Mr. Freidhoff`s Biology Keystone Study Guide (7th Edition)
advertisement
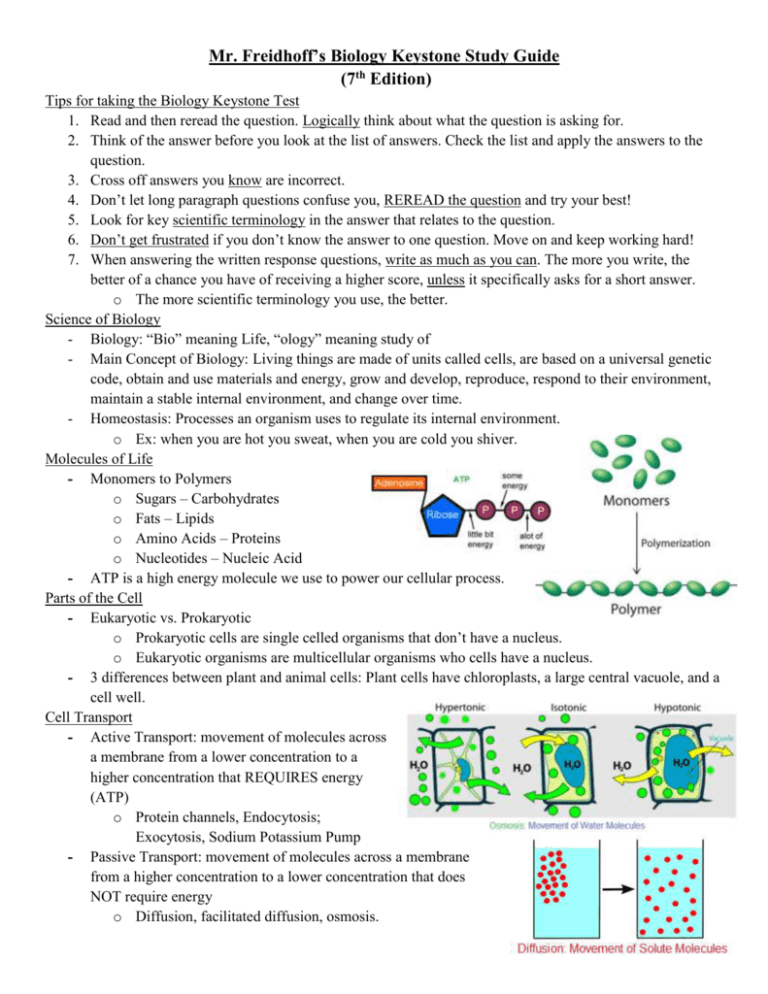
Mr. Freidhoff’s Biology Keystone Study Guide (7th Edition) Tips for taking the Biology Keystone Test 1. Read and then reread the question. Logically think about what the question is asking for. 2. Think of the answer before you look at the list of answers. Check the list and apply the answers to the question. 3. Cross off answers you know are incorrect. 4. Don’t let long paragraph questions confuse you, REREAD the question and try your best! 5. Look for key scientific terminology in the answer that relates to the question. 6. Don’t get frustrated if you don’t know the answer to one question. Move on and keep working hard! 7. When answering the written response questions, write as much as you can. The more you write, the better of a chance you have of receiving a higher score, unless it specifically asks for a short answer. o The more scientific terminology you use, the better. Science of Biology - Biology: “Bio” meaning Life, “ology” meaning study of - Main Concept of Biology: Living things are made of units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain and use materials and energy, grow and develop, reproduce, respond to their environment, maintain a stable internal environment, and change over time. - Homeostasis: Processes an organism uses to regulate its internal environment. o Ex: when you are hot you sweat, when you are cold you shiver. Molecules of Life - Monomers to Polymers o Sugars – Carbohydrates o Fats – Lipids o Amino Acids – Proteins o Nucleotides – Nucleic Acid - ATP is a high energy molecule we use to power our cellular process. Parts of the Cell - Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic o Prokaryotic cells are single celled organisms that don’t have a nucleus. o Eukaryotic organisms are multicellular organisms who cells have a nucleus. - 3 differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have chloroplasts, a large central vacuole, and a cell well. Cell Transport - Active Transport: movement of molecules across a membrane from a lower concentration to a higher concentration that REQUIRES energy (ATP) o Protein channels, Endocytosis; Exocytosis, Sodium Potassium Pump - Passive Transport: movement of molecules across a membrane from a higher concentration to a lower concentration that does NOT require energy o Diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis. Enzymes - Enzymes are large molecules that speed of rates of reaction (catalysts) - Enzymes acts as a lock, while the substrate that is change acts like its key. Life Processes - Cellular Respiration: Process where chemical energy is converted to ATP in the Mitochondrion o C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + Energy - Photosynthesis: Process where light energy is combined with CO2 and H2O to create sugar molecules o CO2 + H2O + Energy → C6H12O6 + O2 Cell Cycle - Interphase: G1, S, G2 - Mitotic phase: Mitosis, Cytokinesis Mitosis - Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis - All body cells divide by this process - Creates two genetically identical daughter cells - Creates two diploid cells (2n), full set of genetic