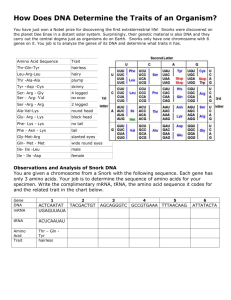
Name Pd and Date Mutations Below are two partial sequences of
advertisement

Name ______________________________________ Pd and Date _______________ Mutations Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases (shown for only one strand of DNA) Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, this sequence is part of a set of instructions for controlling a bodily function. In this case, the sequence contains the gene to make the protein insulin. Insulin is necessary for the uptake of sugar from the blood. Without insulin, a person cannot use digested sugars the same way others can, and they have a disease called diabetes. For the following DNA sequences, make a complimentary RNA strand and determine which amino acids are assembled to make the insulin protein in both the cow and the human. Sequence 1: Human DNA: C C A T A G C A C G T T A C A A C G T G A A G G T A A mRNA: Amino Acids: Sequence 2: Cow DNA: C C G T A G C A T G T T A C A A C G C G A A G G C A C mRNA: Amino Acids: Analysis 1. The DNA sequence is different for the cow and the human, but the amino acid chain produced by the sequence is almost the same. How can this happen? 2. Could two humans (or two cows) have some differences in the DNA sequence for insulin, yet still make exactly the same insulin proteins? Explain your answer. Mutations Diabetes is a disease characterized by the inability to break down sugars. Often a person with diabetes has a defective DNA sequence that codes for the making of the insulin protein. Therefore, they do not properly make the insulin protein. This mutation is called a POINT MUTATION because only one amino acid is affected. 3. Suppose a person has a mutation in their DNA, and the first triplet for the gene coding for insulin is CCC (instead of CCA). Determine what amino acid the new DNA triplet codes for. Will this person be diabetic? Amino Acid _____________________ 4. Diabetic?___________________ What if the first triplet was CAA (instead of CCA) Amino Acid _____________________ Diabetic?___________________ Frameshift Mutations occur when a base is added (or removed) from a DNA/RNA sequence causing the rest of the DNA sequence to be “moved” up or down one letter. For questions 5-8, use the following DNA sequence to determine what type of mutation has occurred and list the affect it has on the amino acid sequence (which means you will have to find the AA sequence for all of them .) Correct DNA sequence: T A C A A A C C T A G T T T A T A G C C A T T C mRNA: Amino Acid chain Correct DNA sequence: T A C A A A C C T A G T T T A T A G C C A T T C DNA sequence: mRNA: Amino Acid chain Type of mutation AND affect on amino acid sequence (choose one from each line) DNA sequence: mRNA: Amino Acid chain Type of mutation AND affect on amino acid sequence (choose one from each line) DNA sequence: mRNA: Amino Acid chain Type of mutation AND affect on amino acid sequence (choose one from each line) DNA sequence: mRNA: Amino Acid chain Type of mutation AND affect on amino acid sequence (choose one from each line) 5. T A C A A G C C T A G T T T A T A G C C A T T C Point Mutation (substitution, addition or deletion) Affect on AA Sequence: Silent, Nonsense, Missense, or Frameshift Description of Affect: No change, Stops coding, Changes one AA, Changes entire AA sequence following mutation. 6. T A C A A A C C C T A G T T T A T A G C C A T T C Point Mutation (substitution, addition or deletion) Affect on AA Sequence: Silent, Nonsense, Missense, or Frameshift Description of Affect: No change, Stops coding, Changes one AA, Changes entire AA sequence following mutation. 7. T A C A A A C C T A G T T A T A G C C A T T C Point Mutation (substitution, addition or deletion) Affect on AA Sequence: Silent, Nonsense, Missense, or Frameshift Description of Affect: No change, Stops coding, Changes one AA, Changes entire AA sequence following mutation. 8. T A C A A A A C T A G T T T A T A G C C A T T C Point Mutation (substitution, addition or deletion) Affect on AA Sequence: Silent, Nonsense, Missense, or Frameshift Description of Affect: No change, Stops coding, Changes one AA, Changes entire AA sequence following mutation.