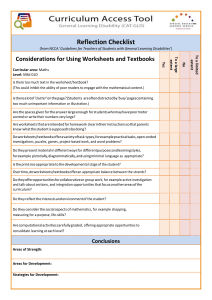
3/16-3/20 Career Clusters Bridge Act
advertisement
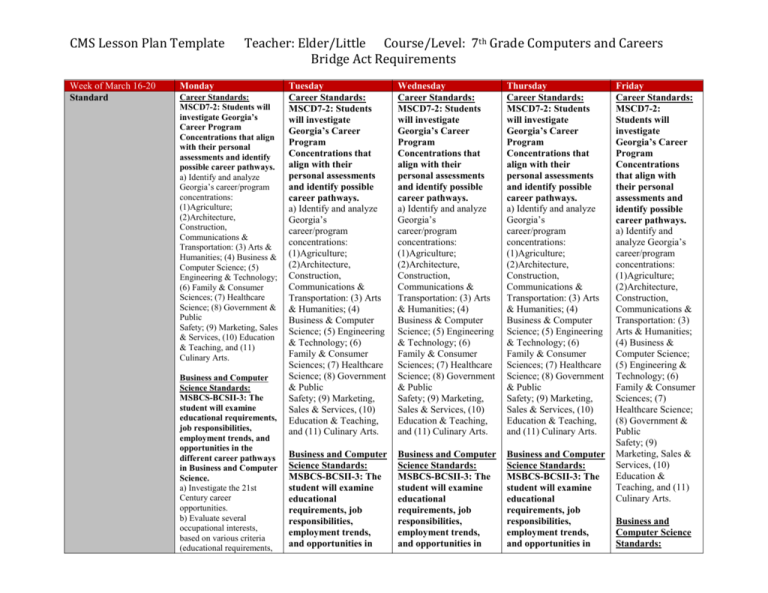
CMS Lesson Plan Template Week of March 16-20 Standard Teacher: Elder/Little Course/Level: 7th Grade Computers and Careers Bridge Act Requirements Monday Career Standards: MSCD7-2: Students will investigate Georgia’s Career Program Concentrations that align with their personal assessments and identify possible career pathways. a) Identify and analyze Georgia’s career/program concentrations: (1)Agriculture; (2)Architecture, Construction, Communications & Transportation: (3) Arts & Humanities; (4) Business & Computer Science; (5) Engineering & Technology; (6) Family & Consumer Sciences; (7) Healthcare Science; (8) Government & Public Safety; (9) Marketing, Sales & Services, (10) Education & Teaching, and (11) Culinary Arts. Business and Computer Science Standards: MSBCS-BCSII-3: The student will examine educational requirements, job responsibilities, employment trends, and opportunities in the different career pathways in Business and Computer Science. a) Investigate the 21st Century career opportunities. b) Evaluate several occupational interests, based on various criteria (educational requirements, Tuesday Career Standards: MSCD7-2: Students will investigate Georgia’s Career Program Concentrations that align with their personal assessments and identify possible career pathways. a) Identify and analyze Georgia’s career/program concentrations: (1)Agriculture; (2)Architecture, Construction, Communications & Transportation: (3) Arts & Humanities; (4) Business & Computer Science; (5) Engineering & Technology; (6) Family & Consumer Sciences; (7) Healthcare Science; (8) Government & Public Safety; (9) Marketing, Sales & Services, (10) Education & Teaching, and (11) Culinary Arts. Wednesday Career Standards: MSCD7-2: Students will investigate Georgia’s Career Program Concentrations that align with their personal assessments and identify possible career pathways. a) Identify and analyze Georgia’s career/program concentrations: (1)Agriculture; (2)Architecture, Construction, Communications & Transportation: (3) Arts & Humanities; (4) Business & Computer Science; (5) Engineering & Technology; (6) Family & Consumer Sciences; (7) Healthcare Science; (8) Government & Public Safety; (9) Marketing, Sales & Services, (10) Education & Teaching, and (11) Culinary Arts. Thursday Career Standards: MSCD7-2: Students will investigate Georgia’s Career Program Concentrations that align with their personal assessments and identify possible career pathways. a) Identify and analyze Georgia’s career/program concentrations: (1)Agriculture; (2)Architecture, Construction, Communications & Transportation: (3) Arts & Humanities; (4) Business & Computer Science; (5) Engineering & Technology; (6) Family & Consumer Sciences; (7) Healthcare Science; (8) Government & Public Safety; (9) Marketing, Sales & Services, (10) Education & Teaching, and (11) Culinary Arts. Business and Computer Science Standards: MSBCS-BCSII-3: The student will examine educational requirements, job responsibilities, employment trends, and opportunities in Business and Computer Science Standards: MSBCS-BCSII-3: The student will examine educational requirements, job responsibilities, employment trends, and opportunities in Business and Computer Science Standards: MSBCS-BCSII-3: The student will examine educational requirements, job responsibilities, employment trends, and opportunities in Friday Career Standards: MSCD7-2: Students will investigate Georgia’s Career Program Concentrations that align with their personal assessments and identify possible career pathways. a) Identify and analyze Georgia’s career/program concentrations: (1)Agriculture; (2)Architecture, Construction, Communications & Transportation: (3) Arts & Humanities; (4) Business & Computer Science; (5) Engineering & Technology; (6) Family & Consumer Sciences; (7) Healthcare Science; (8) Government & Public Safety; (9) Marketing, Sales & Services, (10) Education & Teaching, and (11) Culinary Arts. Business and Computer Science Standards: starting salaries, trends, opportunities, and career ladders). c) Describe and demonstrate effective communication skills (reading, writing, speaking, and listening) in a business environment. d) Explain why people need to work (e.g., social contacts, make purchases for necessities) expand knowledge, develop skills to meet basic needs and for personal satisfaction and enjoyment. e) Construct and/or update a Career Plan as a tool to explore self-knowledge and academic aptitude and understand that career paths should relate to your individual traits. English Language Proficiency Standard 