Lab04-GL Rev. 3
advertisement

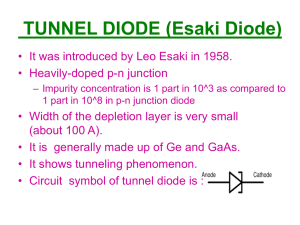
New Mexico Tech EE321L - Analog Electronics Fall 2013 Laboratory Exercise 4 Diode IV Characteristics Pre-Lab 1. Find the 1N4001, 1N5229 and 1N5237 data sheets. 1N4001 Rectifier Diode IV Characteristics In this section you will measure the IV characteristics of the 1N4001 rectifier diode using a floating function generator. The floating function generator is not grounded and can thus be inserted in a circuit anywhere. This allows you to choose ground where it is convenient for your measurement. Use a transformer between the wall socket and the function generator to float the function generator, and make sure you then don’t connect the function generator ground to ground of the oscilloscope or DC power supply. Note: Utilizing a floating ground increases the possibility for being shocked/electrocuted, make sure to be extra vigilant about turning the function generator on and off and not shorting things. Note: Save and print all graphs of use. 1. On the primary side of the transformer: Attach pin 1 to the function generator ground terminal (black lead) and pin 3 to function generator output terminal (red lead). Adjust the load output: Channel -> Output Load -> Set to High Z. Preform a functionality check. Use a 100 Hz sine wave with a 12 Vpp amplitude. 2. Measure the input and output of the transformer and determine the turns ratio (N) using the equation N1Vi = N2Vo -> N2 / N1 =Vo /Vi. 3. What does this imply about the transformer? 4. Next build a circuit to measure the IV characteristic of the diode using a floating function generator. The circuit consists of the floating function generator, the diode, and a 100 Ω resistor connected in a loop with the point between the diode and the resistor grounded. 5. Measure the voltage across the diode (1N4001) and the voltage across the resistor using your oscilloscope probes. On the secondary side of the transformer: Attach one probe (CH1) between pin six and the diode, with the ground clip connected between the diode and resistor. Attach the other probe (CH2) between pin four and the 100 Ω resistor, with the ground clip connected between the diode and resistor. Note: If pin 1 was set as the “+ input” and pin 3 was “– input” (ground) then Pin 6 with be the “+ output” and Pint 4 will be the “– output” (new ground). 6. Using the oscilloscope cursors measure the conducting diode voltage drop. Then select: Display -> Format -> XY. This is your diode IV graph, except it is upside down. To correct this, select: CH2 -> Invert -> On. Adjust your scaling knobs to make your IV graph look identical to what is seen in your book. 7. Switch back to YT mode and determine the diode power consumption by selecting: Math -> CH1 x CH2. Notice that the red colored signal is the diode’s power scaled by R. 8. What is the max power of the diode? 9. What is the average power of the diode? (Hint: Measure -> Source -> Math -> Type -> Mean) New Mexico Tech EE321L - Analog Electronics Fall 2013 10. Compare these values to the datasheet. 1N5229 and 1N5237 Zener Diode IV Characteristics In this section you will measure the IC Characteristics of the zener diodes. Use the same set up, but switch out the diodes. 11. Insert the 1N5229 and view the IV graph. Is it as you expect? 12. Adjust the input signal to 20Vpp. Why did you need to increase the voltage? 13. Switch back to the graph that shows diode voltage, resistor voltage and power consumption. Where is the reverse breakdown? What is its value? What current does this correspond to? 14. Insert the 1N5237 and view the IV graph. Is it as you expect? 15. Why can’t you see the reverse breakdown? 16. What needs to change to fix this? Measure n and Is 17. Build a new circuit using a loop connection of a 10V DC power supply, a resistor, and the 1N4001 diode. 18. Choose resistors to obtain currents of approximately 1mA (10 k Ω) and 10 mA (1 kΩ.) 19. In each case, measure the voltage across the diode and the resistor carefully (using a multimeter) to get vD and iD. Use these two measurements to calculate n and Is in the diode current-voltage equation. 20. Using your previously obtained graphs, find n and Is for both the zener diodes. Mystery Challenge #4: 1. How do you talk for one minute with out repeating the same word or using a word containing the letter “a”? 2. Who is bold?