Biodiversity, Phylogeny & Taxonomy Worksheet
advertisement
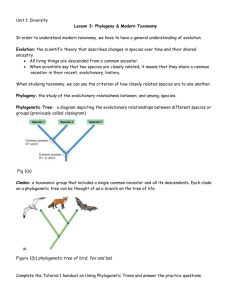
Unit 1: Biodiversity Lesson 3: Phylogeny & Modern Taxonomy How do we define a species? 1. Morphological Species Concept key ideas: ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES 2. Biological Species Concept Key Ideas ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES 3. Phylogenetic Species Concept Key Ideas ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES PHYLOGENETICS: • Phylogeny refers to the evolutionary history of a species • Phylogenies are determined through: 1. Developmental Traits (Embryology) They show similar stages of embryonic development 2. Structural Traits (Homology) They have similar anatomical structures, regardless of function 3. Molecular Traits (Genetics & Molecular Biology) They are genetically similar International Barcode of Life Project (iBOL) Please go to ibol.org and take some time to read through the website to understand what this project is about and how it works. Be sure to read the page titled, "What is DNA Barcoding". Traditional Versus Modern Classification Methods: Traditional: 7 taxonomic levels, dichotomous keys Modern: Phylogenetic Trees Phylogenetic Tree: a diagram depicting the evolutionary relationships between different species or groups (previously called cladogram) Clades: a taxonomic group that includes a single common ancestor and all its descendants. Each clade on a phylogenetic tree can be thought of as a branch on the tree of life. Why should we care about how species are related through evolution? Drugs Disease Agriculture Conservation Thinking Question: In northwestern Ontario, there are two similar-looking garter snakes: the red-sided garter snake and the eastern garter snake. The two interbreed successfully in nature in that part of Ontario, producing offspring that have a mix of physical traits of the two. The eastern garter snake also coexists in southern Ontario with another very similar snake, the eastern ribbon snake. However, these two snakes are not known to interbreed successfully. Infer whether these three snakes are the same species or not. Explain your reasoning. How to Read a Phylogenetic Tree Complete the Tutorial 1 handout on Using Phylogenetic Trees and answer the practice questions. Tutorial 1 Practice Questions: 1. Using figure 1b (phylogenetic tree of bird, fox and bat) a) Indicate the location of the species that is: i) The most recent common ancestory of foxes and bats ii) The most common recent ancestor of all three species b) Based on this tree, is a bird more closely related to a fox or to a bat? Explain your reasoning. 2. Draw Figure 7 from the Tutorial 1 handout into your notebook. Do not include the coloured outlines. a) Use different colours to show the following clades: i) The smallest clade that contains the bat and the rabbit ii) The smalled clade that contains the seal and the rat b) What is the maximum number of unique clades (of any size) that can be found in this tree? Homework Questions: