Heat As Energy, Conduction, Convection, Radiation Intro
advertisement
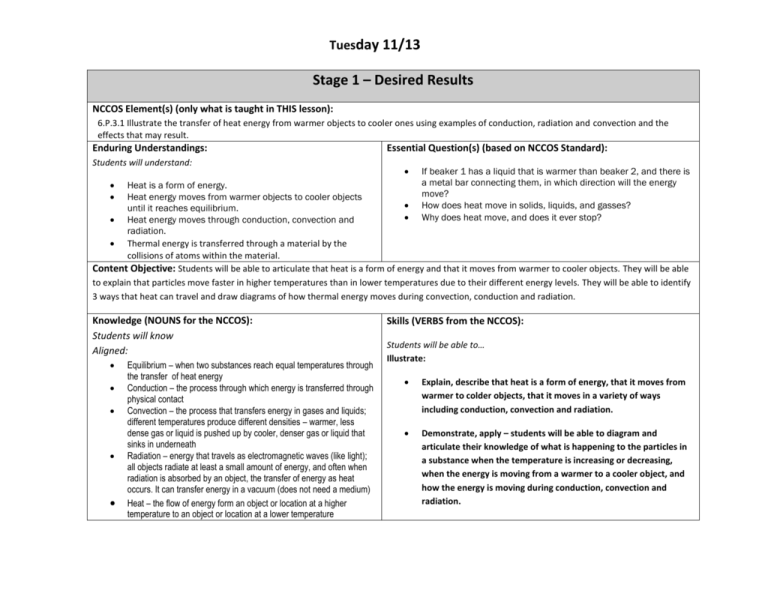
Tuesday 11/13 Stage 1 – Desired Results NCCOS Element(s) (only what is taught in THIS lesson): 6.P.3.1 Illustrate the transfer of heat energy from warmer objects to cooler ones using examples of conduction, radiation and convection and the effects that may result. Enduring Understandings: Essential Question(s) (based on NCCOS Standard): Students will understand: If beaker 1 has a liquid that is warmer than beaker 2, and there is a metal bar connecting them, in which direction will the energy Heat is a form of energy. move? Heat energy moves from warmer objects to cooler objects How does heat move in solids, liquids, and gasses? until it reaches equilibrium. Why does heat move, and does it ever stop? Heat energy moves through conduction, convection and radiation. Thermal energy is transferred through a material by the collisions of atoms within the material. Content Objective: Students will be able to articulate that heat is a form of energy and that it moves from warmer to cooler objects. They will be able to explain that particles move faster in higher temperatures than in lower temperatures due to their different energy levels. They will be able to identify 3 ways that heat can travel and draw diagrams of how thermal energy moves during convection, conduction and radiation. Knowledge (NOUNS for the NCCOS): Students will know Aligned: Equilibrium – when two substances reach equal temperatures through the transfer of heat energy Conduction – the process through which energy is transferred through physical contact Convection – the process that transfers energy in gases and liquids; different temperatures produce different densities – warmer, less dense gas or liquid is pushed up by cooler, denser gas or liquid that sinks in underneath Radiation – energy that travels as electromagnetic waves (like light); all objects radiate at least a small amount of energy, and often when radiation is absorbed by an object, the transfer of energy as heat occurs. It can transfer energy in a vacuum (does not need a medium) Heat – the flow of energy form an object or location at a higher temperature to an object or location at a lower temperature Skills (VERBS from the NCCOS): Students will be able to… Illustrate: Explain, describe that heat is a form of energy, that it moves from warmer to colder objects, that it moves in a variety of ways including conduction, convection and radiation. Demonstrate, apply – students will be able to diagram and articulate their knowledge of what is happening to the particles in a substance when the temperature is increasing or decreasing, when the energy is moving from a warmer to a cooler object, and how the energy is moving during conduction, convection and radiation. Thermal Energy – the total kinetic energy (how much the particles are moving) of particles in a substance or location Real World knowledge Application (Where do they use this KNOWLEDGE in their real world): Convection causes currents in bodies of water. Convection causes winds in the atmosphere. When your hands are cold, and you hold a cup of hot chocolate, your hands get warmer and the hot chocolate gets colder. That’s conduction. Real World Skills Applications (Where do they use these SKILLS in their real world): When students draw a map for a friend, they are illustrating. They are showing how something happens and giving an explanation. When they answer questions in class and explain what they know, they are illustrating their knowledge. When we draw diagrams in class, we are illustrating what we learned. A sunburn is an example of radiation. Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Performance Task(s) and Product(s) to be assessed (What will they put in my hand to be assessed that they created individually): Students will create diagrams from our demo, record their observations, and use this information to answer analysis questions. Students will take guided notes and record their answers to think-pair-share questions. Formal Assessment Grading Format(s) (How will I grade it, letting them know in advance how to receive every point in my grading scale): Students will receive 2 points for creating 2 diagrams showing what happened to the food coloring in the cups (1 point for the food coloring in the warm water, 1 for the food coloring in the cold water). Students will receive 3 points for recording at least 2 observations about the demo. Students will receive 1 point for writing a concluding statement about what they saw/learned. Total = 6 points Students will get a participation grade for filling in the guided notes and answering the questions. 90-100% complete = 100%, 80-90% complete = 85%, 75-80% complete = 77%, less than 75% complete = 65% Stage 3 – Learning Plan Activating Strategies/Models (+/- 10): Probe prior knowledge: Students will answer 3 Science Starter questions about particle movement, temperature, and levels of energy. Hook (+/- 15): I will do a demonstration for the students. I will have 2 containers of water. One will be nearly boiling, and the other will be chilled. I will tell the students that I am going to put equal amounts of food coloring in each container. They will write a hypothesis to predict whether the food coloring will spread through the hot or the cold water faster. Procedures/Sequence (+/- 15 min): The students will watch the color spread and record at least 3 observations. They will work in with their table groups to construct a diagram of the particles in each substance and to write a concluding statement explaining why the food dye spread faster in the warmer water than the colder water. We will discuss our answers whole group. Enrichment (+/- 30 min): We will discuss that heat is a form of energy. I will present a slideshow that introduces heat energy. Students will take guided notes and answer think-pair-share questions. o o Explain that heat is a form of energy Are you hotter when you are sitting still or running? The hotter a substance is, the more energy the particles have Heat moves from warmer to colder substances: Foreshadow: Conduction, convection, radiation Materials needed: 2 clear glass or Tupperware containers Icebox/cold packs Water boiler Food coloring Water Differentiated guided notes LCD projector PPT/Computer Summary (What we covered today +/- 3 min): Students will answer an exit ticket question to review what we learned Differentiation: 1. Student EC: Partially filled in guided notes for EC students Preferential seating for student on 504 Strategic grouping of students Closure: Academic – What is heat? How does it move and why? Social – What was your role in the group during the demonstration analysis? List one way that you contributed to the group discussion throughout class today. Reflection:










