Study Guide
advertisement

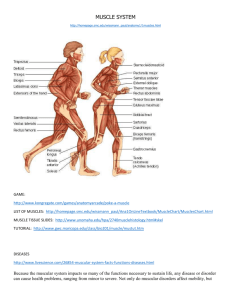
Honors Human Anatomy & Physiology Study Guide for Final Intro/Body Organization Differences between anatomy & physiology; why are they closely interrelated? Divisions of the body ie. axial vs. appendicular Cavities: dorsal, ventral, abdominal, pelvic What & where the mediastinum is Body systems overview ie. digestive, respiratory, integumentary, muscular, etc & what they do Cuts: ie. transverse, sagittal, coronal, oblique Terms for body parts ie. pedal, popliteal, tarsal, inguinal Hierarchy from atoms to organ systems Histology Epithelial tissues: characteristics & what the types look like Connective tissues: characteristics & what the types look like What are the functions of fat? Of nervous tissue? Muscular tissues (cardiac, skeletal, smooth) Which are voluntary? Involuntary? How does cardiac muscle tissue differ from other muscle tissue? Skeletal Bones: normal number, types ie. long, short, flat, irregular, compact, spongy, functions of bones What type tissues do bones replace as they form in fetus? What are the differences between intramembranous & endochondrial bones? Bone vocab: ie. osteoblasts, osteocytes, etc Differences between red & yellow marrow What is hematopoesis? Where is the epiphysis of a bone? The diaphysis? What are fontanels? What are joints? How can they be classified? What are the differences between synarthrotic, amphiarthrotic, etc What are the types of fibrous joints? What are examples of fibrous joints ie. what is a gomphosis? What is a meniscus? What are 6 functions of the synovial membrane? What is flexion? Extension? Adduction? Abduction? Names of bones ie. radius, ulna, etc. What comprises a coxal bone? Muscular What are fascia? What kinds of proteins make up myofibrils? What causes muscle striations? Know the bands: I, A, H, Z What is a threshold stimulus? What is the all or none response? Does it occur with muscular contraction? With nerve impulses? Which muscle type causes peristalsis? Nervous How do motor neurons interact with the motor end plate of a muscle to initiate a muscle contraction? What are the functions of the nervous system (sensory, motor, integrative) What comprises the CNS? PNS? What is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system? Which nerve fibers conduct impulses toward the cell body? Away? What is cell membrane polarization due to? What is a synapse? What is the difference between convergence, facilitation & divergence? How many membranes cover the CNS? What are they called? How many neurons are in the brain? What are the major fissures of the brain? Where are they located? What are sulci? Gyri? Where is the frontal lobe of the brain? The parietal? The temporal? The occipital? What is the significance of Broca’s area? What is hemisphere dominance? Which side is dominant in most people? What percent of people are dominant for this side? What are ventricles? How do they compare in size? What is the reticular formation in the brain? What is it responsible for? What are the divisions of the peripheral nervous system? What do they “connect”? How do the divisions work together (synergistic or antagonistic?) What are the actions of the parasympathetic nervous system? What are the actions of the sympathetic nervous system? Be able to give names of body parts/regions and indicate the actions both systems have on them. What are the differences between pre and post ganglionic fibers or axons? What are the muscles of the eye? What is the blind spot and why? What are the differences between rods & cones? What are characteristics of the retina? Be able to compose an eye diagram (sagittal section). Know the parts of the ear & their functions. What are the ossicles? How do they work? In what order? Where are the hearing receptors found? What is the function of the Eustachian tubes? Circulatory/Cardiovascular What are the functions of blood? Study features/characteristics of erythrocytes, ie. Their shape, numbers, appearance, where they come from & what their production is called, how long they live, what cells destroy them, etc. What is the % of red blood cells in a sample called? What is erythropoietin & when is it released? Study features/characteristics of WBC, what are they properly called, their primary functions, conditions that arise when there are too many, too few, etc. What are thrombocytes? Who was Karl Landesteiner? What is an agglutinogen? What are the ABO blood groups? What is erythroblastosis fetalis? Can it be prevented? If so, how? What are the most abundant plasma proteins? What is hemostasis? What is fibrin? What is fibrinogen? Why & how do you need to change one into the other? What is an embolus? Study heart, function & structure. Know the functions of the heart chambers, ie. Which pumps the blood to the lungs? Which receives the blood from the lungs? What composes heart tissue? How is the heartbeat initiated? What vessels supply its blood? Which side is generally bigger/heavier/more muscular? What is the AV node? SA node? Bundle of His? Purkinje fibers? What is the pacemaker? Know the phases of the cardiac cycle & what occurs. What are the 2 heart circuits? Be able to describe the sequence of the vessels, organs, chambers & valves blood passes through in one circuit as it returns to the heart form the legs. What are the 4 heart valves? Where are they located? How do they function? Which vessels have the thickest walls? Which vessels have valves? What is exchanged in the capillaries? What is the most important way materials are exchanged in the capillaries? Blood vessel diagram. Digestive What is the uvula? Study the parts & secretions of the stomach (ie. what are the 3 cell types in the gastric glands and what do they produce?) What are the parts of the small intestine? What is peristalsis? What does saliva do? Which food is retained in the stomach longest? What are the functions of the liver? What are the bile pigments? What are their functions? What is emulsification? How does it occur? What are the parts of the large intestine? Study all the pancreatic enzymes and the foods they act on. Lab Practical Identify the structures/functions discussed during the brain, eye, and heart dissections. Note: med terms for the units are on the test in matching questions Final Format: 115 Multiple Choice 35 Matching 30 Lab Practical Fill Ins 4 Essays (choose 4 of 5 different units with multiple options in each unit)