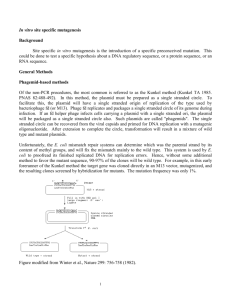
Site-directed mutagenesis
advertisement

BIOL463 2014 A technique in five minutes TECHNIQUES SPEED-DATING PRESENTATIONS: WRITE-UP TEMPLATE Names and contributions of group members: Andrew Moffatt – research for mini-report, power point presentation Saikrishna Venakatsubramanian – group coordination, research for mini-report and presentation, crate power point presentation Jelena Grabeljsek – research for mini-report, put mini-report together Tracy Pham – research for mini-report, power point presentation, preparation of props for “speed-dating” session Yao Liu – research for mini-report and presentation Technique chosen: Site directed mutagenesis a.k.a. site specific mutagenesis or oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis What does this technique ‘do’? Introduces a specific mutation point (point mutation) or couple-bases mutation with insertions or deletions, frame shift, nonsense mutations into a gene to alter the primary amino acid sequence of proteins What applications is this technique employed for? Engineer gene products with a certain functionality (or loss of) Investigate the effects of specific mutations on gene product function Screen an array of mutants to determine sequence in question The methods used for these applications include: PCR extension for an insertion and/or deletion, cassette mutagenesis, inverse PCR, oligonucleotide heteroduplex and random point mutations/chemical alterations What questions (give a couple of examples) relating to gene regulation and/or development can be addressed using this technique? Identifying function of genes and mechanisms of gene regulation in development Roles of different genes at different stages in development What critical reagents are required to use this technique? Synthetic oligonucleotide (RNA/DNA) primer that contains desired mutation Template DNA sequence: any vector, DNA fragment or product of PCR that comprises of complementary DNA (to be mutated) can be used as the initial template BIOL463 2014 A technique in five minutes Thermostable DNA polymerase (pfu) Buffer for DNA polymerase (pfu, ligase) What critical information is required to be able to employ this technique? Knowledge of the wild type sequence and protein structure Knowledge of wild-type protein function References: Adereth, Y., Champion, K.J., Hsu, T., and Dammai, V. 2005. Site-directed mutagenesis using Pfu DNA polymerase and T4 DNA ligase. Biotechniques, 38(6): 864-868 Bachman, J. 2013. Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Methods in Enzymology, 529: 241248 Liu, L., and Lomonossoff, G. 2006. A site-directed mutagenesis method utilising large double-stranded DNA templates for the simultaneous introduction of multiple changes and sequential multiple rounds of mutation: Application to the study of whole viral genomes. Journal of Virological Methods, 137: 63-71. Smith, M. 1982. Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Trends In Biochemical Sciences, 7(12): 440-442 Reikofski, J., and Tao, B.Y. 1992. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Techniques for Site Directed Mutagenesis. Biotechnology Advances, 10: 535-547 Smith, M. 1986. Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 317: 295-304 Wagner, C.R., and Benkovic, S.J. 1990. Site Directed Mutagenesis: A Tool For Enzyme Mechanism Dissertation. Trends In Biotechnology, 8: 263 - 270