Literary terms
advertisement

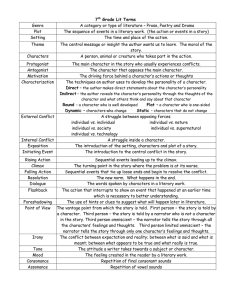
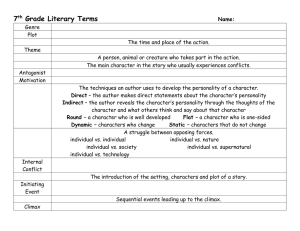
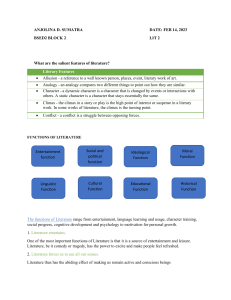
Mrs. Wehinger ELA 7th Grade Name: Literary Terms to Know Types of Writing Genre - how literature is categorized based on literary conventions Short Story - a type of fictional narrative story usually written in prose; often shorter in length and focuses on one event, character, or incident Novel - a longer work of fictional prose Poetry - a type of literary art form where writers use figurative language and other poetic devices to get the point of their subject across Drama - a type of fiction characterized by performance of actors Fiction - a type of narrative literature that contains imaginary characters and events Nonfiction - a type of narrative literature where the characters and events actually happened Biography - a type of literature written about someone by another person Autobiography - a type of literature written by someone about his or her own life Fable - a type of fictional story where the main characters non-humans, such as animals or mythical creatures, but have the qualities of humans Science fiction - a type of genre where characters and events are often set in the future where science and technology far surpasses the present Tragedy - a type of narrative that often involves human suffering, including death, in the story Comedy - a type of story designed for humor or irony Parts of a Story Setting - this is where a story takes place in time and location Character - the people that move the plot along and the reason that many readers stay with a story o Protagonist – the main character; the person we want to win (the good guy) o Antagonist – the character that gets in the way of the protagonist; the “bad” guy o Hero/heroine – the main character (protagonist) o Dynamic characters – a dynamic, or round, character is a major character in a work of fiction who encounter conflict and are changed by it. Dynamic characters tend to be more fully developed and described than flat, or static, characters. o Static characters – a static, or flat, characters are minor characters in a work of fiction who do not undergo substantial change or growth in the course of a story. The play a supporting role to the main character. Point of view – who is telling the story: o 1st person – the story is told by one of the characters in his/her own words. o 2nd person limited – the narrator is telling from a single person perspective. o 3rd person omniscient – the narrator sees into the minds of all the characters and includes most character ideas/ feelings in the narration of the story. Plot - these are the events in the story from the beginning until the end Conflict - this important part of a story often prevents the characters from achieving their goals but allows them to grow from the experiences and then continue onward in their journey Climax - a very exciting section of the story where the main conflict is resolved Resolution - this is how the story ends and happens after the climax Theme - is the central idea of the story, which is often abstract (greed, love, coming of age) Tone - words used to express how the author feels about the text Mood - how the reader feels about the text while reading Narrator - is the person who tells the story and can be limited or omniscient Mrs. Wehinger ELA 7th Grade Name: Prologue – a preference to the story, setting up the story, giving background information and other miscellaneous information. Epilogue – a piece of writing at the end of a literary work – giving a finality or ending and bringing closure to the work. Literary Devices Allusion - when an author intentionally makes a reference to another work, such as another piece of literature, a piece of artwork, or a time, place or person Imagery - words used to evoke pictures in the minds of the readers Hyperbole - an exaggeration Dialogue - the words that characters speak Symbolism - a symbol is a physical object that represents an abstraction (Example: a flag is a decorated piece of fabric, but is symbolizes the values of a country) Characterization – the methods an author uses to acquaint a reader with the people, animals or machines in the story (an author may do this by describing the appearance, speech, actions, or reactions) Irony - words used that often mean something different or the opposite of what they mean Flashback - part of a story that happened before the current action which is brought out through characters’ dreams or storytelling Foreshadowing - is when the author alludes to upcoming events without directly stating that they will happen Suspense - happens when the storyteller or narrator builds excitement in a scene, often prior to the climax Repetition - when words, symbols, themes or other parts of the story are used more than once Sensory language - descriptive language that attempts to invoke one or more of the five senses Sound Devices Rhyme - when words that sound alike are paired together or near each other Rhyme scheme - a repetition of a rhyming pattern Alliteration - repetition of consonant sounds at the beginning of words Onomatopoeia - words that represent sounds Assonance - repetition of vowel sounds at the beginning of words Meter - combinations of accented and unaccented syllables which often form a pattern Refrain - pattern of words or phrases that repeats throughout a literary work Figurative Language Metaphor - compares two things where one is the other Simile - compares two things using like or as Personification - this is where animals or inanimate objects are given human qualities Idiom - type of phrase where the meanings cannot be inferred by the literal meaning of the words