Math SOL 2.16 - Augusta County Public Schools
advertisement

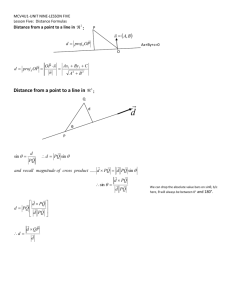
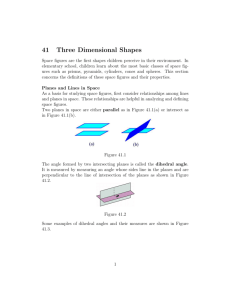
AUGUSTA COUNTY SCHOOLS CURRICULUM MAP MATH Submitted By CLES CONTENT: 2.16 The student will identify, describe, compare, and contrast plane and solid geometric figures (circle/sphere, square/cube, and rectangle/rectangular prism). TOPIC: Geometry CONTENT What do your students need to KNOW? DEMONSTRATORS What do your students need to be able to DO? All students will know: Students will: Understand the differences between plane and solid figures while recognizing the interrelatedness of the two. Understand that a solid figure is made up of a set of plane figures. Trace faces of solid figures to create the set of plane figures related to the solid figure. Identify and describe plane and solid figures, according to the number and shape of their faces, edges, and vertices using models. Determine similarities and differences between related plane and solid figures, using models and cutouts. Compare and contrast plane and solid geometric figures according to the number and shape of their faces (sides, bases), edges, vertices, and angles. ASSESSMENT How will you assess what your students ALREADY KNOW, and assess WHAT THEY’VE LEARNED? Pre-test: Use solid figures. Have students name each one. Place solid figures on a table. Provide name cards. Have students match the name card to the shape. Assessment: Why is it important to use the vocabulary we learned today? How can you describe a rectangular prism based on its faces, edges, vertices, and angles? Does this solid figure look similar to any of the plane shapes we have learned about? If so, which one? . ACTIVITIES HOW will you teach it? Visual/Spatial Lesson: On the white board before class draw and label the following shapes: circle, square, triangle, rectangle, hexagon, trapezoid and parallelogram. Have students study the plane figures and then draw their own on index cards. In small groups have the students put all of their cards in the center of the table. Have students say the name of the shape on the card as they sort the cards into piles of the same shape. (Have students save their cards for the next lesson) Verbal/Linguistic Lesson Objective: to develop the math terms plane shapes, circles, square, triangle, rectangle, hexagon, trapezoid, and parallelogram. Before the lesson make Vocabulary cards. Discuss the meaning of the plane shapes. Have volunteers put the vocabulary words on the Math Word Wall. Have students say each word and write on their card from the previous lesson. Visual/Linguistic lesson Objective: to develop the math terms vertices, vertex, angle, face, edge, solid figure, cube, sphere, rectangular prism, triangular pyramid. Repeat the lesson above and add theses words to the Math Word Wall. Ask each student to bring an object from home that is three –dimensional but resembles a plane shape such as a circle, square, or rectangle (cereal box, tennis ball, dice) Assemble these objectives in front of the room. Ask the students how these objects could be sorted. Have students share their ideas. The goal is for them to articulate how three-dimensional objects can relate to plane geometric shapes- a cube to a square, a rectangular prism to a rectangle, and a sphere to a circle. Use the other vocabulary words to describe three dimensional objects and how they relate to geometric shapes. Lesson plans in detail for this can be found on the Virginia Department of education website under Mathematics Enhanced Scope and Sequence reporting category: Measurement, topic: Investigating plane and solid geometric figures. KinestheticLesson objective: to construct a cube and identify its faces, edges, and vertices. Have students use 4 toothpicks and clay to build a square. Ask them to build 2 of these squares. Ask children to lay the square on construction paper and trace it. Have them cut out 6 of the paper squares. Have students stick 4 toothpicks into the the clay of one of their squares facing upward. Have them set the other square on top of the toothpicks to form a cube. Explain that the construction paper represents the faces, the toothpicks represent the edges and the clay represents vertices. DIFFERENTIATION How will you meet the needs of all students? 1. Set up a learning station with a basket of solid figures where students can investigate objects. Distribute comparing figure charts and have students record data about the faces, edges, vertices, and angles found in solid figures. 2. Have students make a book of magazine pictures to illustrate solid figures. 3. Have students create clay creatures based on solid figures. 4. Tessellations (for the advanced) Students fill the screen with colorful tessellations as they practice copying, pasting, and moving graphics. 5. Invent a Figure. Students create a closed figure by counting sides and corners, and then give it a name. Use a dot grid . RESOURCES 1. Harcourt Math Teacher Edition, Volume 2 2. Virginia Department of Education Mathematics Enhanced Scope and Sequence Grade 2 3. Laminations.nctm.org 4. Visit the learning site at www.harcourtschool.com 5. Evan Moor Math Activities on the Computer TEACHER NOTES: Literature Connection: The Village of Round and Square Houses by Ann Grifalconi Solid Surprises by C.C. Paris Shape Up! By David A. Adler. Anno’s Math Games III by Mitsumasa Anno Mathamusements by Raymond Blum The Shape of Things by Dayle Ann Dodds Checklist of Math Activities and Checklist of Computer Skills included in the Evan Moor Math Activities on the Computer