247988_RG1_6_WaterEtc
AP BIOLOGY Reading Guide 1.6
NAME_____________________Text Reference: Biology in Focus, chapter 2
WATER, ACIDS, BASES, BUFFERS
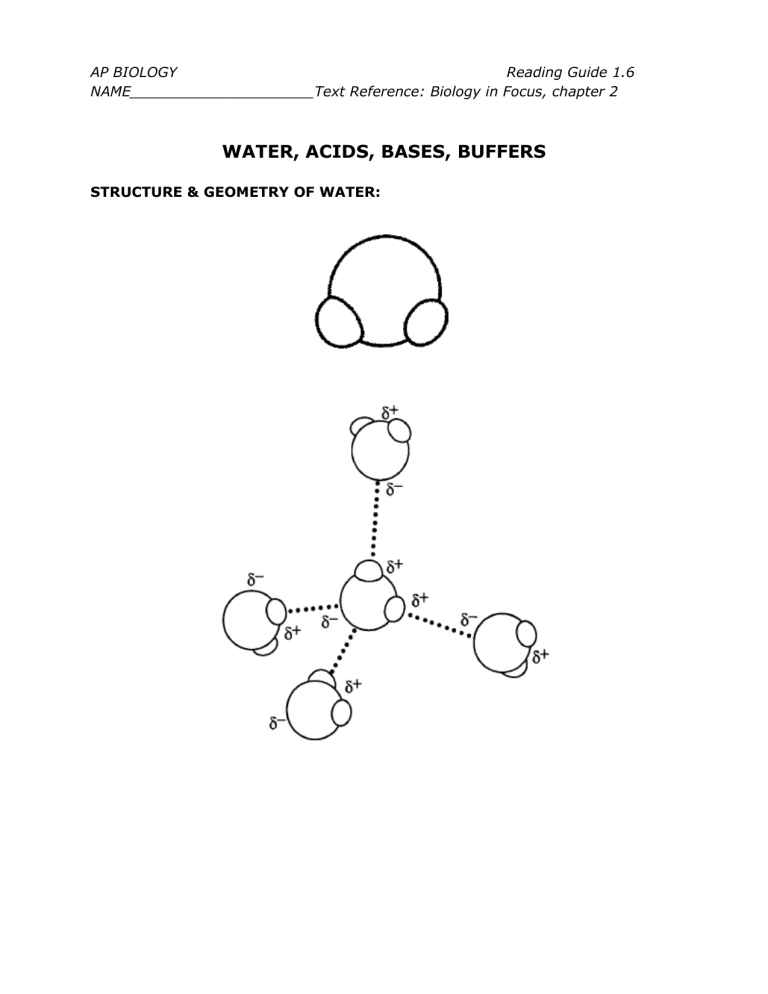
STRUCTURE & GEOMETRY OF WATER:
AP BIOLOGY Reading Guide 1.6
NAME_____________________Text Reference: Biology in Focus, chapter 2
AP BIOLOGY Reading Guide 1.6
NAME_____________________Text Reference: Biology in Focus, chapter 2
AP BIOLOGY Reading Guide 1.6
NAME_____________________Text Reference: Biology in Focus, chapter 2
AP BIOLOGY Reading Guide 1.6
NAME_____________________Text Reference: Biology in Focus, chapter 2
QUESTIONS:
1. Explain what is meant by the phrase water is a polar molecule.
2. Explain how water is able to form 4 hydrogen bonds.
3. List the 5 properties of water.
4. Define the following terms.
Cohesion
Adhesion
6. Describe one biological importance of water’s cohesive and adhesive properties?
AP BIOLOGY Reading Guide 1.6
NAME_____________________Text Reference: Biology in Focus, chapter 2
7. Why does water have a greater surface tension than most other liquids?
8. Why does water have a high specific heat?
9. Describe one biological importance of water’s high specific heat?
10. Why does water have a relatively high heat of vaporization?
11. Describe one biological importance of water’s relatively high heat of vaporization?
12. Why does water expand when it freezes?
13. How does a fish in an Alaskan lake benefit by the expansion of water when it freezes.
AP BIOLOGY Reading Guide 1.6
NAME_____________________Text Reference: Biology in Focus, chapter 2
14. Match the description/definition with the correct term.
A. Aqueous solution D. Solute
B. Hydrophilic
C. Hydrophobic
E. Solution
F. Solvent
______ Homogenous mixture of 2 or more substances
______ Dissolving agent
______ Material being dissolved
______ Solution where water is solvent
______ Water loving; molecules with an affinity for water
______ Water fearing; molecules that do not have an affinity for water
15. Water a versatile solvent, what kinds of materials will not dissolve in water?
16. At equilibrium in pure water at 25oC: a. How does the [H+] compare to the [OH]?________________________
b. What is the [H+]? _________________________________________
17. Each of the following will affect the equilibrium established in pure water during the dissociation of water. Describe what effect each will have on the equilibrium by completing the following chart.
Addition of: Effect on [H+] Effect on [OH-] Direction
Equilibrium Shifts
H 2 SO 4
KOH
NH 3
AP BIOLOGY Reading Guide 1.6
NAME_____________________Text Reference: Biology in Focus, chapter 2
18. How does the [H+] compare to the [OH-] in each of the following: a. A neutral solution: _________________________________________ b. An acidic solution: _________________________________________ c. A basic solution: __________________________________________
19. Complete the following chart.
[H+]
10 -2 pH [OH-] pOH
4
10 -4
2
20.What is the pH range for most biological fluids? _____________________
What fluid is the exception to this range? __________________________
21. Scientists use the pH scale to quantify the amount of hydrogen ions in aqueous solution. Which of the following is a correct statement about the relationship between pH and the hydrogen-ion concentration of a solution?
A) There are no hydrogen ions present in a solution with a basic pH.
B) There are no hydrogen ions present in a solution with a neutral pH of 7.0.
C) The concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution with a pH of 7.0 is 100 times as great as that in a solution with a pH of 9.0.
D) The concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution with a pH of 4.0 is 400 times as great as that in a solution with a pH of 1.0.
AP BIOLOGY Reading Guide 1.6
NAME_____________________Text Reference: Biology in Focus, chapter 2
22. (This one is a challenge) A patient has been vomiting for a prolonged period of time, resulting in significant dehydration.
a. What effect would this have on the [H+] in the blood? _____________ b. How will the bicarbonate buffer system respond to this change?
________________________________________________________ c. What effect will the buffer system response have on the rate of respiration? In other words, would the person breathe more quickly or more slowly? Why??
________________________________________________________ d. If the buffer system does not return the blood pH to within the normal range or if the vomiting continues, how will the kidneys respond?
Will the kidneys excrete or reabsorb H+?________________________
Will the kidneys excrete or reabsorb HCO 3 —?_____________________








