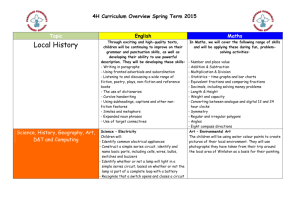
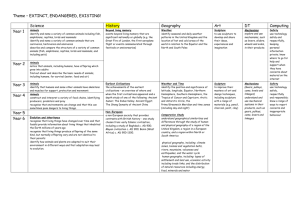
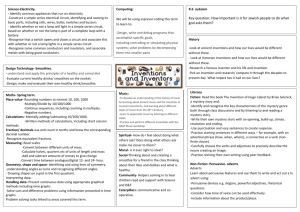
Let`s Explore
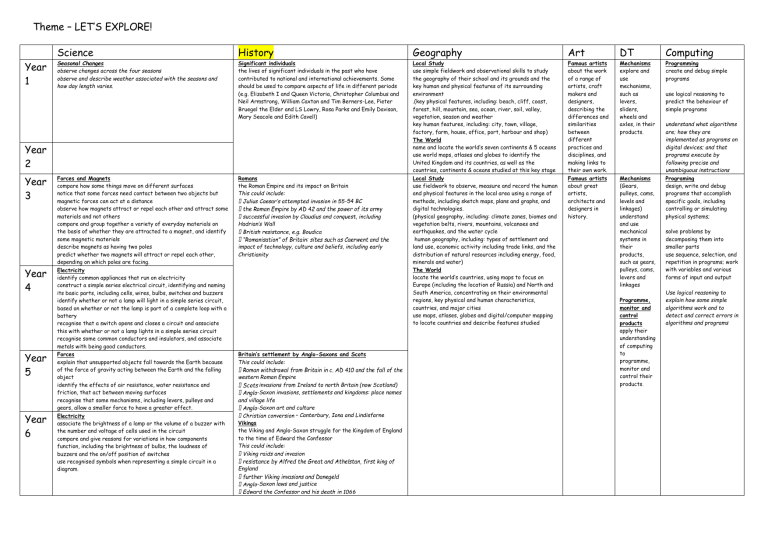
Theme – LET’S EXPLORE!
Year
1
Science
Seasonal Changes observe changes across the four seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and
how day length varies.
History
Significant individuals the lives of significant individuals in the past who have contributed to national and international achievements. Some should be used to compare aspects of life in different periods
(e.g. Elizabeth I and Queen Victoria, Christopher Columbus and
Neil Armstrong, William Caxton and Tim Berners-Lee, Pieter
Bruegel the Elder and LS Lowry, Rosa Parks and Emily Davison,
Mary Seacole and Edith Cavell)
Year
2
Year
3
Year
4
Year
5
Year
6
Forces and Magnets compare how some things move on different surfaces notice that some forces need contact between two objects but magnetic forces can act at a distance observe how magnets attract or repel each other and attract some materials and not others compare and group together a variety of everyday materials on the basis of whether they are attracted to a magnet, and identify some magnetic materials describe magnets as having two poles predict whether two magnets will attract or repel each other, depending on which poles are facing.
Electricity identify common appliances that run on electricity construct a simple series electrical circuit, identifying and naming its basic parts, including cells, wires, bulbs, switches and buzzers identify whether or not a lamp will light in a simple series circuit, based on whether or not the lamp is part of a complete loop with a battery recognise that a switch opens and closes a circuit and associate this with whether or not a lamp lights in a simple series circuit recognise some common conductors and insulators, and associate metals with being good conductors.
Forces explain that unsupported objects fall towards the Earth because of the force of gravity acting between the Earth and the falling object identify the effects of air resistance, water resistance and friction, that act between moving surfaces recognise that some mechanisms, including levers, pulleys and gears, allow a smaller force to have a greater effect.
Electricity associate the brightness of a lamp or the volume of a buzzer with the number and voltage of cells used in the circuit compare and give reasons for variations in how components function, including the brightness of bulbs, the loudness of buzzers and the on/off position of switches use recognised symbols when representing a simple circuit in a diagram.
Romans the Roman Empire and its impact on Britain
This could include:
-54 BC
Hadrian’s Wall impact of technology, culture and beliefs, including early
Christianity
Britain’s settlement by Anglo-Saxons and Scots
This could include: western Roman Empire invasions from Ireland to north Britain (now Scotland)
-Saxon invasions, settlements and kingdoms: place names and village life
-Saxon art and culture
– Canterbury, Iona and Lindisfarne
Vikings the Viking and Anglo-Saxon struggle for the Kingdom of England to the time of Edward the Confessor
This could include:
England
-Saxon laws and justice
Geography
Local Study use simple fieldwork and observational skills to study the geography of their school and its grounds and the key human and physical features of its surrounding environment
.(key physical features, including: beach, cliff, coast, forest, hill, mountain, sea, ocean, river, soil, valley, vegetation, season and weather key human features, including: city, town, village, factory, farm, house, office, port, harbour and shop)
The World name and locate the world’s seven continents & 5 oceans use world maps, atlases and globes to identify the
United Kingdom and its countries, as well as the countries, continents & oceans studied at this key stage
Local Study use fieldwork to observe, measure and record the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies.
(physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes, and the water cycle
human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water)
The World locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on
Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and
South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied
Art
Famous artists about the work of a range of artists, craft makers and designers, describing the differences and similarities between different practices and disciplines, and making links to their own work.
Famous artists about great artists, architects and designers in history.
DT
Mechanisms explore and use mechanisms, such as levers, sliders, wheels and axles, in their products.
Mechanisms
(Gears, pulleys, cams, levels and linkages) understand and use mechanical systems in their products, such as gears, pulleys, cams, levers and linkages
Programme, monitor and control products apply their understanding of computing to programme, monitor and control their products.
Computing
Programming create and debug simple programs use logical reasoning to predict the behaviour of simple programs understand what algorithms are; how they are implemented as programs on digital devices; and that programs execute by following precise and unambiguous instructions
Programing design, write and debug programs that accomplish specific goals, including controlling or simulating physical systems; solve problems by decomposing them into smaller parts use sequence, selection, and repetition in programs; work with variables and various forms of input and output
Use logical reasoning to explain how some simple algorithms work and to detect and correct errors in algorithms and programs