will be scheduled at those times to involve families in planning and implementing assessments. Orientation: Parent orientation will be held in the evening before classes begin. Parents will be informed about school policies and will have the opportunity to meet their child’s teachers. Student orientation is a staggered schedule held during the first few days of school. Students meet in small groups which provide a calm, gradual introduction to our classroom routines.