1: English language learners communicate in English for Social and Instructional purposes within the school setting.English Language Proficiency Standard 1: English language learners communicate in English for Social and Instructional purposes within the school setting. the different career pathways in Business and Computer Science. a) Investigate the 21st Century career opportunities. b) Evaluate several occupational interests, based on various criteria (educational requirements, starting salaries, trends, opportunities, and career ladders). c) Describe and demonstrate effective communication skills (reading, writing, speaking, and listening) in a business environment. d) Explain why people need to work (e.g., social contacts, make purchases for necessities) expand knowledge, develop skills to meet basic needs and for personal satisfaction and enjoyment. e) Construct and/or update a Career Plan as a tool to explore selfknowledge and academic aptitude and understand that career paths should relate to your individual traits. English Language Proficiency Standard 1: English language learners communicate in English for Social and Instructional purposes within the school setting. the different career pathways in Business and Computer Science. a) Investigate the 21st Century career opportunities. b) Evaluate several occupational interests, based on various criteria (educational requirements, starting salaries, trends, opportunities, and career ladders). c) Describe and demonstrate effective communication skills (reading, writing, speaking, and listening) in a business environment. d) Explain why people need to work (e.g., social contacts, make purchases for necessities) expand knowledge, develop skills to meet basic needs and for personal satisfaction and enjoyment. e) Construct and/or update a Career Plan as a tool to explore selfknowledge and academic aptitude and understand that career paths should relate to your individual traits. English Language Proficiency Standard 1: English language learners communicate in English for Social and Instructional purposes within the school setting. the different career pathways in Business and Computer Science. a) Investigate the 21st Century career opportunities. b) Evaluate several occupational interests, based on various criteria (educational requirements, starting salaries, trends, opportunities, and career ladders). c) Describe and demonstrate effective communication skills (reading, writing, speaking, and listening) in a business environment. d) Explain why people need to work (e.g., social contacts, make purchases for necessities) expand knowledge, develop skills to meet basic needs and for personal satisfaction and enjoyment. e) Construct and/or update a Career Plan as a tool to explore selfknowledge and academic aptitude and understand that career paths should relate to your individual traits. English Language Proficiency Standard 1: English language learners communicate in English for Social and Instructional purposes within the school setting. MSBCS-BCSII-3: The student will examine educational requirements, job responsibilities, employment trends, and opportunities in the different career pathways in Business and Computer Science. a) Investigate the 21st Century career opportunities. b) Evaluate several occupational interests, based on various criteria (educational requirements, starting salaries, trends, opportunities, and career ladders). c) Describe and demonstrate effective communication skills (reading, writing, speaking, and listening) in a business environment. d) Explain why people need to work (e.g., social contacts, make purchases for necessities) expand knowledge, develop skills to meet basic needs and for personal satisfaction and enjoyment. e) Construct and/or Essential Question 1. What is the purpose of a Career Interest Inventory? 2. What is your highest Career Cluster Area based on your Career Interest Inventory. 3. What Pathways are associated with your Career Cluster? 4. What is the purpose of the Reality Check Assessment? 1. What is the purpose of a Career Interest Inventory? 2. What is your highest Career Cluster Area based on your Career Interest Inventory. 3. What Pathways are associated with your Career Cluster? 4. What is the purpose of the Reality Check Assessment? 1. What is the purpose of a Career Interest Inventory? 2. What is your highest Career Cluster Area based on your Career Interest Inventory. 3. What Pathways are associated with your Career Cluster? 4. What is the purpose of the Reality Check Assessment? 1. What is the purpose of a Career Interest Inventory? 2. What is your highest Career Cluster Area based on your Career Interest Inventory. 