B - Mrscienceut.net
advertisement
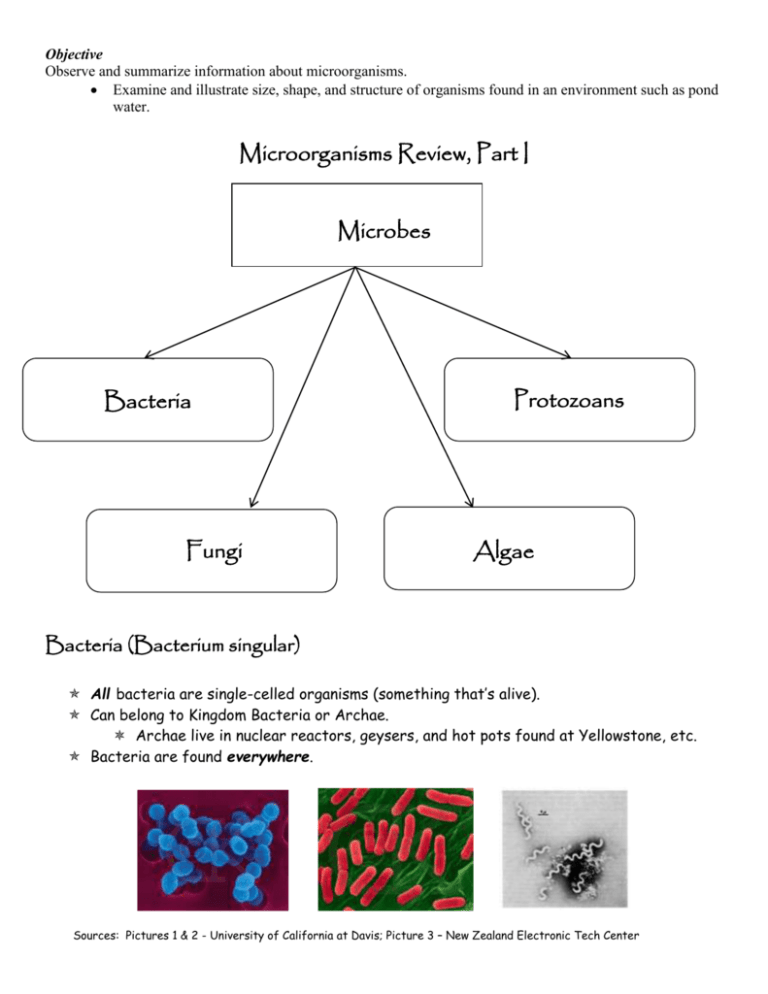
Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Microorganisms Review, Part I Microbes Bacteria Fungi Protozoans Algae Bacteria (Bacterium singular) All bacteria are single-celled organisms (something that’s alive). Can belong to Kingdom Bacteria or Archae. Archae live in nuclear reactors, geysers, and hot pots found at Yellowstone, etc. Bacteria are found everywhere. Sources: Pictures 1 & 2 - University of California at Davis; Picture 3 – New Zealand Electronic Tech Center Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Come in three shapes. Round (coccus [plural cocci]) Rod (bacillus [plural bacilli] ) Spiral (spirillum) Some bacteria are consumers. Consumer – must find and consume food to survive [animal-like]. Some bacteria are producers. Producer - a living thing that makes food from simple substances and sunlight [plant-like]. its Source: Learning with Online Exercises in Soil Science Protozoans (Protozoa/Protista) All are single-celled organisms. Found in water. Can be consumer or producer. Major types of protozoan. Amoeba Is the simplest form of protozoan. Moves using pseudopods (False feet). Has no set shape. (Source: Biology Teaching & Learning Resources) Clear. Is a consumer. Eats algae, bacteria, other protozoan, dead plant or animal matter. Euglena Oval shaped. Is green. Is a producer. Can also be a consumer. Moves using a whip-like flagellum (flagella plural). (Source: Biology Teaching & Learning Resources) Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Paramecium Oval shaped. Translucent. Moves using cilia (hair-like structures (Source: Biology Teaching & Learning around body) Resources) Consumer. Eats algae, bacteria, other protozoan, dead plant or animal matter. Algae Plant-like Primarily green Can also be brown or red. Produce 50% of the oxygen we breathe. Primary source for organisms living in water. Free-floating (go-with-the-flow). Range from single-cell to 100 meters long. Live in water. Spirogyra Simple plant. Producer. Free-floating (go-with-theflow). Has no form of movement. Only moves with the flow of the water. Volvox (Source: Minnesota State Legislature Youth website) Source: Biology Teaching & Learning Resources Fungi (fungus singular) Consumer. Eat by absorbing food. Get food from soil, wood, decaying organic (once living) matter, and living plants/other organisms. Can be from single-celled to largest organism alive. Can’t move. Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Decomposers. Feeds on and breaks down dead plant or animal matter. Examples. Mushrooms. Truffles. A mushroom like fungus that grown underground; primarily found in Europe; a highly valued food. Lichen Fungus often found as white or yellow patches on old walls, etc. Microorganisms Notes Review Worksheet, Part I 1. Bacteria are… a. single-celled. b. multi-celled. 2. Bacteria belong to which Kingdom? a. Plantae b. Moneran c. Animalia d. Fungi 3. Bacteria come in which shapes? a. Rod b. Round c. Spiral d. All of the above Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. 4. What is the difference between a consumer and producer? a. Both have to find their own food. b. A consumer has to find and consume its food; a producer makes its own food. c. Both can make their own food. d. A producer has to find and produce its food; a consumer makes its own food. 5. Protists are found in… a. soil only. b. both soil and water. c. water only. d. the air only. Match the facts with the correct protozoan. (Answers may be used more than once.) ______ 6. This protozoan is green. A. Amoeba ______ 7. This protozoan has no shape. B. Euglena ______ 8. This protozoan is both a consumer and producer. C. Paramecium ______ 9. Moves using cilia. ______ 10. Moves using a flagellum. ______ 11. This protozoan is clear. ______ 12. This protozoan moves using pseudopods. 