w - ECVS
advertisement

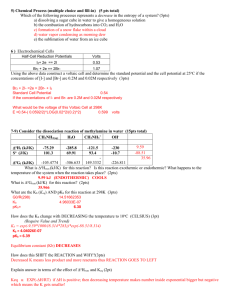
PAGE 1 PART II SOFT TISSUE CASE BASED EXAMINATION DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED PAGE 2 FOUR MINUTES A nine month old entire male West Highland White Terrier is presented with a history of depression, polyuria, polydipsia and intermittent vomiting. On clinical examination you find a quiet, underweight dog with mild ascites. Blood results are shown on the slide. 1. Based on this information give FOUR differential diagnoses. 4pts 2. What is a possible cause of the mild ascites? 1pt 3. List THREE causes of reduced blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 3pts 8pt DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED PAGE 3 FOUR MINUTES The dog underwent ultrasonography. A congenital portosystemic shunt was identified. A urine sample was obtained by cystocentesis. 1. List TWO abnormalities that could be found on urinalysis in this patient. 2pts 2. Briefly explain how EACH of these abnormalities occur with portosystemic shunts 4pts The patient underwent three weeks of medical management. Surgical correction was considered in this patient, but melena was reported at admission. The slide shows the results of haematology and coagulation screen. 3. What is your interpretation of the haematology results? 1pt 4. What is the likely cause of the abnormalities in PT and APTT in this patient? 1pt 5. Based on the laboratory results shown on the slide what would be your next step prior to surgery? 2pts 10pt DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED PAGE 4 FOUR MINUTES There is no image for this slide. A whole blood transfusion was performed prior to surgery. 6. List THREE KEY steps when ADMINISTERING the blood? 3pts After the transfusion the dog was pre-medicated and anaesthetised for surgery. 7. List TWO effects of acepromazine which CONTRAINDICATE its use in this patient. BE SPECIFIC. 2pts 8. List TWO reasons why halothane should be avoided in patients with HEPATIC dysfunction. 2pts 7pt DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED PAGE 5 FOUR MINUTES An exploratory coeliotomy was performed. Portovenograms were undertaken with digital subtraction. Both images are shown on the slide. Image 1 shows the portovenogram before temporary occlusion Image 2 shows the portovenogram after temporary occlusion 1. Name structures A, B and C on Image 1. 3pts 2. List the TWO clinically significant radiographic findings of Image 2 2pts 3. According to Lee et al (2006) what grade would you assign to the portovenograms in Images 1 and 2? 2pts 7pt DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED PAGE 6 FOUR MINUTES An intraoperative view is shown on the slide. A cellophane band has been placed around the shunt. 4. List THREE other techniques that can be used to achieve PARTIAL occlusion of an extrahepatic portosystemic shunt. 3pts 5. What combination of cellophane band and ligaclips has been reported to be the most secure configuration? 2pts 6. When using cellophane banding, what is the difference in postoperative clinical grade between dogs with no attenuation versus dogs with partial attenuation? 1pt 6pt DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED PAGE 7 FOUR MINUTES There is no image for this slide The cellophane band was placed around the shunt with no attenuation and a liver biopsy was obtained. The patient was recovered from anaesthesia. 7. List TWO most likely short–term complications in THIS case. 2pts The liver histopathology revealed arteriolar hyperplasia, moderate fibrosis, biliary hyperplasia and evidence of lipidosis. 8. How does the severity of liver histopathological changes correlate with long-term survival in dogs with congenital extrahepatic shunts? 1pt 9. List THREE imaging techniques to objectively evaluate long-term clinical outcome in this patient. 3pts 10. In addition to bile acids and ammonia, what other serum parameter has been suggested as a potential biomarker when assessing post-operative progress of PSS patients? 1pt 7pt DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED