1C1 Basic Concepts in Genetics MSWord Lesson Plan Science KS3
advertisement
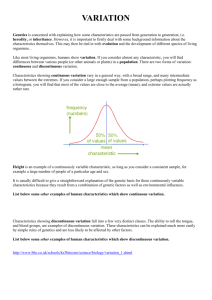
KS3 SCIENCE Curriculum link: Genetics and evolution (variation between individuals) BASIC CONCEPTS IN GENETICS LESSON PLAN Introduce your students to basic concepts in genetics. This section introduces the concept of genetic variation through considering inherited and environmental variations. Students will also research the structure of DNA. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Resources required: Iguana images, genetics terminology dominoes. 1. FIRE STARTER 3. MAKING WAVES Show students two pictures of iguanas and ask them to write down as many ways they think they are different and why they might be different. From the list of ideas identified discuss the concepts of inherited and environmental variation as a way to introduce the concept of genetic variation. In pairs students can put the genetics terminology dominoes in the correct order to display knowledge of the key terms for this section of the module. 2. GAINING GROUND To know that heredity is the process by which genetic information is transmitted from one generation to the next. To understand that genetic variation between individuals within a species can be due to inherited or environmental variation. To understand how the double helix is formed. 4. FUTURE FOCUS Students should research the structure of DNA molecule to understand how the double helix is formed. Students read the basic concepts in genetics chapter on the Discovering Galapagos website which introduces the key concepts related to genetic variation and why it is relevant to learning about the Galapagos Islands. Talk students through the links between the cell, nucleus, chromosome and gene so that they can draw an annotated diagram, introducing key concepts and terminology as listed in the online glossary. A RESOURCE BROUGHT TO YOU BY THE GALAPAGOS CONSERVATION TRUST (REGISTERED CHARITY NO. 1043470) AND THE ROYAL GEOGRAPHICAL SOCIETY (WITH IBG) STUDENTS’ OUTCOMES To explain how individual variation can be due to inherited or environmental forces. To explain how the double helix is formed.