Industrialization and Reform
advertisement
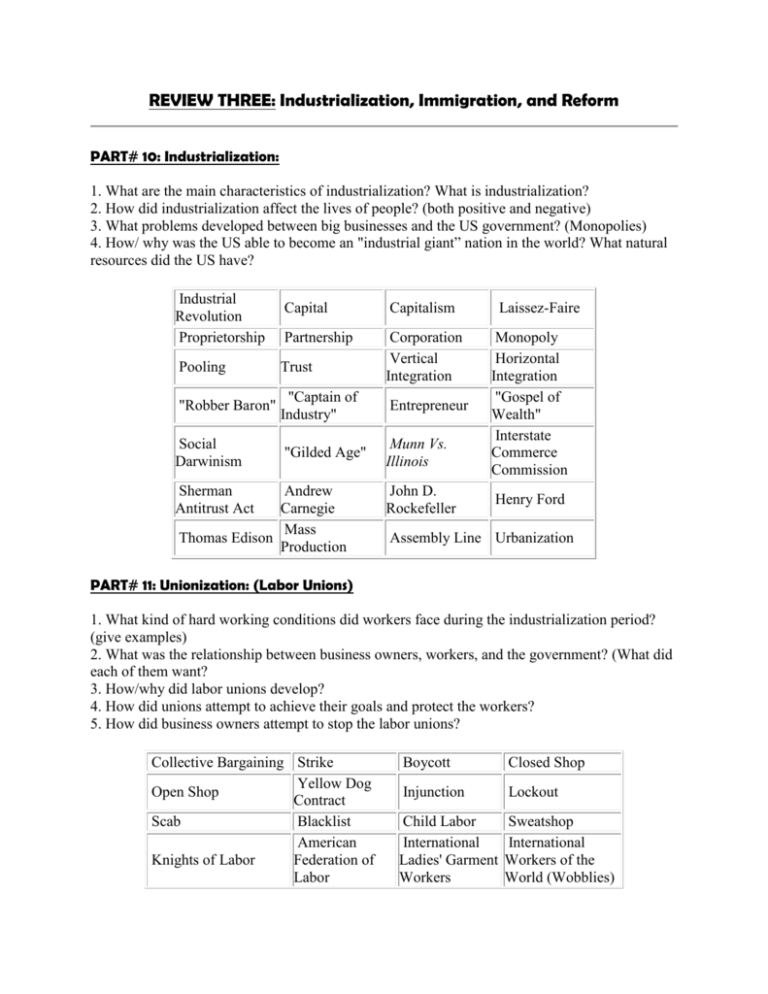
REVIEW THREE: Industrialization, Immigration, and Reform PART# 10: Industrialization: 1. What are the main characteristics of industrialization? What is industrialization? 2. How did industrialization affect the lives of people? (both positive and negative) 3. What problems developed between big businesses and the US government? (Monopolies) 4. How/ why was the US able to become an "industrial giant” nation in the world? What natural resources did the US have? Industrial Revolution Proprietorship Capital Capitalism Partnership Corporation Vertical Integration Pooling Trust "Robber Baron" "Captain of Industry" Entrepreneur Social Darwinism "Gilded Age" Munn Vs. Illinois Sherman Antitrust Act Andrew Carnegie Mass Thomas Edison Production John D. Rockefeller Laissez-Faire Monopoly Horizontal Integration "Gospel of Wealth" Interstate Commerce Commission Henry Ford Assembly Line Urbanization PART# 11: Unionization: (Labor Unions) 1. What kind of hard working conditions did workers face during the industrialization period? (give examples) 2. What was the relationship between business owners, workers, and the government? (What did each of them want? 3. How/why did labor unions develop? 4. How did unions attempt to achieve their goals and protect the workers? 5. How did business owners attempt to stop the labor unions? Collective Bargaining Strike Yellow Dog Open Shop Contract Scab Blacklist American Knights of Labor Federation of Labor Boycott Closed Shop Injunction Lockout Child Labor International Ladies' Garment Workers Sweatshop International Workers of the World (Wobblies) Great Railway Strike of 1877 Samuel Gompers Haymarket Riot Homestead Strike Pullman Strike PART# 12: Immigration: 1. From what parts of the world did most immigrants come from in the late 19th and early 20th centuries? 2. Why did people migrate to the US from other countries? 3. Why did "Nativism" develop? What is “Nativism”? 4. How did the US government limit immigration in the late 19th and early 20th centuries? 5. What is a “Melting Pot”? What are the positives and negatives of it? "Old Immigrants" "Salad Bowl" "New Immigrants" Cultural Mosaic Assimilation "Melting Pot" Cultural Pluralism Americanization Nativism Know-nothing Chinese Party Exclusion Act Literacy Tests Emergency Quota Act of 1921 Gentlemen's Agreement with Japan National Origins Acts of 1924 & 1929 PART# 13: The Populist Movement: 1. What problems did farmers face at the end of the 19th century? Grange Populist Movement "Free Silver" "Cross of Gold" Gold Standard William Jennings Bryan PART# 14: The Progressive Movement: 1. What problems did industrialization and urbanization create for people? 2. In what ways did the political system (government) become corrupt? 3. How did progressives hope to reform (change) society? 4. How did Theodore Roosevelt advance the progressive movement’s plans? 5. How did Woodrow Wilson advance the progressive movement’s plans? Progressive Movement Muckrakers Urbanization Tammany Hall "Machine Politics" Tenements Initiative Referendum Recall Election How the Other The Shame of the The Jungle by Half Lives by Cities by Lincoln Upton Sinclair Jacob Riis Steffens Theodore Roosevelt's Square Deal Northern Securities Vs. US Woodrow Wilson's New Freedom Federal Reserve System 16th Amendment "TrustBusting" 1902 Coal Strike Conservation Commerce Commission Underwood Tariff Graduated Clayton (Progressive)Income Antitrust Act Tax Settlement Houses 17th Amendment Jane Adams 1. What was Prohibition? 2. Why was Prohibition repealed (ended)? Speakeasy Primary Election A History of Standard Oil by Ida Tarbell Meat Pure Food and Inspection Act Drug Act PART# 15: The Temperance (Prohibition) Movement: Temperance Movement Political Boss Women's Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) Bootlegging Al Capone Hull House 19th Amendment