AGGRESSION
advertisement

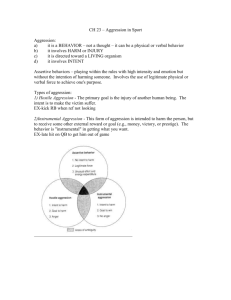
AGGRESSION There seems to be a clear divide between the word “aggression” in everyday life, its meaning in sports and the working definition that sociologists use. SOCIETY Drive Ambition Determination EXAMPLE; An aggressive salesman SPORTS Extreme effort Playing hard EXAMPLE; aggressive baserunning SOCIOLOGISTS “Behaviour designed to harm another” The harm can be either PHYSICAL or PSYCHOLOGICAL The key is INTENT! Types of Aggressive Behaviour A) INSTRUMENTAL - Behavior in which the ultimate goal is NOT injury to another person - The intent to harm is still there, but not for the sole purpose of harming - Goal is some other external reward such as winning, praise from fans and/or coach etc B) REACTIVE/INSTRUMENTAL - Behavior in which the ultimate goal IS injury to another person - Usually resultant of anger or frustration …and often confused with aggression is….. ASSERTIVENESS behaviors that are purposeful and goal-directed in which performers, often striving for competitive success, make forcefully decisive plays, WITH NO INTENT TO HARM. - Play within the rules What types of aggression are these A) B) C) D) E) F) G) Throwing your elbows to clear some room for yourself after getting a rebound in basketball; Running hard to save a ball from going out of bounds, diving into the first row as you do so, knocking out a fan in the process Throwing at a batter in baseball to get them to stop crowding the plate A baseball player gets hit by a pitch and charges the mound Karlee Deacon has scored three goals to give her team a 3-1 lead. She is the only skilled player on her team. An opposing player, known by her nickname, “The Parents”, goes out and kicks Deacon on the side of the knee, shredding all her ligaments A hockey player gets annoyed by a player skating behind him poking him, hooking him etc. He has had enough – turns around and swings his stick at him with two hands An open ice, bone rattling hit in hockey It is very difficult to gather accurate information for aggression in sport. Sociologists have used several different methods to collect data…… Interview athletes and/or coaches Watch sporting contest, gathering data form their own observations They study penalty statistics What are the pros and cons of each of these methods? THEORIES OF AGGRESSION Theory #1 – The Instinct explanation “he was born bad” Premise: Aggression is innate. We have a fighting and death instinct. EVIDENCE: None. It is simply a theory. Although there seems to be historical trends that support it. (examples; gladiatorial contests, popularity of MMA) Theory #2 – The PHYSIOLOGICAL explanation “he is a weirdo” Premise: Because of blood chemistry and/or brain dysfunction individuals become aggressive EVIDENCE: Testosterone is associated with aggression in males. Also it has been documented that individuals with brain tumors exhibit violent behaviours PROBLEM: Does not explain why people with these physiological conditions aggress in one situation but not another – which suggests there must be other factors in play. Theory #3 – The Frustration explanation “things were not going well for him” Premise: When individuals are kept from obtaining a goal they feel frustrated. This feeling of frustration leads to feelings of anger which, in turn, leads to feelings of wanting to hurt another EVIDENCE: Study results – kids with room full of new toys. ½ kids got to play right away, ½ had to watch. The kids that had to watch exhibited WAY more aggression when it was there turn to play. PROBLEM: Some people aggress without being frustrated. Examples? Theory #4 – The social learning explanation Premise: Individuals have learned that by engaging in aggression, they can obtain rewards by a) Direct reinforcement b) Modelled behavior (see someone get rewarded for aggressive behavior) EVIDENCE: The Bobo Doll Experiment Consequences of Aggression in Sport For the Receipient: A) Injury B) Pyschological Harm C) Altered Arousal Level Consequences for the Aggressor: A) Penalty (suspension, fine) B) become a target C) altered arousal level D) injury to self E) direct catharsis Consequences to OBSERVER of aggression A) Entertained B) The learning of aggression C) Indirect catharsis