SOLUTIONS - PHY430 - Test 3
advertisement
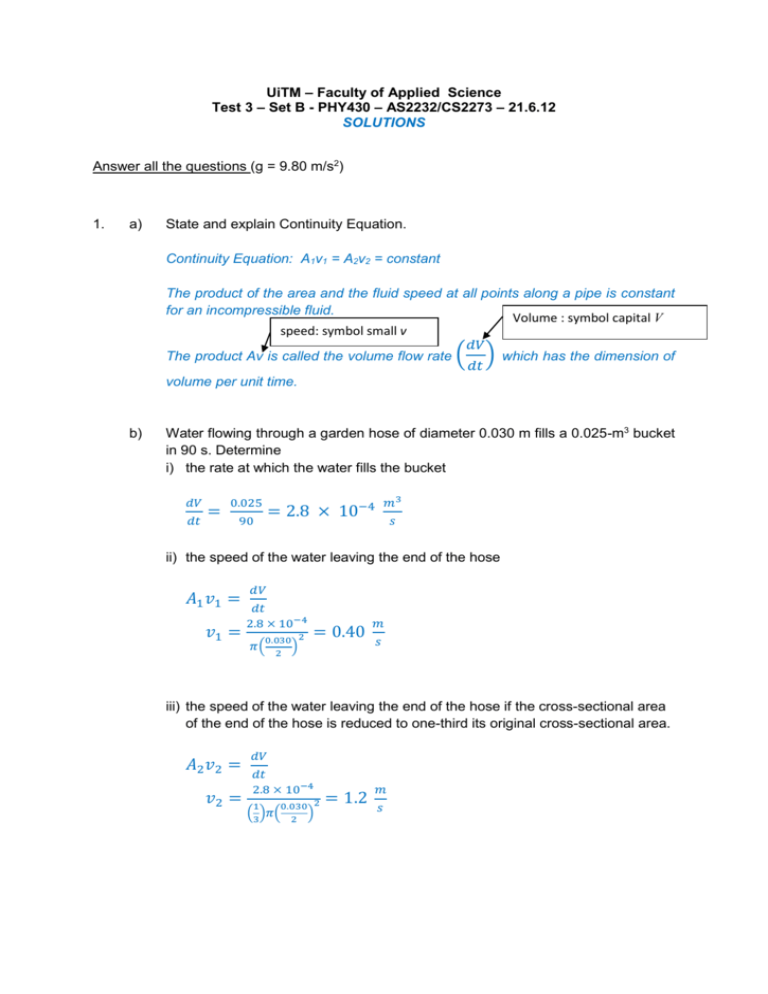
UiTM – Faculty of Applied Science Test 3 – Set B - PHY430 – AS2232/CS2273 – 21.6.12 SOLUTIONS Answer all the questions (g = 9.80 m/s2) 1. a) State and explain Continuity Equation. Continuity Equation: A1v1 = A2v2 = constant The product of the area and the fluid speed at all points along a pipe is constant for an incompressible fluid. Volume : symbol capital V speed: symbol small v 𝑑𝑉 The product Av is called the volume flow rate ( ) which has the dimension of 𝑑𝑡 volume per unit time. b) Water flowing through a garden hose of diameter 0.030 m fills a 0.025-m3 bucket in 90 s. Determine i) the rate at which the water fills the bucket 𝑑𝑉 𝑑𝑡 = 0.025 90 𝑚3 = 2.8 × 10−4 𝑠 ii) the speed of the water leaving the end of the hose 𝐴1 𝑣1 = 𝑣1 = 𝑑𝑉 𝑑𝑡 2.8 × 10−4 0.030 2 𝜋( ) 2 = 0.40 𝑚 𝑠 iii) the speed of the water leaving the end of the hose if the cross-sectional area of the end of the hose is reduced to one-third its original cross-sectional area. 𝐴2 𝑣2 = 𝑣2 = 𝑑𝑉 𝑑𝑡 2.8 × 10−4 1 0.030 2 ( )𝜋( ) 3 2 = 1.2 𝑚 𝑠 2. A sinusoidal travelling wave on a string is represented by y = 0.15 sin (0.80x + 50t) where y and x are in meters and t is in seconds. For this wave determine Compare y = 0.15 sin (0.80x + 50t) y = A sin (kx + t) k = 0.80 m1 and = 50 rad/s a) the wavelength 𝑘= 2𝜋 2𝜋 2𝜋 ⟹𝜆= = = 7.9 𝑚 𝜆 𝑘 0.80 b) frequency 𝜔 = 2𝜋𝑓 ⟹ 𝑓 = 50 = = 8.0 𝑠 −1 2 2 c) velocity of the wave (magnitude and direction) 𝑣 = 𝜆𝑓 = (7.9)(8.0) = 63 𝑚 𝑡𝑜 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑙𝑒𝑓𝑡 𝑠 d) maximum and minimum speed of the particles of the string. 𝑣𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑙𝑒 = 𝑑𝑦 = 0.15 𝑐𝑜𝑠(0.80𝑥 + 50𝑡)(50) 𝑑𝑡 = 7.5 𝑐𝑜𝑠(0.80𝑥 + 50𝑡) 𝑣𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑙𝑒 𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑚𝑢𝑚 = 0 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑐𝑜𝑠(0.80𝑥 + 50𝑡) = 0 𝑚 𝑣𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑙𝑒 𝑚𝑎𝑥𝑖𝑚𝑢𝑚 = 7.5 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑐𝑜𝑠(0.80𝑥 + 50𝑡) = 1 𝑠 3. a) State the meaning of i) specific heat capacity Heat needed to increase the temperature of a 1 kg substance by 1 K. 𝐽 The unit is 𝑘𝑔∙𝐾. ii) latent heat of vaporization. Heat needed to change a 1 kg substance from liquid to gas without any temperature change. The unit is 𝐽 . 𝑘𝑔 b) Calculate the amount of thermal energy needed to change a 0.720-kg ice at 10C to water at 15C. Q needed = Q to increase the temperature of ice from 10C to 0C + Q to melt all the ice at 0C + Q to increase the temperature of water from 0C to 15C = mi ci i + mi Lf + mw cw w = (0.720)(2100)(0 10) + (0.720)( 3.33 105) + (0.720)(4200)(15 0) = 3.00 105 J Specific heat of ice = 2100 J/kg.K Specific heat of water = 4200 J/kg.K Latent heat of fusion of water = 3.33 105 J/kg