13. Algae can be… a. brown. b. green. c. red. d. all of the above. 14. Algae produce what percentage of the oxygen we breathe? a. 25% b. 50%` c. 75% d. 100% 15. Algae are a primary source of good for water organisms. a. True b. False 16. Algae move using… a. cilia. b. flagella. c. go-with-the-flow (free floating). d. psuedpods. Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. 17. Algae are found in… a. soil only. b. both soil and water. c. water only. d. the air only. 18. Fungi are... a. consumers. b. producers. 19. Fungi are decomposers (feed on and break down dead plant or animal matter). a. True b. False 20. An example of a fungus is a… a. cup of ice cream. b. serving of corn. c. mushroom. d. a bolt of cloth. It’s Still Pretty Simple: Kingdom Protista (Protozoan) Cell Structure Protozoans do have a nucleus and it’s surrounded by a nuclear membrane. They are called eukaryotes, which means “true nucleus.” They also have cell organelles that help the nucleus perform all the life processes. Number of Cells Most Protozoans are single-celled organisms. A few are made up of two or more cells. Kinds of Movement Some Protozoans do not move at all, but many of them are able to move. Some protists use psuedpods, or false feet. The cell in this type of protists is able to change its shape. It is able to extend some of the cytoplasm to make a fake foot or two. The feet are able to push or pull the cell along. Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Other protists move using tiny, hair-like structures called cilia. The cilia are found on the outside of the cell. They are able to move very quickly back and forth, moving the protists along through water or another liquid. Finally, some protists move using flagella. These are simple, whip-like structures that propel the protist through its environment. Nutrition Some protists are producers and have chloroplasts and chlorophyll. Others are consumers. Is it a Protist or Not? Any organism that has these specific characteristics is a Protista. If it doesn’t have these characteristics, it’s not a Protista. 1. Guess what? I have found some new organisms. I think they should be classified as either Moneran or Protist, but I’m not sure. Look at the following characteristics and see if you can decide which kingdom they should be in. a. When I look at one of the organisms in the microscope, I notice a tiny nucleus inside the cell. A membrane surrounds the nucleus. This organism should be classified as a Moneran Protist b. When I look at the next organism, I notice it has more than one cell. I don’t see any tissues or organs, but the group of cells seems to be one organism, not a colony. This organism should be classified as a Moneran Protist c. This organism is moving. I notice that it is a single cell, with a flagellum. I cannot tell if this organism has a nucleus or not. This organism should be classified as a Moneran Protist Could be either Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. d. This is a simple organism with chloroplasts in its cell. It makes its own food. This organism should be classified as a Moneran Protist Could be either This organism is most likely a: Moneran Protist Protozoan Posters Your assignment is to make three posters about three different protozoans. The three protozoans are: a. Amoeba b. Paramecium c. Euglena Procedure 1. Using the fact sheet, draw a picture of each protist on the appropriate poster. 2. Provide the following information about each protozoan: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Color Shape Size How it moves Where it lives What it eats What eats it 6. Cut your paper so it will fit on the construction paper. Glue the report on the construction paper. Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Protozoan Fact Sheet Amoeba Color – Clear. Shape – Irregular (always changing). Size - .03 inches. Moves Using – Pseudopods (false feet). Lives – Fresh water at the bottom of pond or puddle. Eats – Algae, bacteria, other protozoans, dead plant or animal matter. Eats It – Zooplankton, other protozoans. Euglena Color – Green. Shape – Oval. Size - .002 inches. Moves Using – Flagellum (flagella plural). Lives – Marine and fresh water. Eats – Makes own food; can also eat green algae. Eats It – Water Fleas, fish, and other aquatic animals. Paramecium Color – Pale. Shape – Oval. Size - .003 to .01 inches. Moves Using – Cilia. Lives – Fresh water. Eats – Algae, bacteria, other protozoans, dead plant or animal matter. Eats It – Didinium, amoeba, Euglena, rotifers, copepods, and other small animals that live in water. Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Amoeba Color - ________________________________________________________ Shape - _______________________________________________________ Size - ________________________________________________________ How does it move? _______________________________________________ Where does it live? ______________________________________________ What does it eat? _______________________________________________ What eats it? __________________________________________________ Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Euglena Color - ________________________________________________________ Shape - _______________________________________________________ Size - ________________________________________________________ How does it move? _______________________________________________ Where does it live? ______________________________________________ What does it eat? _______________________________________________ What eats it? __________________________________________________ Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Paramecium Color - ________________________________________________________ Shape - _______________________________________________________ Size - ________________________________________________________ How does it move? _______________________________________________ Where does it live? ______________________________________________ What does it eat? _______________________________________________ What eats it? __________________________________________________ Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Microorganisms Review, Part II Bacteria (Bacterium singular) Beneficial uses of bacteria. Provides nitrogen for plants. Fixes the soil (changes the nitrogen to a form the plant can use). Get minerals from ores. Used to make plastics and laundry detergents. Help make antibiotics. Food production. Yogurt Sauerkraut Pickles Olives Chocolate Cheese Soy Sauce Harmful effects of bacteria. Cause Diseases (<1% of bacteria cause diseases) Three ways to get disease. Through air (breathe in). Through touch. Eating contaminated food. Examples of bacterial diseases. Dental caries (cavities). Strep throat. Salmonella. Typhoid fever. Causes disease in farm animals. Causes metal to rust and wear away. How to treat/prevent diseases. Vaccinations. Antibiotics. Wash hands after using bathroom or whenever dirty. Cook food properly. Store food properly. Cover mouth when sneezing, coughing. Protozoans (Protozoa/Protista) Harmful effects of Protozoans. Cause diseases Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Giardia (diarrhea and abdominal pain) Amebiasis Don’t drink untreated water Benefits of algae. Used in … livestock feed. cosmetics. prescription drug production. identifying possible environmental problems. food production. Sushi. Ice cream. Pudding Salad dressing. Syrup. Primarily used as a thickener. Harmful