info Meiosis - Sex cells (Sperm/Eggs) divide in this process - Creates 4 genetically different daughter cells - These four cells are haploid (n), half the set of genetic information DNA/RNA - Blueprint for life, codes for proteins - Nucleotides are made up of three parts: Nitrogenous base, Phosphate group, Sugar Molecule - DNA is double stranded, RNA is single stranded - Central Dogma of Molecular Biology = DNA →RNA →Proteins Genetic Terminology - Gene: a discrete unit of hereditary information that usually specifies a protein; a region of DNA located on a chromosome that specifies a trait - Genotype: the genetic make-up of an individual. - Phenotype: the physical or chemical expression of an organism’s genes. - Dominant allele: (Capital Letter: A) An allele that is always expressed when present, regardless of whether the organism is homozygous or heterozygous for that gene. - Recessive allele: (Lower case Letter: a) An allele that is only expressed when the organism is homozygous for that allele and not expressed when heterozygous (when paired with a dominant allele). - Homozygous: possessing a pair of identical alleles for a particular gene (Ex: AA, aa). - Heterozygous: possessing a pair of unlike alleles for a particular gene (Ex: Aa). - Mutation: Error in the genetic code, sometimes creates a new phenotype. - Haploid (n): the condition of having only one set of chromosomes per cell, half the genetic information. - Diploid (2n): the condition of having two sets of chromosomes per cell, full set of genetic information. Theory of Evolution - Natural occurrence of CHANGE OVER TIME, occurred over billions of years. - Theory: Large amount of indisputable evidence that supports an explanation of how and why something happens. - Mutations lead to changes in the phenotype. - First Explained by Charles Darwin o Went on voyage upon the HMS Beagle to the Galapagos Islands o Noticed small differences in the beaks of Finches on different islands. o Wrote On the Origin of Species - Natural Selection: Organisms that have beneficial genes will survive and reproduce more than organisms that don’t have these genes and won’t reproduce. - Artificial Selection: Humans select what traits they want passed on in a species and control reproduction rates (Ex: Dogs) Ecology - Abiotic is a non-living factor in an ecosystem, biotic factors are living factors. - Producer: Usually photosynthetic plants, convert light to chemical energy in organic compounds - Consumer: These organisms eat producers or other consumers, Obtain energy from another organism - Decomposers: Break down wastes of other organisms, Usually prokaryotic bacteria or fungi - Types of Consumers o Herbivore: Organisms that only eat producers in the form of plant life Ex: Deer, Rabbits, Caterpillar o Carnivore: Organisms that only eat consumers Ex: Lions, cheetahs, alligator o Omnivore: Organisms that eat both producers and consumers Ex: Humans, Bears, Raccoons - Food Web: Interconnected and branching food chains that represents flow of energy through an ecosystem, arrows represent where energy travels to GOOD LUCK!!! WE ALL BELIEVE YOU CAN DO THIS! *You can NOT use this study guide or any other material on the Biology Keystone Test