3. What Pathways are associated with your Career Cluster? 4. What is the purpose of the Reality Check Assessment? Opening (5-10 min) Students have an instructional warm-up each day. They have journal topics related to the content that they are learning for the week. Monday, students have a “research topic” to discover the content of the current topic. If a student finishes before guided instruction, they work on Micro-type Students have an instructional warm-up each day. They have journal topics related to the content that they are learning for the week. If a student finishes before guided instruction, they work on Micro-type lessons and practice for weekly tests. (Writing Initiative) Students have an instructional warm-up each day. They have journal topics related to the content that they are learning for the week. If a student finishes before guided instruction, they work on Micro-type lessons and practice for weekly tests After reading the article “How to Build a Good Work Ethic”, Purpose-What is the purpose of this article, and who is the intended audience? Inference-Why is having good work ethics important to employees? General UnderstandingWhat step in the article “How to Build a Good Work Ethics” means being update a Career Plan as a tool to explore self-knowledge and academic aptitude and understand that career paths should relate to your individual traits. English Language Proficiency Standard 1: English language learners communicate in English for Social and Instructional purposes within the school setting. 1. What is the purpose of a Career Interest Inventory? 2. What is your highest Career Cluster Area based on your Career Interest Inventory. 3. What Pathways are associated with your Career Cluster? 4. What is the purpose of the Reality Check Assessment? Students have an instructional warmup each day. They have journal topics related to the content that they are learning for the week. If a student finishes before guided instruction, they work on Microtype lessons and practice for weekly on time? Make sure you support your claim using 2 or more examples from the article, and elaborate on those examples to fully support your claim. lessons and practice for weekly tests. Work-time Activities (40 min) Students will create a power point presentation on the Georgia Career Clusters and pathways. Students will use www.gacollege411.org to research the clusters and pathways. In the content area, students will list each pathway for the cluster area and choose 1 pathway to learn more about. After researching the clusters and pathways, students will choose a career of their choice to learn about. Power point slides will include the following information about their career: Working Conditions, Skills, Wages and Employment Outlook, and Summary Students will create a power point presentation on the Georgia Career Clusters and pathways. Students will use www.gacollege411.org to research the clusters and pathways. In the content area, students will list each pathway for the cluster area and choose 1 pathway to learn more about. After researching the clusters and pathways, students will choose a career of their choice to learn about. Power point slides will include the following information about their career: Working Conditions, Skills, Wages and Employment Outlook, and Summary Students have an instructional warm-up each day. They have journal topics related to the content that they are learning for the week. If a student finishes before guided instruction, they work on Micro-type lessons and practice for weekly tests. Students will create a power point presentation on the Georgia Career Clusters and pathways. Students will use www.gacollege411.org to research the clusters and pathways. In the content area, students will list each pathway for the cluster area and choose 1 pathway to learn more about. After researching the clusters and pathways, students will choose a career of their choice to learn about. Power point slides will include the following information about their career: Working Conditions, Skills, Wages and Employment Outlook, and Summary Students will take the Career Cluster Inventory using GCIS. They will Students will save their top 3 career clusters in their portfolio. Students will log in GCIS using their username and password. tests Students will create a power point presentation on the Georgia Career Clusters and pathways. Students will use www.gacollege411.org to research the clusters and pathways. In the content area, students will list each pathway for the cluster area and choose 1 pathway to learn more about. After researching the clusters and pathways, students will choose a career of their choice to learn about. Power point slides will include the