effects of algae. Algal blooms. Certain types of algae grow rapidly. Grow large enough to form visual patches. Can deplete oxygen in water. Blocks sunlight. Can release toxins dangerous to animals and humans. Fungi (fungus singular) Benefits of fungi. Used to make chemicals used in manufacturing. Produce antibiotics (example – penicillin). Clean the environment. Food production. Cheese Mushrooms Yeast Truffles Soy sauce Harmful effects of fungi. Causes 70% of all crop diseases. Diseases in humans. Respiratory (lung) diseases (example – pneumonia). Athlete’s foot. Ringworm (makes a raised round circle that looks like it was caused by a worm). Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Highlights in the History of the Study of Microorganisms Microorganisms not known until 1670’s. Had to have a microscope first. Invented in 1595 by Zacharias Janssen Was considered a toy for the rich. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek 1670’s Improved the microscope so much he’s considered the father of the microscope. First looked at water under a microscope Discovered small animals. Called them “animalcules” (small animals) Probably were bacteria Edward Jenner 1790’s Developed the first vaccine Noticed that milk maids who had cowpox did not get smallpox Injected cowpox in volunteers They did not get smallpox Ignaz Semmelweis and Oliver Wendell Holmes 1840’s Women were dying after giving birth from Child Bed Fever Semmelweis and Holmes suggested washing hands between patients When hands were washed, Child Bed Fever almost vanished. Joseph Lister 1860’s Many patients got sick and died after operations. Lister proposed disinfecting operating room and instruments between operations. Louis Pasteur 1860’s People believed life arose “spontaneously.” Mice came from grain bags. Pasteur proved that life had to come from existing life. Proposed that germs caused disease. Developed pasteurization. (Rapidly heating something to kill germs.) Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Robert Koch 1880’s Germs cause disease Sir Alexander Fleming 1928 Discovered the “miracle drug” penicillin (Picture sources: Janssen – Math/Science Nucleus; van Leeuwenhoek – Mrs. Zell’s Website; Jenner – BBC; Semmelweiss – Human Disease and Conditions; Holmes – http://www.general-anesthesia.com; Lister http://telem.openu.ac.il/courses/c20237/listeria-g.htm; Pasteur – Wikimedia Commons; Koch – http://raw-milk-facts.com; Fleming – http:// www.xtec.es) Microorganisms Notes Review Worksheet, Part II If the statement about bacteria is true, select true; if it is false, select false. _____ 1. Provides nitrogen for plants. A. True _____ 2. Cannot be used to make antibiotics. B. False _____ 3. Cause metal to rust. _____ 4. Can do nothing to soil. _____ 5. Does not cause disease in animals. _____ 6. Over 90% cause diseases. 7. Identify how we can get a disease. a. Through air b. Through touch c. Eating contaminated food d. all of the above. Match the disease with the microbe that causes it. _____ 8. Amebiasis A. Bacteria _____ 9. Athlete’s foot B. Fungi Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. _____ 10. Dental caries (cavities) C. Protist _____ 11. Giardia _____ 12. Ringworm _____ 13. Salmonella. _____ 14. Strep throat _____ 15. Typhoid fever 16. Which is not a way to prevent diseases? a. Antibiotics. b. Cook food properly . c. Not washing your hands. d. Store food properly. Identify the food with the microbe that is used to make it. ______ 17. Cheese A. Algae ______ 18. Chocolate B. Bacteria ______ 19. Ice cream C. Fungi ______ 20. Olives D. Both bacteria and fungi ______ 21. Pickles ______ 22. Sauerkraut ______ 23. Soy sauce ______ 24. Yeast ______ 25. Yogurt Match the scientist with his accomplishment. _____ 26. Sir Alexander Fleming A. Invented the microscope. _____ 27. Oliver Wendell Holmes B. Discovered microbes (called them “animalcules”). _____ 28. Zacharias Janssen C. Developed the first vaccine. Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. _____ 29. Edward Jenner D. Suggested washing hands between patients. (This choice is used twice!) _____ 30. Robert Koch E. Disinfecting operating rooms and instruments between operations. _____ 31. Anton van Leeuwenhoek F. Proposed germs caused disease; developed pasteurization. _____ 32. Joseph Lister G. Proved germ theory (germs cause disease). _____ 33. Louis Pasteur H. Discovered penicillin (“the miracle drug”). _____ 34. Ignaz Semmelweis History of Microorganisms Timeline Using your notes, complete the timeline showing the major discoveries in the history of microorganisms. On the line, make a mark and write the year the event happened. Above the line, identify the name of the person who made the discovery. Below the line, write what the person discovered or did. 1590 1600 1610 1620 1630 1640 Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. 1640 1650 1800 1810 1660 1820 1670 1790 1800 1830 1840 1850 Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. 1850 1860 1870 1880 1920 1930 Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Beneficial and Harmful Effects of Microbes Identify the beneficial use with the microbe. _____ 1. Cheese A. Algae _____ 2. Chocolate B. Bacteria _____ 3. Cosmetics. C. Fungi _____ 4. Get minerals from ores D. Bacteria and Fungi _____ 5. Help make antibiotics _____ 6. Ice cream _____ 7. Livestock feed. _____ 8. Mushrooms _____ 9. Olives _____ 10. Pickles _____ 11. Pudding _____ 12. Salad dressing. _____ 13. Sauerkraut _____ 14. Soy Sauce _____ 15. Yeast _____ 16. Yogurt Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. 17. Identify a way you could get a disease. a. Through air (breathe in) b. Eating contaminated food c. Through touch d. All of the above Match the disease or harmful effect with the microbe. _____ 18. Amebiasis A. Protozoan _____ 19. Athlete’s foot B. Bacteria _____ 20. Causes 70% of all crop diseases C. Fungi _____ 21. Causes disease in farm animals D. Bacteria and Fungi _____ 22. Causes metal to rust and wear away _____ 23. Dental caries (cavities). _____ 24. Giardiasis _____ 25. Pneumonia _____ 26. Ringworm _____ 27. Salmonella. _____ 28. Strep throat _____ 29. Typhoid fever Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. Microorganisms Notes Review Worksheet, Part I - Key 1. Bacteria are… a. single-celled. (2 choices) 2. Bacteria belong to which Kingdom? b. Moneran 3. Bacteria come in which shapes? d. all of the above 4. What is the difference between a consumer and producer? b. A consumer has to find and consume its food; a producer makes its own food. 5. Protists are found in… c. water only. B 6. This protozoan is green. A 7. This protozoan has no shape. B 8. This protozoan is both a consumer and producer. C 9. Moves using cilia. B 10. Moves using a flagellum. C 11. This protozoan is translucent. A 12. This protozoan moves using pseudopods. 13. Algae can be… d. all of the above. Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. 14. Algae produce what percentage of the oxygen we breathe? b. 50% 15. Algae are a primary source of good for water organisms. a. True (2 choices) 16. Algae move using… c. go-with-the-flow (free floating). 17. Algae are found in… c. water only. 18. Fungi are... a. consumers. (2 choices) 19. Fungi are decomposers (feed on and break down dead plant or animal matter). a. True (2 choices) 20. An example of a fungus is a… c. mushroom. It’s Still Pretty Simple: Kingdom Protista (Protozoan) - Key Is it a Protist or Not? Any organism that has these specific characteristics is a Protista. If it doesn’t have these characteristics, it’s not a Protista. 