Nutrition Study Guide
advertisement

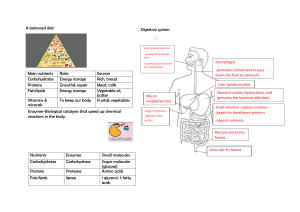
Nutrition Study Guide Vocab Terms - Calorie – the amount of energy released when nutrients are broken down is measured. - Metabolism – the chemical process by which your body breaks down food to release energy - Foods that are nutrient dense have a lot of nutrients, but few calories. o Kale, Greek yogurt and salmon are all examples. Nutrients - Carbohydrates, fats and proteins all provide your body with energy o Carbohydrates are the body’s go to energy source o Trans fats are made when food manufacturers add hydrogen to the fat molecules in vegetable oils o Proteins are the building blocks for muscle o Fats help protect nerves and internal organs; can also be used as energy source. - Vitamins and minerals help you USE energy/other nutrients more effectively. o Minerals are found in rocks and soil o Vitamins are found in animals, animal byproducts and vegetables Hunger vs. Appetite - Hunger is a physical discomfort that is caused by your body’s need for nutrients. - Appetite is wanting to eat a particular food. Food Labels - The best way to judge the nutritional value of a food is by reading the food label. - Food ingredients are always listed in order of volume, from greatest to least. - Serving size will tell you how much should be eaten in one sitting. Body Composition - Body Mass Index (BMI) is determined using your height and weight. - An acceptable body fat range for females is 25-31% and for males is 18-24%. - The safest and most sensible way to lose weight is through diet and exercise Health Risks Related To Nutrition - High cholesterol o Causes plaque build up on the walls of blood vessels, making individuals more likely to suffer from a heart attack. - Heart disease - High blood pressure - Cardiovascular disease – women are more likely to suffer from strokes than men - Plant products and vegetables will help reduce the risk of cancer and cardiovascular disease. o Cancer is the rapid, uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells. - Diabetes o Two types: Type 1, Type 2 o Type 1 (Juvenile Diabetes) – the pancreas does not produce enough insulin. o Type 2 – affects the way body processes glucose o Both types result in high glucose levels in the blood.