following information about their career: Working Conditions, Skills, Wages and Employment Outlook, and Summary Keyboarding/Hard Skills Assessment Students will create a power point presentation on the Georgia Career Clusters and pathways. Students will use www.gacollege411. org to research the clusters and pathways. In the content area, students will list each pathway for the cluster area and choose 1 pathway to learn more about. After researching the clusters and pathways, students will choose a career of their choice to learn about. Power point slides will include the following rate the 80 activities on how much they think they would enjoy doing them. At the end of the assessment they will click “Get Results”. They will view their top career clusters. They will save their results and type a paragraph in GCIS about their top career cluster. Prior to students taking the assessment, they will open a new word document and title it "Passwords". Students will key their username and password information for GCIS. Students will save the file "Passwords". Students will save their top 3 career clusters in their portfolio. Prior to students taking the assessment, they will open a new word document and title it "Passwords". Students will key their username and password information for GCIS. Students will save the file "Passwords". Closing Activity (5-10 min) Discussion of topics covered in class. Demonstration of learned keyboarding and computer skills. Discussion will include the students answering Discussion of topics covered in class. Demonstration of learned keyboarding and computer skills. Discussion will include the students answering Students will watch a short video about "Dave and what he believes about his future lifestyle". To meet the 2nd part of the Bridge Act, students will take the Reality Check. information about their career: Working Conditions, Skills, Wages and Employment Outlook, and Summary Students will use the GCIS website to take “The Reality Check” which is one of their requirements in The Bridge Act. The Reality Check is a tool for students to use to help them see how much it costs to live. When students get the results of their Reality Check, they will find a career that pays them enough to cover their expenses. They will select the type of education they plan to obtain, and their career cluster area. Students may need to change their education criteria several times in order to find a job that provides them the type of money they want to earn. For example, it might be hard for a person to earn $100,000 a year with little or no education. Discussion of topics covered in class. Demonstration of learned keyboarding and computer skills. Discussion will include the students answering Discussion of topics covered in class. Demonstration of learned keyboarding and computer skills. Discussion will include the students answering Discussion of topics covered in class. Demonstration of learned keyboarding and computer skills. Discussion will include the students essential questions. essential questions. essential questions. essential questions. Assessment/Evaluation Rubric attached to worksheets and projected on screen. Performance Assessment while monitoring student’s progress. Portfolio Assessment Rubric attached to worksheets and projected on screen. Performance Assessment while monitoring student’s progress. Portfolio Assessment Rubric attached to worksheets and projected on screen. Performance Assessment while monitoring student’s progress. Portfolio Assessment Rubric attached to worksheets and projected on screen. Performance Assessment while monitoring student’s progress. Portfolio Assessment Differentiation Refer to IEP/Extended time/buddy helpers/On Your Own Projects/Exploration of Computer Skills Projects designed for all learning styles: kinesthetic, auditory, and visual Preferential Seating Modified keyboarding techniques for students with physical disabilities. Students with vision problems will use the magnification tool on the computer as well as have enlarged worksheets and a keyboard with enlarged keys. Peer Teaching: Students are encouraged to help other students when learning computer skills and career content. Keyboarding lessons in Kids Typing Skills and MicroType are selfpaced and students work at their own speed and ability level. Guided Notes: Students will have worksheets with detailed instructions Refer to IEP/Extended time/buddy helpers/On Your Own Projects/Exploration of Computer Skills Projects designed for all learning styles: kinesthetic, auditory, and visual Modified keyboarding techniques for students with physical disabilities. Students with vision problems will use the magnification tool on the computer