1. Guess what? I have found some new organisms. I think they should be classified as either Moneran or Protist, but I’m not sure. Look at the following characteristics and see if you can decide which kingdom they should be in. Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. a. When I look at one of the organisms in the microscope, I notice a tiny nucleus inside the cell. A membrane surrounds the nucleus. This organism should be classified as a Moneran Protist b. When I look at the next organism, I notice it has more than one cell. I don’t see any tissues or organs, but the group of cells seems to be one organism, not a colony. This organism should be classified as a Moneran Protist c. This organism is moving. I notice that it is a single cell, with a flagellum. I cannot tell if this organism has a nucleus or not. This organism should be classified as a Moneran Protist Could be either d. This is a simple organism with chloroplasts in its cell. It makes its own food. This organism should be classified as a Moneran Protist Could be either This organism is most likely a: Moneran Protist Microorganisms Notes Review Worksheet, Part II - Key A 1. Provides nitrogen for plants. B 2. Cannot be used to make antibiotics. A 3. Cause metal to rust. B 4. Can do nothing to soil. B 5. Does not cause disease in animals. B 6. Over 90% cause diseases. 7. Identify how we can get a disease. d. all of the above. Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. C 8. Amebiasis B 9. Athlete’s foot A 10. Dental caries (cavities) C 11. Giardia B 12. Ringworm A 13. Salmonella. A 14. Strep throat A 15. Typhoid fever 16. Which is not a way to prevent diseases? c. Not washing your hands. D 17. Cheese B 18. Chocolate A 19. Ice cream B 20. Pudding B 21. Pickles B 22. Sauerkraut D 23. Soy sauce D 24. Yeast B 25. Yogurt H 26. Sir Alexander Fleming Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. D 27. Oliver Wendell Holmes A 28. Zacharias Janssen C 29. Edward Jenner G 30. Robert Koch B 31. Anton van Leeuwenhoek E 32. Joseph Lister F 33. Louis Pasteur D 34. Ignaz Semmelweis History of Microorganisms Timeline - Key 1590 1600 1595 – Zacharias Janssen invents the microscope. 1610 1620 1630 1640 Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. 1640 1650 1660 1670 1670’s – Improved the microscope, discovered bacteria and protozoans. 1800 1810 1820 1790 1800 1790’s – Edward Jenner develops first vaccine. 1830 1840 1850 1840’s – Ignaz Semmelweis recommended washing hands between patients. Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. 1850 1860 1870 1880 1860’s – Joseph Lister proposes disinfecting operating room & instruments between operations. 1860’s – Louis Pasteur proposed germs cause diseases; developed pasteurization. 1920 1928 – Sir Alexander Fleming discovered the “miracle drug” penicillin. 1880’s – Robert Koch proves germs cause diseases. Beneficial and Harmful Effects of Microbes - Key D 1. Cheese B 2. Chocolate A 3. Cosmetics. B 4. Get minerals from ores D 5. Help make antibiotics A 6. Ice cream A 7. Livestock feed. 1930 Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. C 8. Mushrooms B 9. Olives B 10. Pickles A 11. Pudding A 12. Salad dressing. B 13. Sauerkraut D 14. Soy Sauce C 15. Yeast B 16. Yogurt 17. Identify a way you could get a disease. d. All of the above A 18. Amebiasis C 19. Athlete’s foot. C 20. Causes 70% of all crop diseases. B 21. Causes disease in farm animals. B 22. Causes metal to rust and wear away. B 23. Dental caries (cavities). A 24. Giardiasis D 25. Pneumonia Objective Observe and summarize information about microorganisms. Examine and illustrate size, shape, and structure of organisms found in an environment such as pond water. C 26. Ringworm B 27. Salmonella B 28. Strep Throat B 29. Typhoid Fever