as well as have enlarged worksheets and a keyboard with enlarged keys. Peer Teaching: Students are encouraged to help other students when learning computer skills and career content. Keyboarding lessons in Kids Typing Skills and MicroType are selfpaced and students work at their own speed and ability level. Guided Notes: Students will have worksheets with detailed instructions and screen Refer to IEP/Extended time/buddy helpers/On Your Own Projects/Exploration of Computer Skills Projects designed for all learning styles: kinesthetic, auditory, and visual Modified keyboarding techniques for students with physical disabilities. Students with vision problems will use the magnification tool on the computer as well as have enlarged worksheets and a keyboard with enlarged keys. Peer Teaching: Students are encouraged to help other students when learning computer skills and career content. Keyboarding lessons in Kids Typing Skills and MicroType are selfpaced and students work at their own speed and ability level. Guided Notes: Students will have worksheets with detailed instructions and screen Refer to IEP/Extended time/buddy helpers/On Your Own Projects/Exploration of Computer Skills Projects designed for all learning styles: kinesthetic, auditory, and visual Modified keyboarding techniques for students with physical disabilities. Students with vision problems will use the magnification tool on the computer as well as have enlarged worksheets and a keyboard with enlarged keys. Peer Teaching: Students are encouraged to help other students when learning computer skills and career content. Keyboarding lessons in Kids Typing Skills and MicroType are selfpaced and students work at their own speed and ability level. Guided Notes: Students will have worksheets with detailed instructions and screen answering essential questions. Rubric attached to worksheets and projected on screen. Performance Assessment while monitoring student’s progress. Portfolio Assessment Refer to IEP/Extended time/buddy helpers/On Your Own Projects/Exploration of Computer Skills Projects designed for all learning styles: kinesthetic, auditory, and visual Modified keyboarding techniques for students with physical disabilities. Students with vision problems will use the magnification tool on the computer as well as have enlarged worksheets and a keyboard with enlarged keys. Peer Teaching: Students are encouraged to help other students when learning computer skills and career content. Keyboarding lessons in Kids Typing Skills and MicroType are self- and screen shots/pictures. Projects are divided into small manageable parts. When appropriate, student(s)will use an IPad using the accessibility features: speak selection, invert colors, etc. Materials Needed How is this rigorous Common Core lesson? shots/pictures. Projects are divided into small manageable parts. When appropriate, student(s)will use an IPad using the accessibility features: speak selection, invert colors, etc. shots/pictures. Projects are divided into small manageable parts. When appropriate, student(s)will use an IPad using the accessibility features: speak selection, invert colors, etc. shots/pictures. Projects are divided into small manageable parts. When appropriate, student(s)will use an IPad using the accessibility features: speak selection, invert colors, etc. paced and students work at their own speed and ability level. Guided Notes: Students will have worksheets with detailed instructions and screen shots/pictures. Projects are divided into small manageable parts. When appropriate, student(s)will use an IPad using the accessibility features: speak selection, invert colors, etc. Computers, Worksheets, Computers, Worksheets, Computers, Worksheets, Computers, Worksheets, Computers, Projector, Laptop, OLC Projector, Laptop, OLC Projector, Laptop, OLC Projector, Laptop, OLC Worksheets, Projector, Laptop, OLC Students use appropriate technology such as computers and I-pads to create projects and to show their understanding of the material and technology skills. When teaching a new concept, we do an example together in class, they produce the required assignment, and they have an “On Your Own” Project. The “On Your Own” Project allows students to demonstrate acquired technology skills, critical thinking skills and apply the concept to real life situations. Not only does this allow students to be creative, but it gives students a choice in how they want to demonstrate what they learned. Our lessons constantly build upon students’ prior knowledge and skills. All activities are student centered and hands-on from the beginning of the lesson to the end. This allows students to be actively involved in all parts of the lesson.